ActiveMQ
The ActiveMQ app is a unified logs and metrics app that helps you monitor the availability, performance, health, and resource utilization of your ActiveMQ messaging clusters. Preconfigured dashboards provide insight into cluster status, nodes, producers, consumers, destinations, resource utilization, message rates, and error logs.
Sample log messages
- Kubernetes environments
- Non-Kubernetes environments
{
timestamp:1624348918179,
log:"2021-06-22 08:01:57,993 | DEBUG | Publishing: tcp://activemq-2:61616 for broker transport URI: tcp://activemq-2:61616?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600 | org.apache.activemq.broker.TransportConnector | ActiveMQ Transport: tcp:///10.32.0.1:16932@61616",
stream:"stdout",
time:"2021-06-22T08:01:58.177654533Z"
}
2021-06-22 15:00:41,922 | DEBUG | Stopping transport tcp:///192.168.100.8:36302@61616 | org.apache.activemq.transport.tcp.TcpTransport | ActiveMQ BrokerService[localhost] Task-15300
Host: broker-3-activemq Name: /opt/activemq/data/activemq.log Category:logfile
Collecting logs and metrics for ActiveMQ
This App has been tested with following ActiveMQ versions:
- 5.16.2.
Configure ActiveMQ logs and metrics collection
Choose your environment:
- Kubernetes environments
- Non-Kubernetes environments
In Kubernetes environments, we use the Telegraf Operator, which is packaged with our Kubernetes collection (learn more). The diagram below illustrates how data is collected from ActiveMQ in a Kubernetes environment. In the architecture shown below, there are four services that make up the metric collection pipeline: Telegraf, Telegraf Operator, Prometheus, and Sumo Logic Distribution for OpenTelemetry Collector.
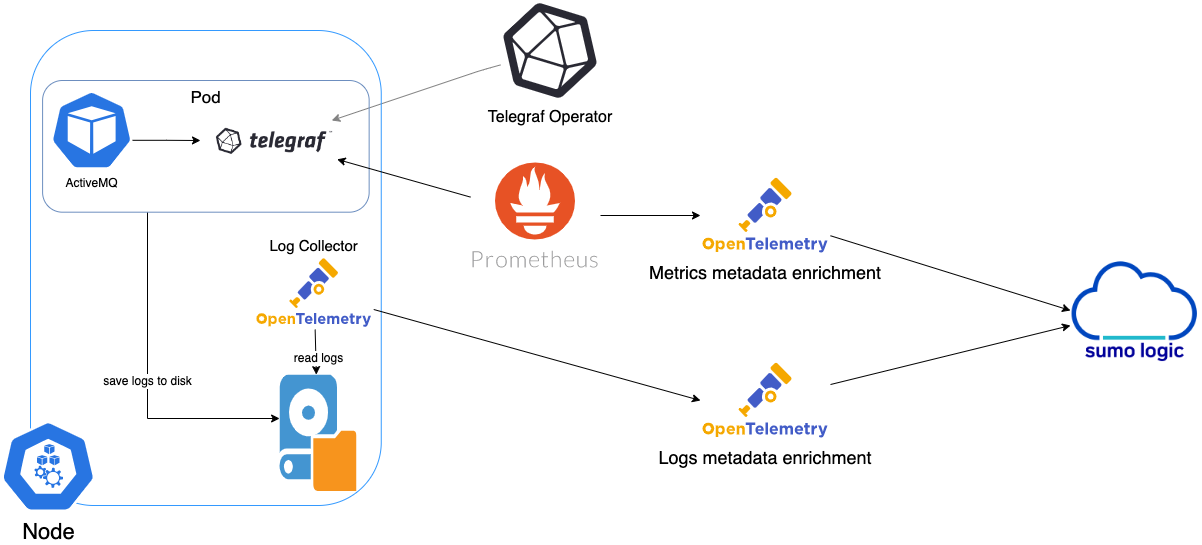
The first service in the metrics pipeline is Telegraf. Telegraf collects metrics from ActiveMQ. Note that we’re running Telegraf in each pod we want to collect metrics from as a sidecar deployment for example, Telegraf runs in the same pod as the containers it monitors. Telegraf uses the Jolokia2 input plugin to obtain metrics. (For simplicity, the diagram doesn’t show the input plugins.) The injection of the Telegraf sidecar container is done by the Telegraf Operator. Prometheus pulls metrics from Telegraf and sends them to Sumo Logic Distribution for OpenTelemetry Collector, which enriches metadata and sends metrics to Sumo Logic.
In the logs pipeline, Sumo Logic Distribution for OpenTelemetry Collector collects logs written to standard out and forwards them to another instance of Sumo Logic Distribution for OpenTelemetry Collector, which enriches metadata and sends logs to Sumo Logic.
It’s assumed that you are using the latest helm chart version. If not, upgrade using the instructions here.
Configure Metrics Collection
This section explains the steps to collect ActiveMQ metrics from a Kubernetes environment.
- Set up Kubernetes Collection with the Telegraf Operator.
- Configure ActiveMQ Image: To enable Telegraf sidecar to get metrics from ActiveMQ Container, you must enable read metrics from ActiveMQ Container via the JMX MBeans and Disable strict-checking.
- Enable reads metrics from ActiveMQ Container via the JMX MBeans. While building the ActiveMQ docker image, setting
useJmx="true”in ActiveMQ.xml config file:
<broker useJmx="true" brokerName="BROKER1">
...
</broker>- Disable strict-checking by editing file
jolokia-access.xml. While building the ActiveMQ docker image, edit filejolokia-access.xmlin<Folder ActiveMQ Installed>/webapps/api/WEB-INF/classes/and comment or remove section below:
<cors>
<strict-checking/>
</cors> - Enable reads metrics from ActiveMQ Container via the JMX MBeans. While building the ActiveMQ docker image, setting
- Add the following annotations on your ActiveMQ pods:
annotations:
telegraf.influxdata.com/class: sumologic-prometheus
prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
prometheus.io/port: "9273"
telegraf.influxdata.com/inputs: |+
[[inputs.disk]]
mount_points = ["/"]
[inputs.disk.tags]
environment="dev"
component="messaging"
messaging_system="activemq"
messaging_cluster="activemq_on_k8s_CHANGE_ME"
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent]]
urls = ["http://localhost:8161/api/jolokia"]
name_prefix = "activemq_"
username = "<username_CHANGE_ME>"
password = "<password_CHANGE_ME>"
[inputs.jolokia2_agent.tags]
environment="prod_CHANGE_ME"
component="messaging"
messaging_system="activemq"
messaging_cluster="activemq_on_k8s_CHANGE_ME"
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "OperatingSystem"
mbean = "java.lang:type=OperatingSystem"
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "jvm_runtime"
mbean = "java.lang:type=Runtime"
paths = ["Uptime"]
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "jvm_memory"
mbean = "java.lang:type=Memory"
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "jvm_garbage_collector"
mbean = "java.lang:name=*,type=GarbageCollector"
paths = ["CollectionCount"]
tag_keys = ["name"]
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "queue"
mbean =
"org.apache.activemq:brokerName=*,destinationName=*,
destinationType=Queue,type=Broker"
tag_keys = ["brokerName","destinationName"]
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "topic"
mbean =
"org.apache.activemq:brokerName=*,destinationName=*,
destinationType=Topic,type=Broker"
tag_keys = ["brokerName","destinationName"]
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "broker"
mbean = "org.apache.activemq:brokerName=*,type=Broker"
tag_keys = ["brokerName"]
Enter values for the following parameters (marked CHANGE_ME above):
-
telegraf.influxdata.com/inputs. This contains the required configuration for the Telegraf ActiveMQ Input plugin. Please refer to this doc for more information on configuring the ActiveMQ input plugin for Telegraf. Note: As telegraf will be run as a sidecar the host should always be localhost.- In the input plugins section, which is
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent]]:url- The URL of the ActiveMQ server for JMX MBeans HTTP Endpoint. Please see this doc for more information on additional parameters for configuring the Jolokia2 input plugin for Telegraf.username. The Username of ActiveMQ’s admin account. The default is “admin”.password. The password of ActiveMQ's admin account. The default is “admin”.
- In the tags section,
[inputs.jolokia2_agent.tags]:environment. This is the deployment environment where the ActiveMQ cluster identified by the value ofserversresides. For example: dev, prod or qa. While this value is optional we highly recommend setting it.messaging_cluster. Enter a name to identify this ActiveMQ cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.
Do not modify these valuesModifying these values will cause the Sumo Logic apps to not function correctly.
telegraf.influxdata.com/class: sumologic-prometheus. Instructs the Telegraf operator what output to use.prometheus.io/scrape: "true". Ensures our Prometheus will scrape the metrics.prometheus.io/port: "9273". Tells prometheus what ports to scrape on.telegraf.influxdata.com/inputs- In the tags section,
[inputs.jolokia2_agent.tags]:component: “messaging”- Used by Sumo Logic apps to identify application components.messaging_system: “activemq”- Identifies the messaging system.
- In the tags section,
- For all other parameters, please see this doc for more parameters that can be configured in the Telegraf agent globally.
- In the input plugins section, which is
- SumoLogic Kubernetes collection will automatically start collecting metrics from the pods having the labels and annotations defined in the previous step.
- Verify metrics in Sumo Logic.
Configure Logs Collection
This section explains the steps to collect ActiveMQ logs from a Kubernetes environment.
-
Collect ActiveMQ logs written to standard output. If your ActiveMQ pod is writing logs to standard output, follow the steps below to collect logs:
- Make sure that the logs from ActiveMQ are sent to stdout. Follow the instructions below to capture ActiveMQ logs from stdout on Kubernetes. Apply the following labels to the ActiveMQ pods:
environment: "prod_CHANGE_ME"
component: "messaging"
messaging_system: "activemq"
messaging_cluster: "activemq_on_k8s_CHANGE_ME"- Enter in values for the following parameters (marked in
CHANGE_MEabove):
environment. This is the deployment environment where the ActiveMQ cluster identified by the value ofserversresides. For example: dev, prod or qa. While this value is optional we highly recommend setting it.messaging_cluster. Enter a name to identify this ActiveMQ cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.
Do not modify these valuesModifying these values will cause the Sumo Logic apps to not function correctly.
component: “messaging”. This value is used by Sumo Logic apps to identify application components.messaging_system: “activemq”. This value identifies the messaging system.
- For all other parameters, see this doc for more parameters that can be configured in the Telegraf agent globally.
- The Sumologic-Kubernetes-Collection will automatically capture the logs from stdout and will send the logs to Sumologic. For more information on deploying Sumologic-Kubernetes-Collection, please see this page.
-
(Optional) Collecting ActiveMQ Logs from a Log File. If your ActiveMQ chart/pod is writing its logs to log files, you can use a sidecar to send log files to standard out. To do this:
- Determine the location of the ActiveMQ log file on Kubernetes. This can be determined from the log4j.properties for your ActiveMQ cluster along with the mounts on the ActiveMQ pods.
- Install the Sumo Logic tailing sidecar operator.
- Add the following annotation in addition to the existing annotations.
annotations:
tailing-sidecar: sidecarconfig;<mount>:<path_of_ActiveMQ_log_file>/<ActiveMQ_log_file_name>Example:
annotations:
tailing-sidecar: sidecarconfig;data:/opt/activemq/data/activemq.log- Ensure that the ActiveMQ pods are running and annotations are applied by using the command:
kubectl describe pod <ActiveMQ_pod_name>- Sumo Logic Kubernetes collection will automatically start collecting logs from the pods having the annotations defined above.
-
FER to normalize the fields in Kubernetes environments. Labels created in Kubernetes environments automatically are prefixed with
pod_labels. To normalize these for our app to work, a Field Extraction Rule is automatically created named AppObservabilityMessagingActiveMQFER
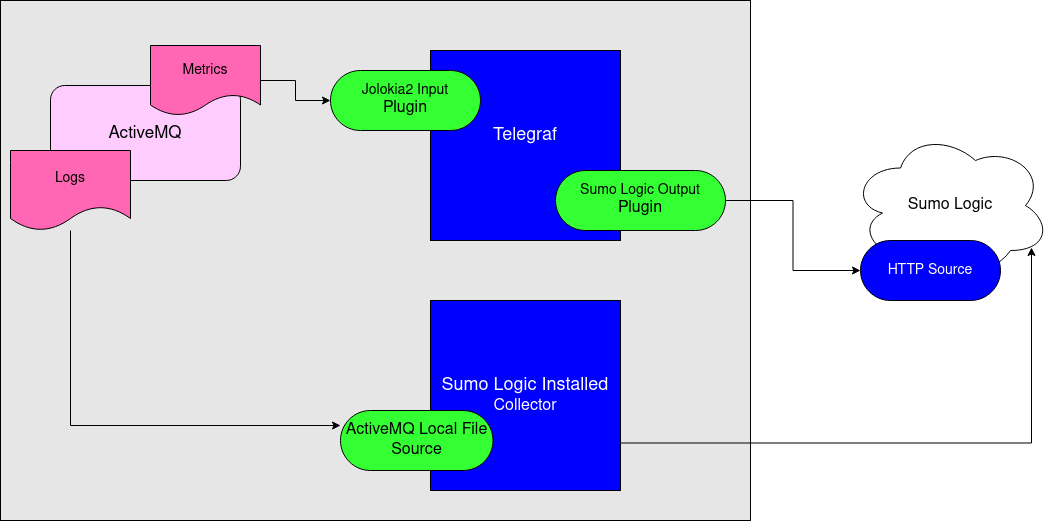
In non-Kubernetes environments, we use the Telegraf operator for ActiveMQ metric collection and Sumo Logic Installed Collector for collecting ActiveMQ logs. The diagram below illustrates the components of the ActiveMQ collection in a non-Kubernetes environment. Telegraf runs on the same system as ActiveMQ, and uses the Jolokia2 input plugin to obtain ActiveMQ metrics. The Sumo Logic output plugin to send the metrics to Sumo Logic. Logs from ActiveMQ on the other hand are sent to a Sumo Logic Local File source.
Configure Metrics Collection
This section provides instructions for configuring metrics collection for the Sumo Logic App for ActiveMQ.
- Configure a Hosted Collector. To create a new Sumo Logic hosted collector, perform the steps in the Configure a Hosted Collector section of the Sumo Logic documentation.
- Configure an HTTP Logs and Metrics Source. Create a new HTTP Logs and Metrics Source in the hosted collector created above by following these instructions. Make a note of the HTTP Source URL.
- Install Telegraf. Use the following steps to install Telegraf.
- Configure and start Telegraf. As part of collecting metrics data from Telegraf, we will use the Jolokia2 input plugin to get data from Telegraf and the Sumo Logic output plugin to send data to Sumo Logic.
- Before you configure telegraf, you will need to:
- Enable reads metrics from ActiveMQ servers via the JMX MBeans by setting
useJmx="true"in file config ActiveMQ.xml<broker useJmx="true" brokerName="BROKER1">
...
</broker> - Disable strict-checking by editing file
jolokia-access.xml.Navigate to directory:<Folder ActiveMQ Installed>/webapps/api/WEB-INF/classes/ - Open file
jolokia-access.xml, and comment or remove section below:<cors>
<strict-checking/>
</cors>
- Enable reads metrics from ActiveMQ servers via the JMX MBeans by setting
- Create or modify
telegraf.confand copy and paste the text below:
[[inputs.disk]]
mount_points = ["/"]
[inputs.disk.tags]
environment="dev"
component="messaging"
messaging_system="activemq"
messaging_cluster="activemq_CHANGE_ME"
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent]]
urls = ["http://localhost:8161/api/jolokia"]
name_prefix = "activemq_"
username = "<username_CHANGE_ME>"
password = "<password_CHANGE_ME>"
[inputs.jolokia2_agent.tags]
environment="dev"
component="messaging"
messaging_system="activemq"
messaging_cluster="activemq__CHANGE_ME"
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "OperatingSystem"
mbean = "java.lang:type=OperatingSystem"
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "jvm_runtime"
mbean = "java.lang:type=Runtime"
paths = ["Uptime"]
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "jvm_memory"
mbean = "java.lang:type=Memory"
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "jvm_garbage_collector"
mbean = "java.lang:name=*,type=GarbageCollector"
paths = ["CollectionCount"]
tag_keys = ["name"]
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "queue"
mbean =
"org.apache.activemq:brokerName=*,destinationName=*,destinationType=Queue,type=Broker"
tag_keys = ["brokerName","destinationName"]
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "topic"
mbean =
"org.apache.activemq:brokerName=*,destinationName=*,destinationType=Topic,type=Broker"
tag_keys = ["brokerName","destinationName"]
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent.metric]]
name = "broker"
mbean = "org.apache.activemq:brokerName=*,type=Broker"
tag_keys = ["brokerName"]
[[outputs.sumologic]]
url = "<URL Created in Step b_CHANGE_ME>"
data_format = "prometheus" - Before you configure telegraf, you will need to:
-
Enter values for the following parameters (marked in
CHANGE_MEabove):- In the input plugins section, which is
[[inputs.jolokia2_agent]]:url- The URL of the ActiveMQ server for JMX MBeans HTTP Endpoint. Please see this doc for more information on additional parameters for configuring the Jolokia2 input plugin for Telegraf.username. The Username of ActiveMQ’s admin account . The default is “admin”.password. The password of ActiveMQ's admin account. The default is “admin”.
- In the tags section, which is
[inputs.jolokia2_agent.tags]environment. This is the deployment environment where the ActiveMQ cluster identified by the value ofserversresides. For example: dev, prod or qa. While this value is optional we highly recommend setting it.messaging_cluster. Enter a name to identify this ActiveMQ cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.
- In the output plugins section, which is
[[outputs.sumologic]]:url- This is the HTTP source URL created in step 3 (Install Telegraf). Please see this doc for more information on additional parameters for configuring the Sumo Logic Telegraf output plugin.
Do not modify these valuesModifying these values set by this Telegraf configuration will cause the Sumo Logic apps to not function correctly.
data_format - "prometheus"In the output plugins section, which is[[outputs.sumologic]]. Metrics are sent in the Prometheus format to Sumo Logic.component: “messaging”- In the input plugins section, which is[[inputs.jolokia2_agent]]. This value is used by Sumo Logic apps to identify application components.messaging_system: "activemq"- In the input plugins sections. In other words, this value identifies the messaging system.
- For all other parameters, see this doc for more parameters that can be configured in the Telegraf agent globally.
- In the input plugins section, which is
Once you have finalized your telegraf.conf file, you can start or reload the telegraf service using instructions from the doc.
At this point, ActiveMQ metrics should start flowing into Sumo Logic.
Configure Logs Collection
This section provides instructions for configuring log collection for ActiveMQ running on a non-kubernetes environment for the Sumo Logic App for ActiveMQ.
By default, ActiveMQ logs are stored in a log file. Sumo Logic supports collecting logs via a local log file. Local log files can be collected via Installed collectors. An Installed collector will require you to allow outbound traffic to Sumo Logic endpoints for collection to work. For detailed requirements for Installed collectors, see this page.
Based on your infrastructure and networking setup choose one of these methods to collect ActiveMQ logs and follow the instructions below to set up log collection:
- Configure logging in ActiveMQ. ActiveMQ uses Log4j for logging. It supports logging via the following methods: local text log files, syslog, stdout, remote storage. ActiveMQ logs have eight levels of verbosity: OFF, FATAL, ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE, ALL. For details, visit this page. For the dashboards to work properly, must set
log level = debug. The default log level is INFO. All logging settings are located in log4j.properties. - Configure ActiveMQ to log to a Local file. By default, ActiveMQ logs are stored in
<Folder ActiveMQ Installed>/data/activemq.log. The default directory for log files is listed in the log4j.properties file. To configure the log output destination to a log file:- Navigate to directory :
<Folder ActiveMQ Installed> - Open file log4j.properties and edit options below:
log4j.appender.logfile.file=${activemq.data}/activemq.log
log4j.appender.logfile.maxFileSize=10240MB
log4j.logger.org.apache.activemq=DEBUG - Logs from the ActiveMQ log file can be collected via a Sumo Logic Installed collector and a Local File Source as explained in the next section.
- Navigate to directory :
- Configuring a Collector. To add an Installed collector, perform the steps as defined on the page Configure an Installed Collector.
- Configuring a Source. To collect logs directly from your ActiveMQ machine, use an Installed Collector and a Local File Source:
- Add a Local File Source.
- Configure the Local File Source fields as follows:
- Name. (Required)
- Description. (Optional)
- File Path (Required). Enter the path to your activemq.log. The files are typically located in
<Folder ActiveMQ Installed>/data/activemq.log. If you're using a customized path, check the log4j.properties file for this information. - Source Host. Sumo Logic uses the hostname assigned by the OS unless you enter a different host name
- Source Category. Enter any string to tag the output collected from this Source, such as ActiveMQ/Logs. (The Source Category metadata field is a fundamental building block to organize and label Sources. For details, see Best Practices.)
- Fields. Set the following fields:
component = messagingmessaging_system = activemqmessaging_cluster = <Your_ActiveMQ_Cluster_Name>environment = <Environment_Name>, such as Dev, QA or Prod.
- Configure the Advanced section:
- Enable Timestamp Parsing. Select Extract timestamp information from log file entries.
- Time Zone. Choose the option, Ignore time zone from log file and instead use, and then select your ActiveMQ Server’s time zone.
- Timestamp Format. The timestamp format is automatically detected.
- Encoding. Select UTF-8 (Default).
- Enable Multiline Processing. Detect messages spanning multiple lines.
- Infer Boundaries - Detect message boundaries automatically
- Click Save.
At this point, ActiveMQ logs should start flowing into Sumo Logic.
Installing the ActiveMQ app
To install the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Install App.
note
Sometimes this button says Add Integration.
- Click Next in the Setup Data section.
- In the Configure section of your respective app, complete the following fields.
- Field Name. If you already have collectors and sources set up, select the configured metadata field name (eg _sourcecategory) or specify other custom metadata (eg: _collector) along with its metadata Field Value.
- Is K8S deployment involved. Specify if resources being monitored are partially or fully deployed on Kubernetes (K8s)
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-installation
Once your app is installed, it will appear in your Installed Apps folder, and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
Each panel slowly fills with data matching the time range query received since the panel was created. Results will not immediately be available but will be updated with full graphs and charts over time.
As part of the app installation process, the following fields will be created by default:
componentenvironmentmessaging_systemmessaging_clusterpod
If you're using ActiveMQ in a Kubernetes environment, the following additional fields will be automatically created as a part of the app installation process:
pod_labels_componentpod_labels_environmentpod_labels_messaging_systempod_labels_messaging_cluster
Viewing the ActiveMQ Dashboards
All dashboards have a set of filters that you can apply to the entire dashboard. Use these filters to drill down and examine the data to a granular level.
- You can change the time range for a dashboard or panel by selecting a predefined interval from a drop-down list, choosing a recently used time range, or specifying custom dates and times. Learn more.
- You can use template variables to drill down and examine the data on a granular level. For more information, see Filtering Dashboards with Template Variables.
- Most Next-Gen apps allow you to provide the scope at the installation time and are comprised of a key (
_sourceCategoryby default) and a default value for this key. Based on your input, the app dashboards will be parameterized with a dashboard variable, allowing you to change the dataset queried by all panels. This eliminates the need to create multiple copies of the same dashboard with different queries.
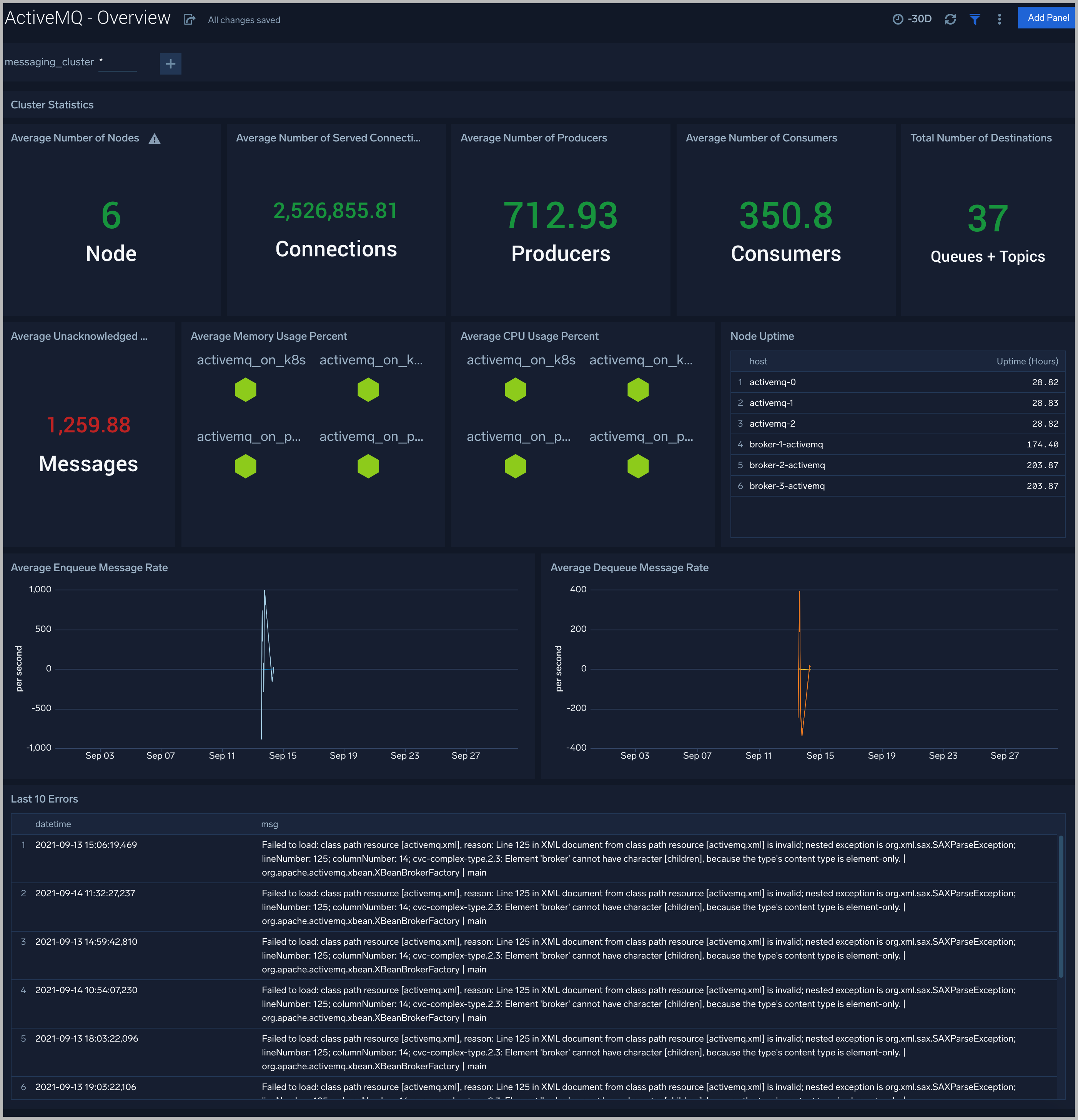
Overview
The ActiveMQ - Overview dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of your ActiveMQ deployment across brokers, queues, topics, and messages.
Use this dashboard to:
- Analyze Memory and CPU utilization.
- Gain insights into Enqueue messages for your ActiveMQ server.
- Gain insights into Dequeue messages for your ActiveMQ server.
- Determine node uptime, the number of nodes, connections, producer, consumer, queues, topics unack messages, across each cluster and ensure they match with expectations.
- Analysis of near errors.
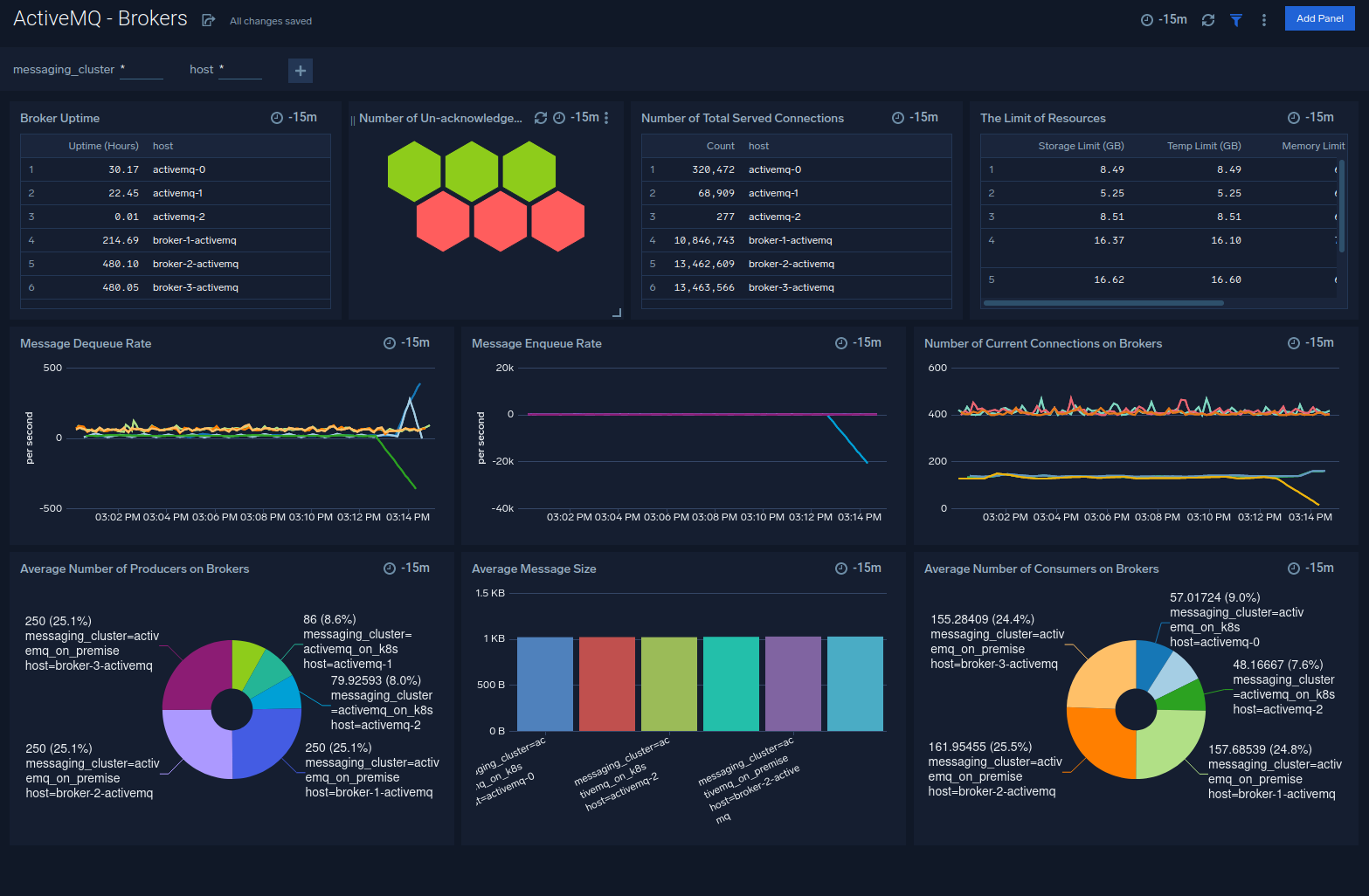
Brokers
The ActiveMQ - Brokers dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of the state of your brokers in the ActiveMQ cluster.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor brokers uptime.
- Analyze unacknowledged messages, serve connections for your ActiveMQ brokers..
- Gain insights into the limit of resources for your ActiveMQ brokers.
- Gain insights into enqueue rate, dequeue rate for your ActiveMQ brokers.
- Determine the amount of current connections, producers, and consumers for your ActiveMQ brokers.
- find average message size.
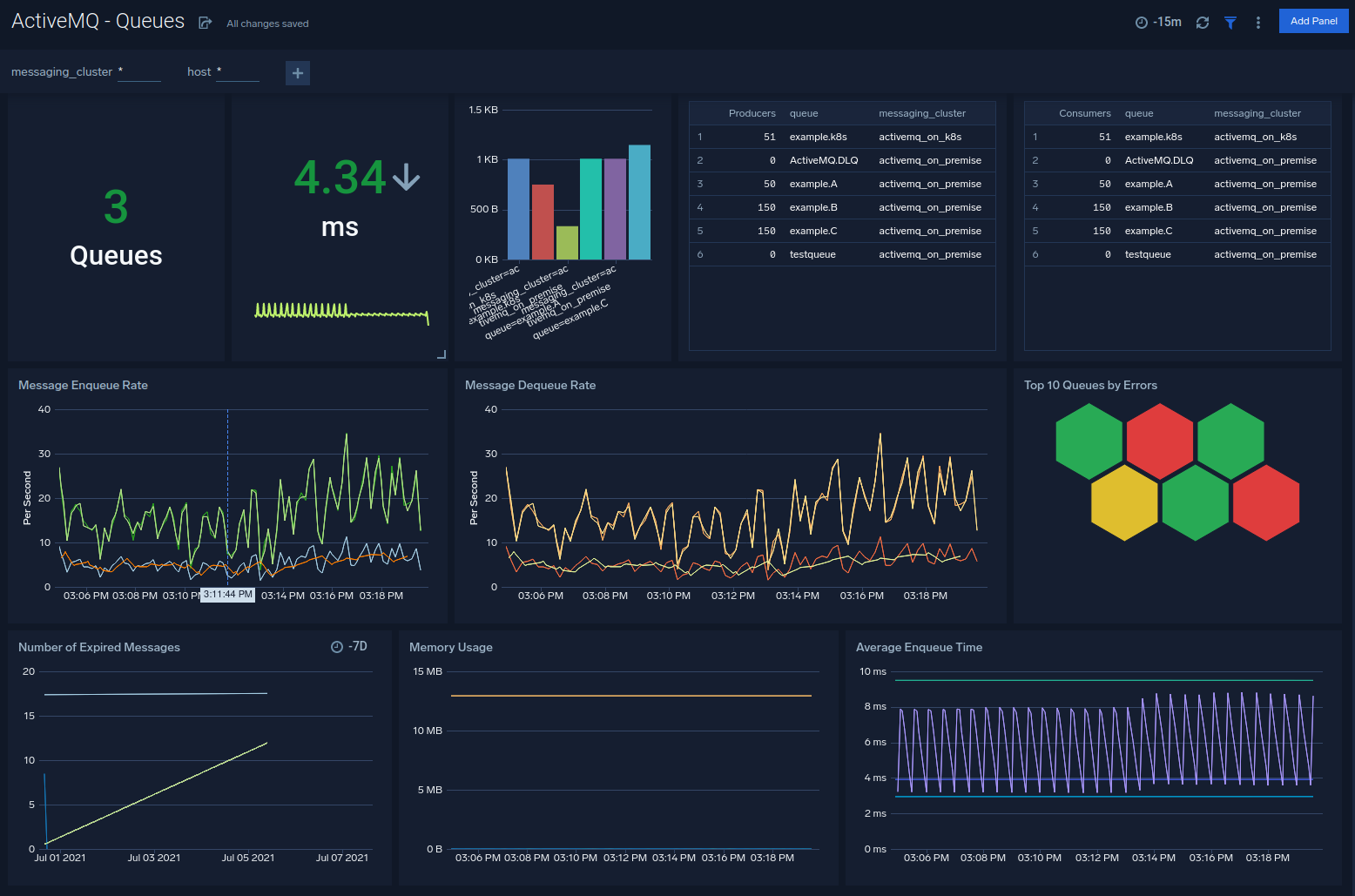
Queues
The ActiveMQ - Queues dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of the state of your queues in ActiveMQ clusters.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor en queue latency, the memory usage of queues.
- Monitor queues, producers on queues, consumers on queues.
- Gain insights into en queue rate, dequeue rate for your ActiveMQ queues.
- Determine the number of current connections, producers, consumers, errors, and expired messages on queues.
- Find average message size on queues.
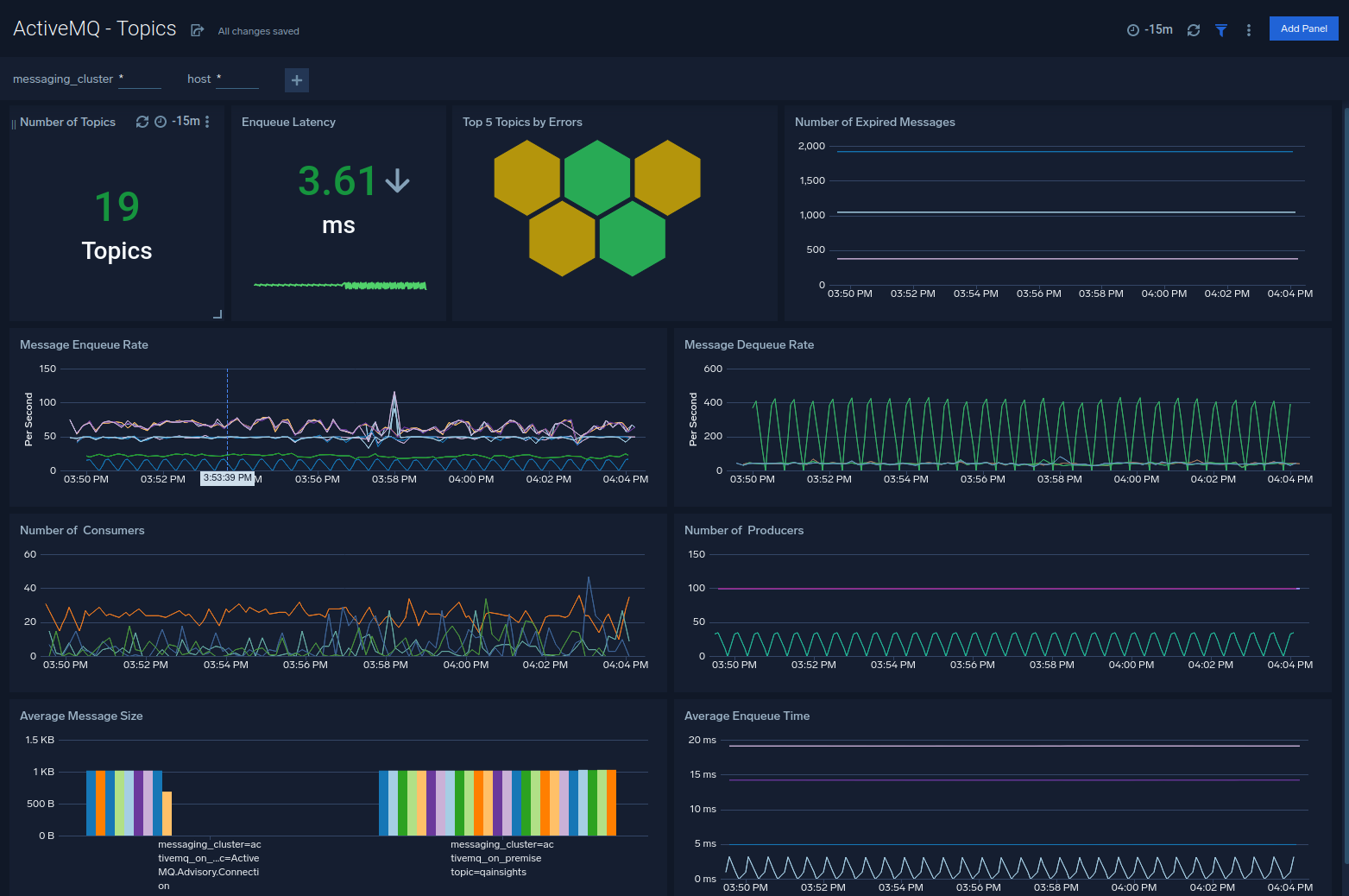
Topics
The ActiveMQ - Topics dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of the state of your topics in ActiveMQ clusters.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor en queue latency, the memory usage of topics.
- Determine the number of topics, producers on topics, consumers on topics.
- Gain insights into en queue rate, dequeue rate for your ActiveMQ topics.
- Analyze current connections, producers, consumers, errors, and expired messages on queues.
- Find average message size on queues.
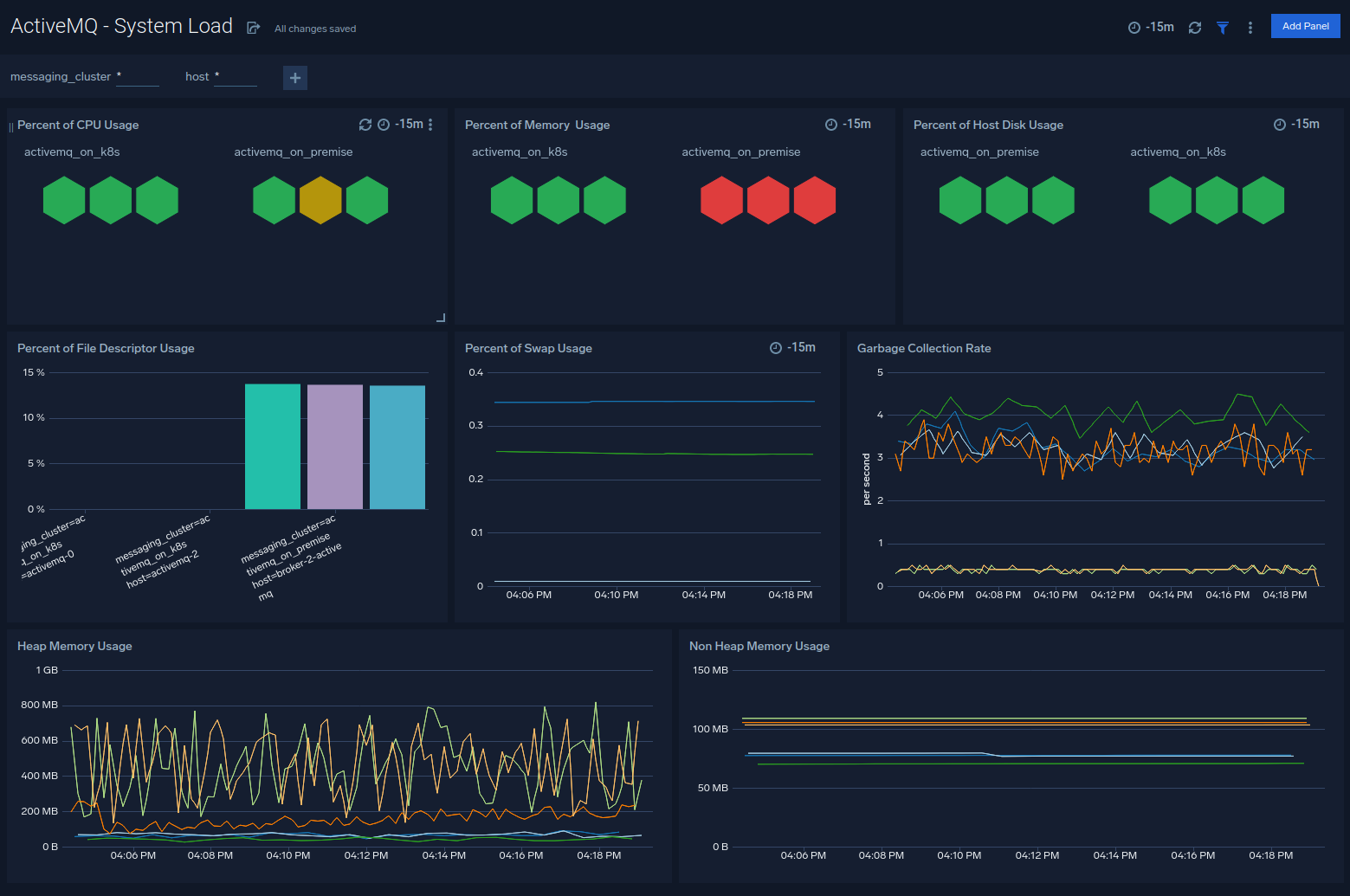
Resource Utilization
The ActiveMQ - Resource Utilization dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of the state of system loads in clusters: CPU usage, memory usage, Swap usage, file descriptor usage, garbage collection rate, heap, and non-heap usage.
Use this dashboard to:
- Analyze memory, CPU, disk, swap, file descriptor utilization of nodes in clusters.
- Gain insights into the garbage collection rate for your ActiveMQ nodes.
- Gain insights into a heap, non-heap usage for your ActiveMQ nodes.
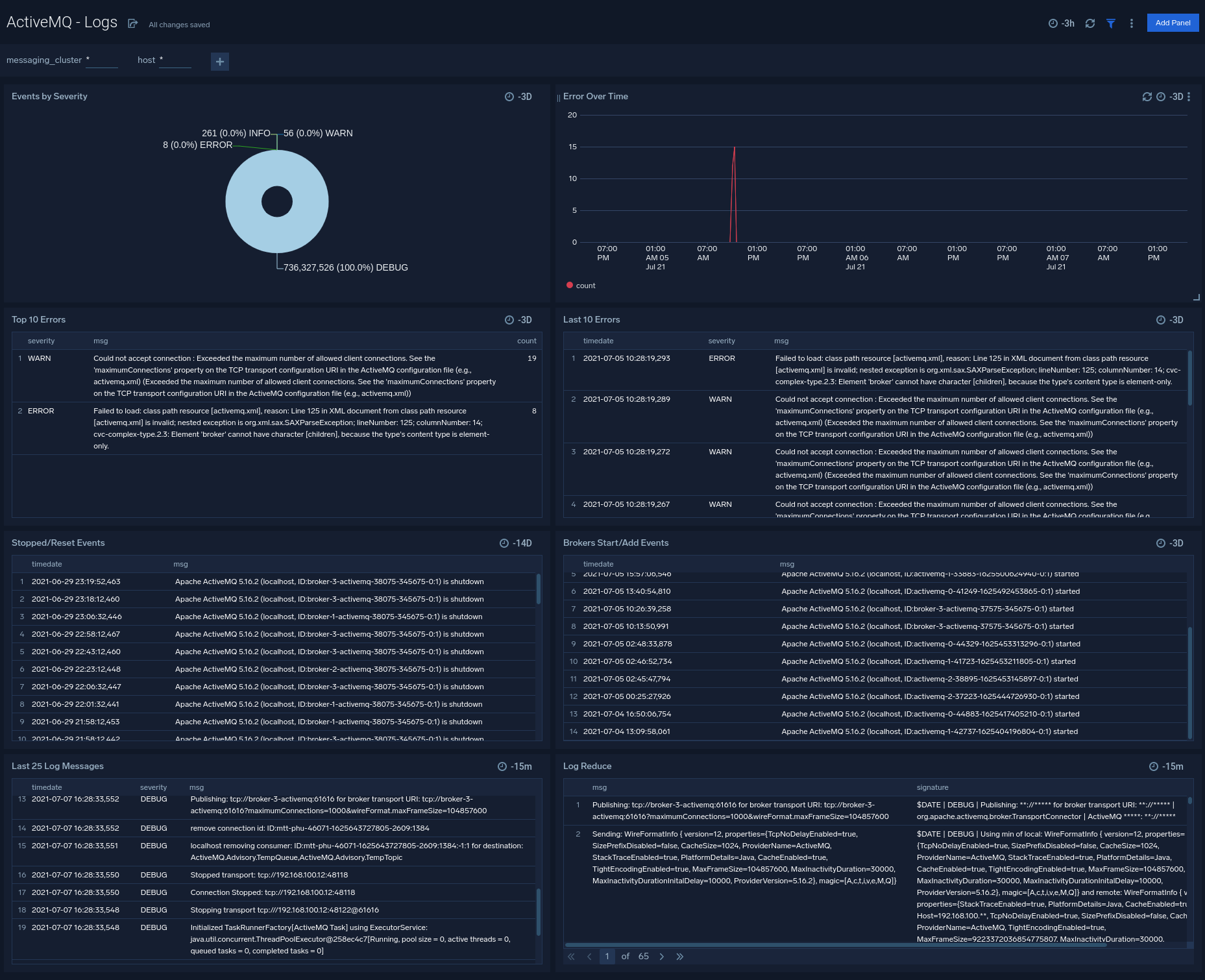
Logs
The ActiveMQ - Logs dashboard helps you quickly analyze your ActiveMQ error logs across all clusters.
Use this dashboard to:
- Identify critical events in your ActiveMQ cluster.
- Examine trends to detect spikes in Error or Fatal events
- Monitor Broker added/started and shutdown events in your cluster.
- Quickly determine patterns across all logs in a given ActiveMQ cluster.
Create monitors for ActiveMQ app
From your App Catalog:
- From the Sumo Logic navigation, select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
- Make sure the app is installed.
- Navigate to What's Included tab and scroll down to the Monitors section.
- Click Create next to the pre-configured monitors. In the create monitors window, adjust the trigger conditions and notifications settings based on your requirements.
- Scroll down to Monitor Details.
- Under Location click on New Folder.
note
By default, monitor will be saved in the root folder. So to make the maintenance easier, create a new folder in the location of your choice.
- Enter Folder Name. Folder Description is optional.
tip
Using app version in the folder name will be helpful to determine the versioning for future updates.
- Click Create. Once the folder is created, click on Save.
ActiveMQ alerts
| Alert Name | Description | Alert Condition | Recover Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
ActiveMQ - High CPU Usage Alert | This alert gets triggered when there is high CPU usage on a node in a ActiveMQ cluster. | Count >= 80 | Count < 80 |
ActiveMQ - High Memory Usage Alert | This alert gets triggered when there is high memory usage on a node in a ActiveMQ cluster. | Count >= 80 | Count < 80 |
ActiveMQ - High Storage Used Alert | This alert gets triggered when there is high store usage on a node in a ActiveMQ cluster. | Count >= 80 | Count < 80 |
ActiveMQ - Maximum Connection Alert | This alert gets triggered when one node in ActiveMQ cluster exceeds the maximum allowed client connection limit. | Count >= 1 | Count < 1 |
ActiveMQ - No Consumers on Queues Alert | This alert gets triggered when a ActiveMQ queue has no consumers. | Count < 1 | Count >= 1 |
ActiveMQ - Node Down Alert | This alert gets triggered when a node in the ActiveMQ cluster is down. | Count >= 1 | Count < 1 |
ActiveMQ - Too Many Connections Alert | This alert gets triggered when there are too many connections to a node in a ActiveMQ cluster. | Count >= 1000 | Count < 1000 |