GitLab

The Sumo Logic App for GitLab provides you a complete overview of your GitLab’s builds, deployments, pipelines, issues, merge requests, and commits. The integration listens for GitLab events and uses the event data to populate the pre-configured Dashboards.
Event types
The Sumo Logic App for GitLab ingests GitLab events using a webhook. Sumo Logic ingests all events, but only uses the following events in the Dashboards:
- Job
- Deployment
- Pipeline
- Merge Request
- Issue
- Push
For information on GitLab events, refer to GitLab documentation. For troubleshooting, see the GitLab Troubleshooting section.
Sample log messages
For more information about log messages, see GitLab documentation.
Sample queries
This section provides a sample query from the Opened Merge Requests panel on the GitLab - Merge Requests dashboard.
_sourceCategory="sumo/GitLab" and _collector="GitLab" %"x-GitLab-event"="Merge Request Hook"
|json "object_attributes.state" as merge_request_state
| where merge_request_state="opened"
|json "object_attributes.action" ,"object_attributes.title", "object_attributes.created_at","object_attributes.updated_at","user.name","repository.name","object_attributes.merge_when_pipeline_succeeds","object_attributes.url","object_attributes.source_branch","object_attributes.target_branch","project.name","object_attributes.id" as action, title, created_time , updated_time,user,repo_name,branch_deleted, url,source_branch,target_branch,project,merge_request_id nodrop
| where user matches "*" and repo_name matches "*" and project matches "*" and merge_request_id matches "*" and merge_request_state matches "*"
| where action in ("open","reopen")
| count by repo_name
| sort by _count
Collecting logs for the GitLab App
This guide provides instructions for collecting logs for the Sumo Logic App for GitLab.
Configuring log collection consists of the following tasks:
- Configuring a Hosted Collector in Sumo Logic to receive GitLab Events: A Hosted Collector is installed to receive the Webhooks from GitLab. The Webhooks configuration helps to notify the app or web application when certain events occur in GitLab. Using the Webhooks the remote applications do not have to monitor whether changes have occurred
- Registering a Webhook in GitLab: Webhooks are registered in GitLab for various events by the GitLab administration console.
For information on GitLab webhooks, refer to GitLab documentation.
Step 1: Configure Hosted Collector to Receive Webhooks
Create a host collector to receive Webhooks from GitLab and set up an HTTP source on it.
- Configure a Hosted Collector, or select an existing hosted collector for the HTTP source.
- Configure an HTTP source on the hosted collector.
- For Source Category, specify GitLab/events.
- Click +Add Field and provide the following:
- Field Name.
_convertHeadersToFields - Value.
true
- Field Name.
- Make note of the HTTP address for the source. You will supply it when you configure a GitLab Webhook in the next step.
Step 2: Register Webhook in GitLab
In GitLab, configure a Webhook to connect to your Sumo Logic HTTP Source. You can configure the Webhook at the Project or Group level. Once configured, it will trigger each time one or more subscribed events occur in that Project or Group.
- Sign in to your GitLab account.
- Go to your Project or Group.
- Click Settings > Webhooks.
- Enter Webhook form data as follows:
- URL. Enter the Sumo Logic HTTP Source Address you created in Step 1.
- Secret Token. Leave blank.
- Trigger. Tick all checkboxes.
- SSL Verification. Check the box to enable.
- Click Add Webhook.
You can register webhooks for a Group or a Project. Group webhooks ensure all projects in the group receive the same webhook settings.
Refer to the GitLab Webhooks documentation to understand more.
Step 3: GitLab Event tagging at Sumo Logic
To properly identify the event type for incoming events, Sumo Logic automatically adds the x-gitlab-event event type to the Fields during app installation.
Installing the GitLab App
To install the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Install App.
note
Sometimes this button says Add Integration.
- Click Next in the Setup Data section.
- In the Configure section of your respective app, complete the following fields.
- Field Name. If you already have collectors and sources set up, select the configured metadata field name (eg _sourcecategory) or specify other custom metadata (eg: _collector) along with its metadata Field Value.
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-installation
Once your app is installed, it will appear in your Installed Apps folder, and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
Each panel slowly fills with data matching the time range query received since the panel was created. Results will not immediately be available but will be updated with full graphs and charts over time.
Troubleshooting
If you are getting the following error in the app dashboards after installation:
Field x-gitlab-event not found, please check the spelling and try again.
Do the following to resolve:
- Close all app dashboards.
- New UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu select Data Management, and then under Logs select Fields. You can also click the Go To... menu at the top of the screen and select Fields.
Classic UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, select Manage Data > Logs > Fields. - Delete the x-gitlab-event field.
- Add it again using the Dropped Fields section:
- At Dropped Fields dropdown, click on x-gitlab-event, then click Create Field to create the field.
- Wait for new events to be pushed from GitLab. The app should work without any
Field x-gitlab-event not founderrors.
- Re-open GitLab dashboards.
Viewing GitLab Dashboards
All dashboards have a set of filters that you can apply to the entire dashboard. Use these filters to drill down and examine the data to a granular level.
- You can change the time range for a dashboard or panel by selecting a predefined interval from a drop-down list, choosing a recently used time range, or specifying custom dates and times. Learn more.
- You can use template variables to drill down and examine the data on a granular level. For more information, see Filtering Dashboards with Template Variables.
- Most Next-Gen apps allow you to provide the scope at the installation time and are comprised of a key (
_sourceCategoryby default) and a default value for this key. Based on your input, the app dashboards will be parameterized with a dashboard variable, allowing you to change the dataset queried by all panels. This eliminates the need to create multiple copies of the same dashboard with different queries.
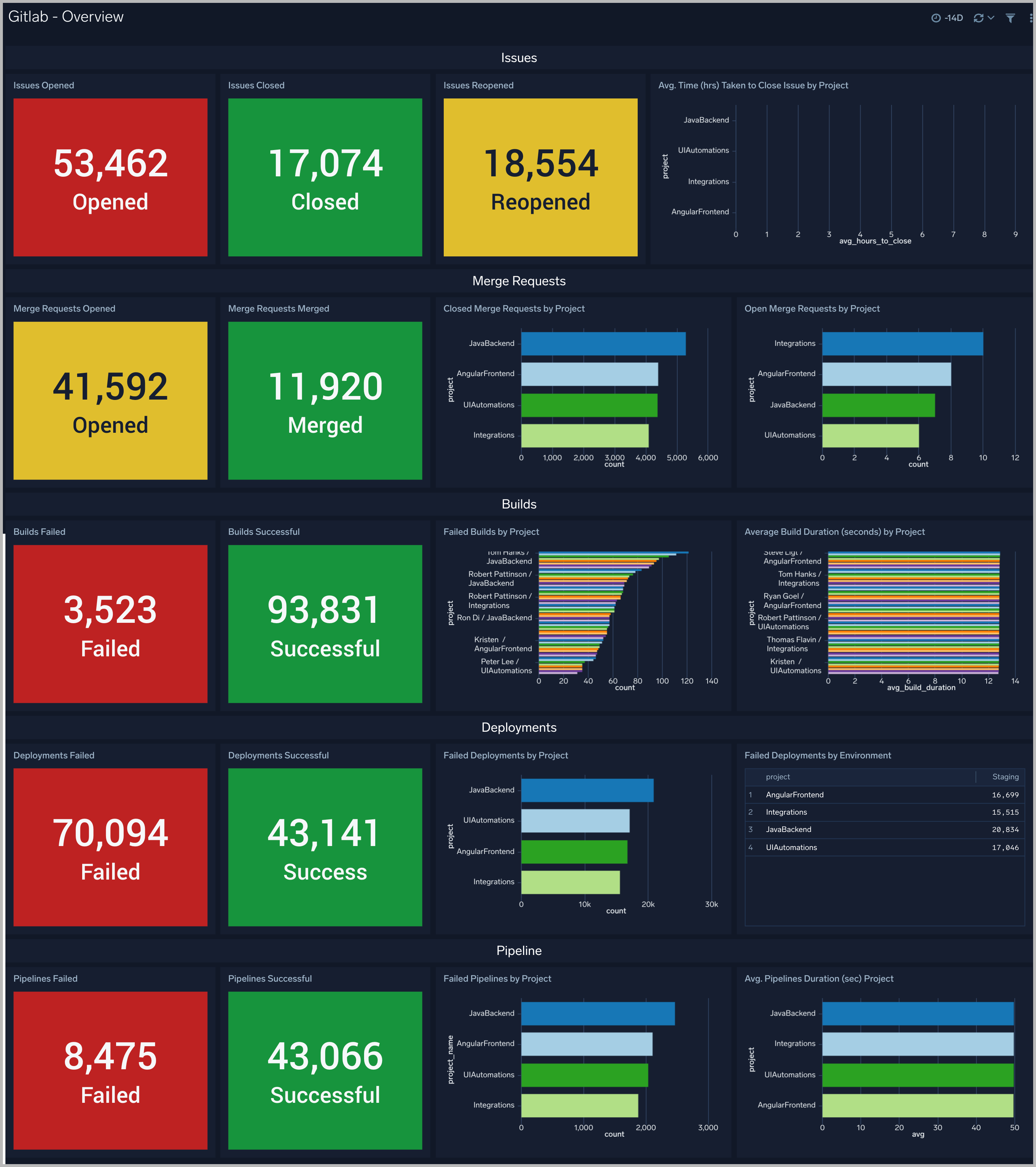
Overview
The GitLab - Overview dashboard provides users with a high-level view of events such as Issues, Merge Requests, Builds, Deployments, and pipelines.
Use this dashboard to:
- Get insight into the number of opened and closed Issues and Merge Requests.
- Get insight into the number of successful and failed Builds, Deployments, and Pipelines.
- Get details like average duration to close issue, the average duration of a build by project, and average duration of a pipeline by projects.
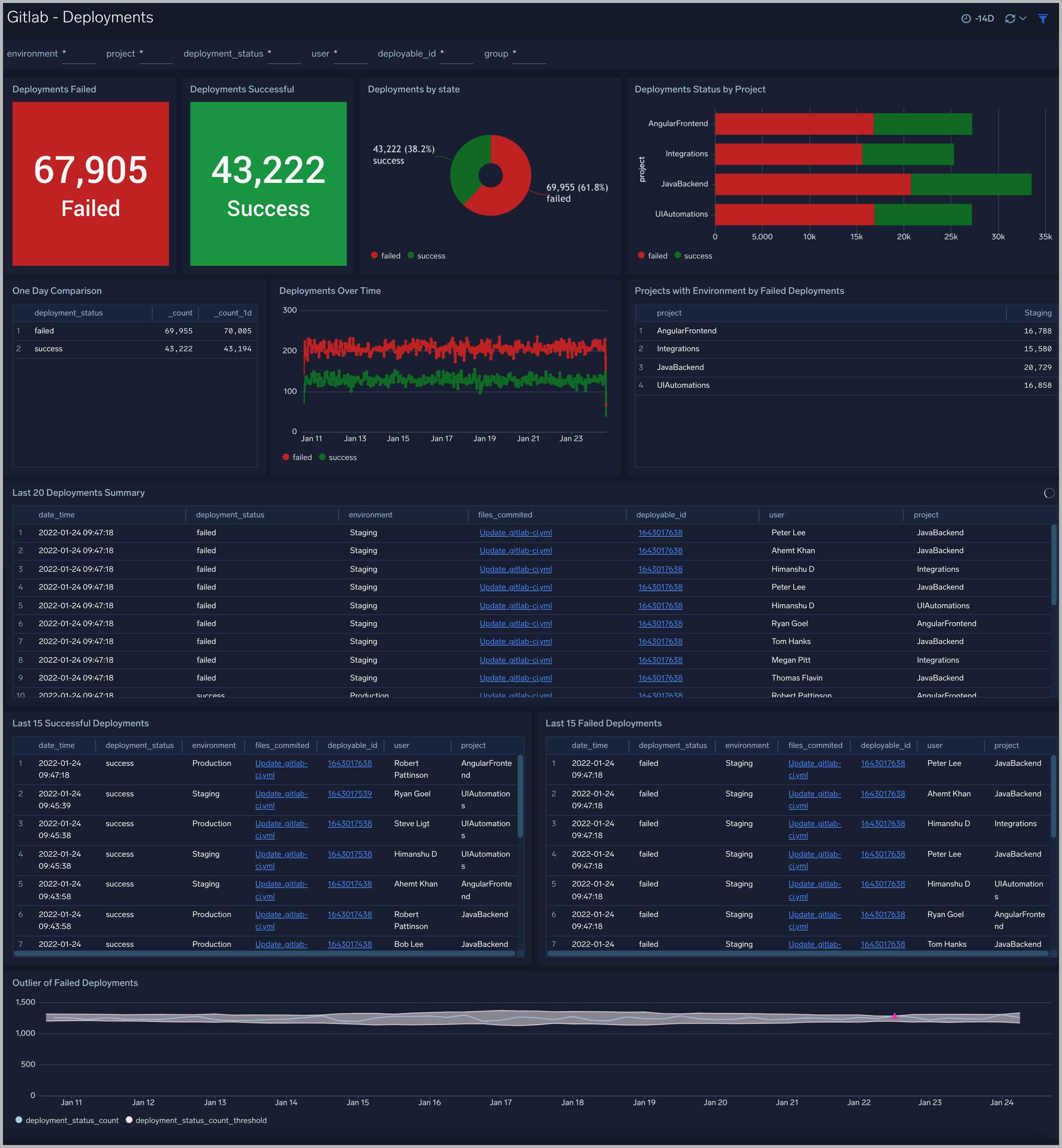
Deployments
The GitLab - Deployments dashboard provides users with a high-level view of activities such as deployments failed or success.
Use this dashboard to:
- Understand the number of deployments that failed or succeeded.
- Get insight into failed deployments by project and environments.
- Identify the Failed and Successful deployments in chronological order. You can use filters to drill down to a more detailed view.
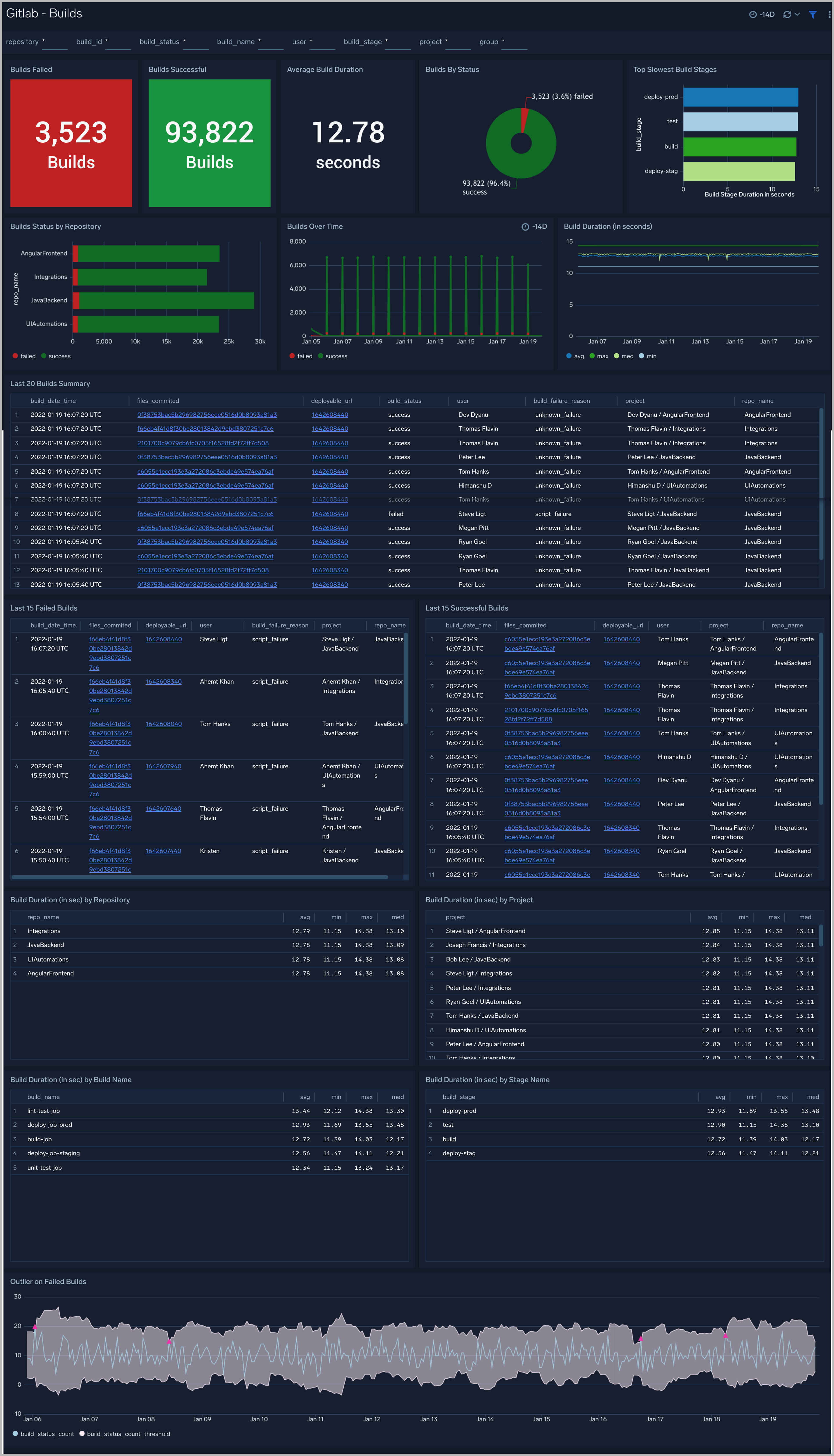
Builds
The GitLab - Builds dashboard provides users with a high-level view of activities such as builds failed or success.
Use this dashboard to:
- Understand the number of builds that failed or succeeded.
- Identify the Failed and Successful deployments in chronological order. You can use filters to drill down to a more detailed view.
- Get statistics of build duration by Repository, Project, Build Name, and Stage Name.
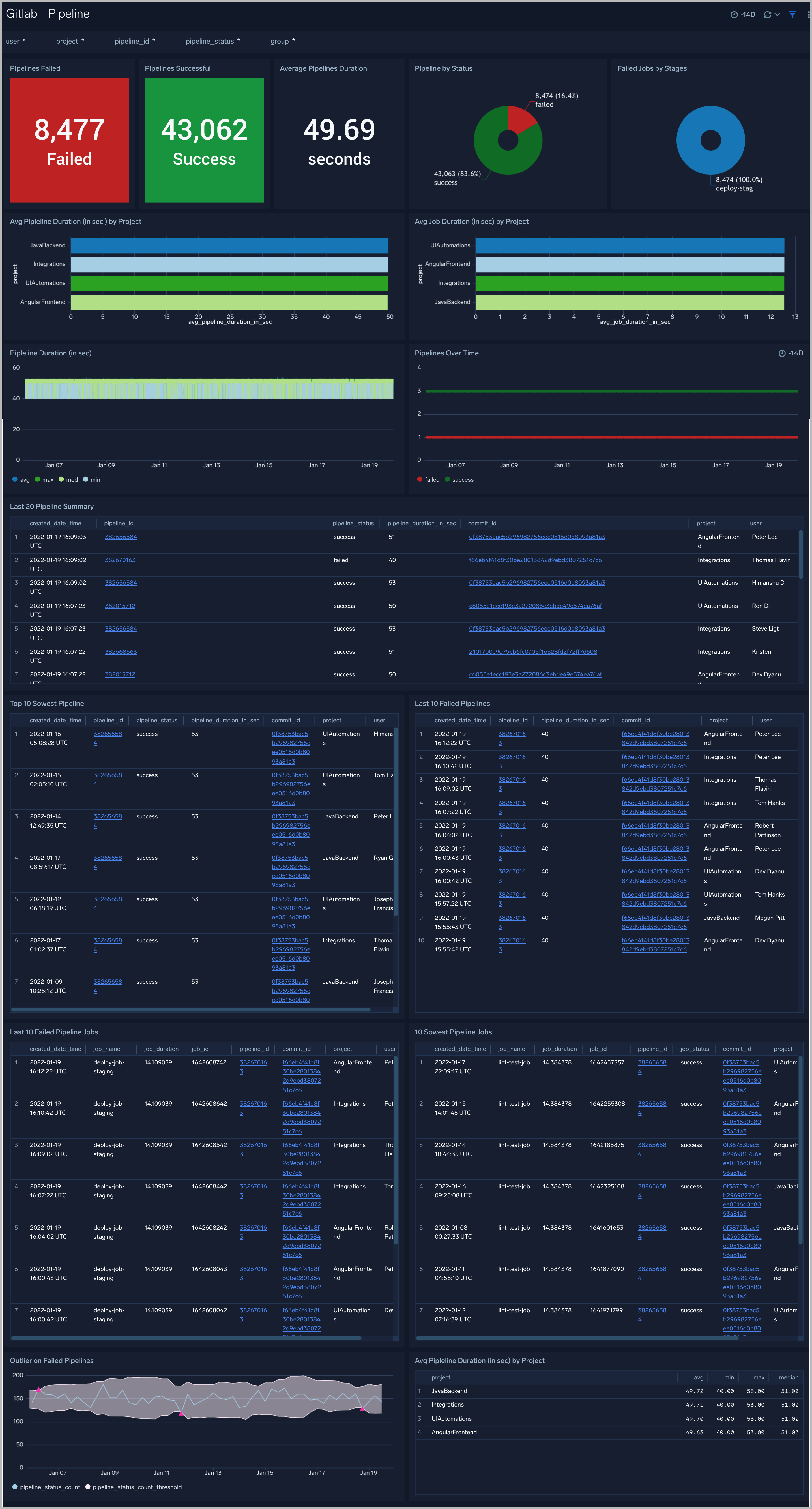
Pipeline
The GitLab - Pipeline dashboard provides users with a high-level view of activities such as builds failed or success.
Use this dashboard to:
- Understand the number of pipelines that failed or succeeded.
- Get insight into the average pipeline and job duration by project.
- Identify the Failed and Successful pipelines in chronological order. You can use filters to drill down to a more detailed view.
- Identify the Failed and Successful pipeline jobs in chronological order. You can use filters to drill down to a more detailed view.
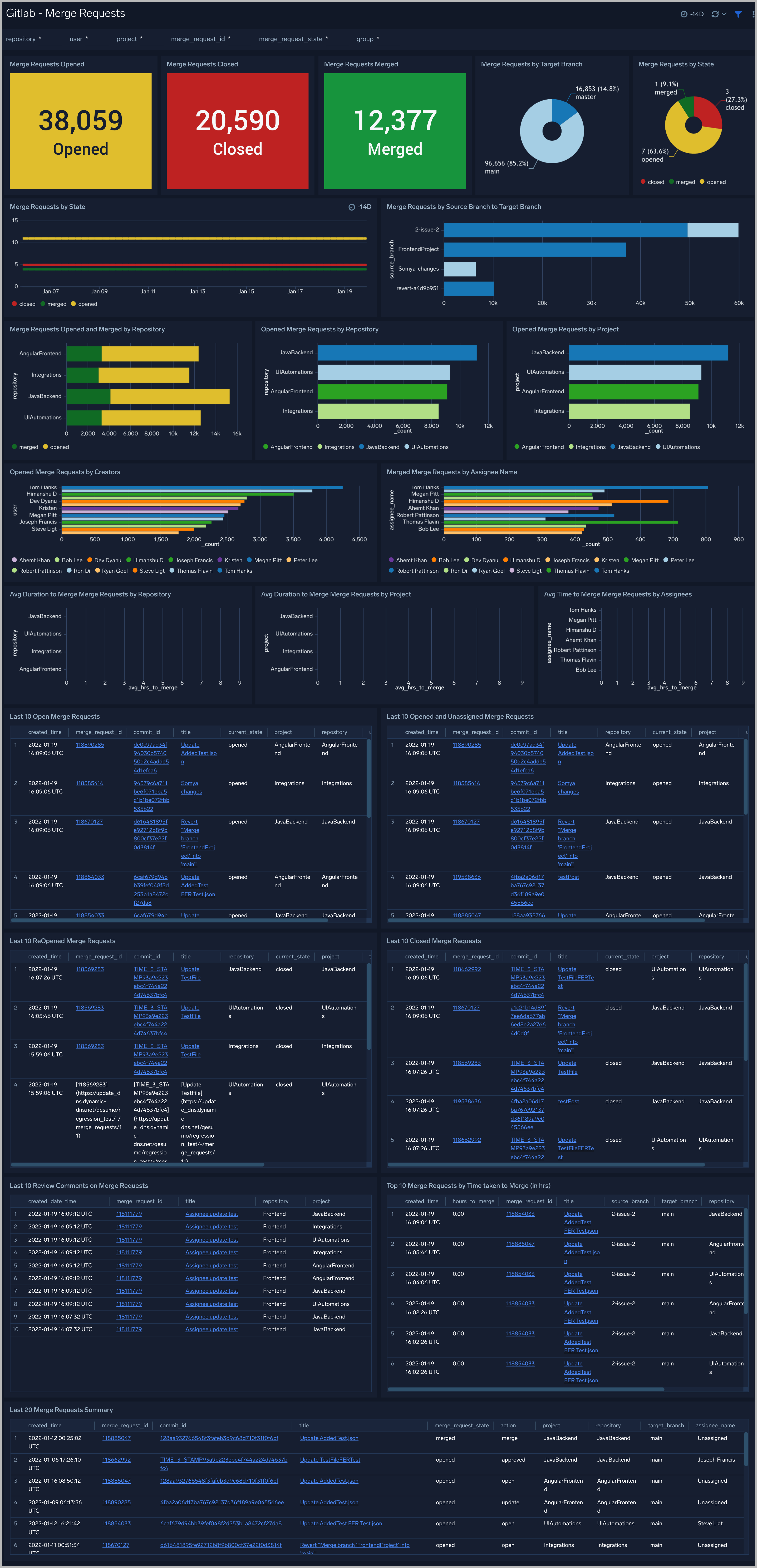
Merge Requests
The GitLab - Merge Requests dashboard provides users with a high-level view of activities such as Merge Requests opened, closed, and merged.
Use this dashboard to:
- Understand the number of merge requests being opened, closed, and merged.
- Get insight into open merge requests by project, repository, and creators
- Get insight into the average duration to merge requests by project, repository, and assignees.
- Get the review comments on the merge requests.
- Identify the Open, Reopened, Unassigned, and Closed merge requests in chronological order. You can use filters to drill down to a more detailed view.
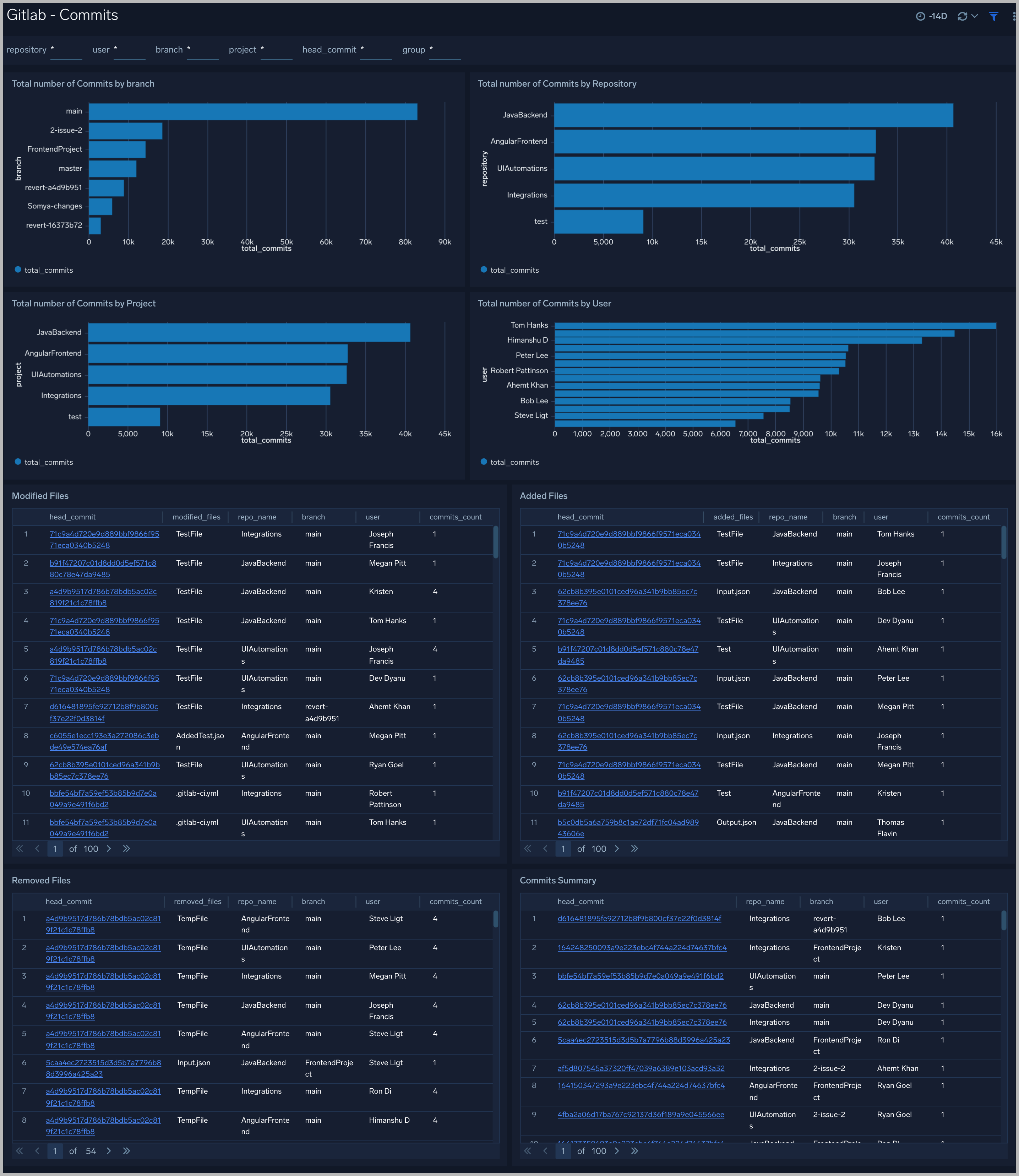
Commits
The GitLab - Commits dashboard provides users with a high-level view of activities such as files modified, added, and removed by commit.
Use this dashboard to:
- Get insight into the total number of commits by branch, project, repository, and user.
- Identify the Modified, Added, and Removed files by commit id in chronological order. You can use filters to drill down to a more detailed view.