ActiveMQ - OpenTelemetry Collector
The ActiveMQ app is a unified logs and metrics app that helps you monitor the availability, performance, health, and resource utilization of your ActiveMQ messaging clusters. Preconfigured dashboards provide insight into cluster status, nodes, producers, consumers, destinations, resource utilization, message rates, and error logs.
We use the OpenTelemetry collector for ActiveMQ metrics and logs collection.
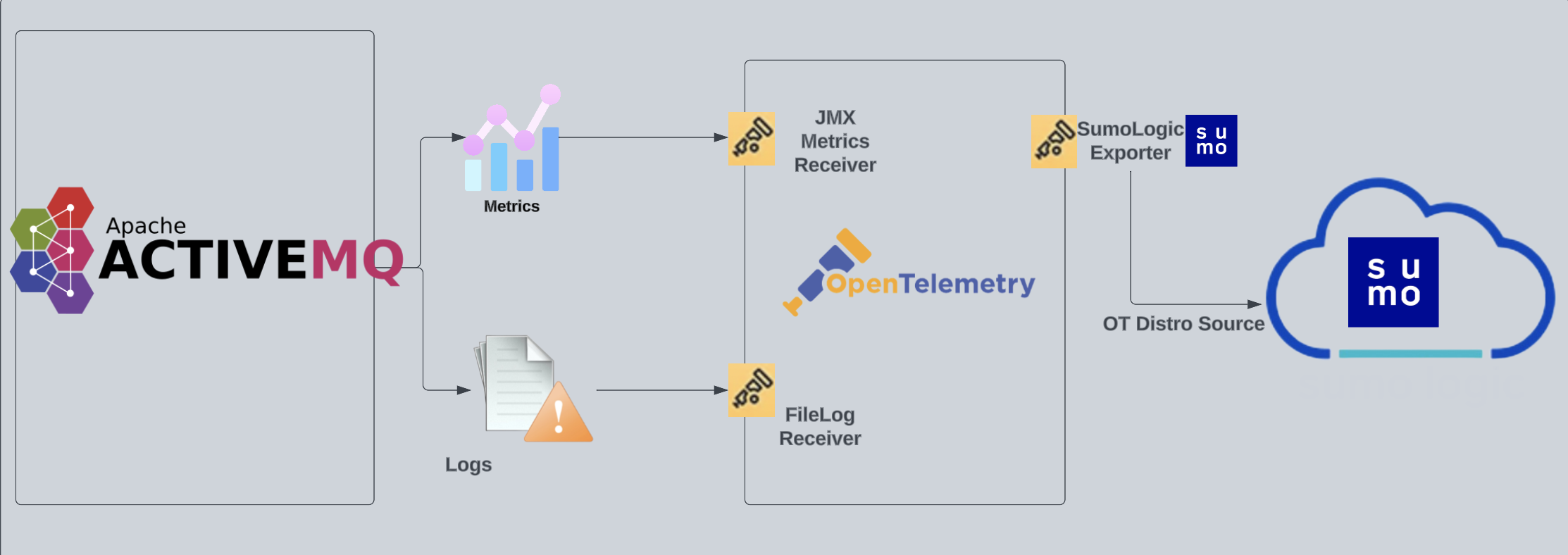
The diagram below illustrates the components of the ActiveMQ collection for each ActiveMQ broker node. OpenTelemetry collector runs on the same host as ActiveMQ broker, and uses the JMX Receiver to obtain ActiveMQ metrics, and the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Exporter to send the metrics to Sumo Logic. ActiveMQ logs are sent to Sumo Logic through a filelog receiver.
This app has been tested with the following ActiveMQ versions:
5.17.45.18.2
This app includes built-in monitors. For details on creating custom monitors, refer to Create monitors for ActiveMQ app.
Log and metrics types
The Sumo Logic app for ActiveMQ uses:
-
ActiveMQ app supports the below log format in the
log4j2.propertiesfile.-
Audit Logs. Every management action made through JMX or Web Console management interface is logged in audit log files.
appender.auditlog.layout.pattern=%d | %-5p | %m | %t%n -
ActiveMQ Logs:
appender.logfile.layout.pattern=%d | %-5p | %m | %c | %t%n%throwable{full}
-
-
For a list of metrics that are collected and used by the app, refer to the ActiveMQ Metrics.
Fields creation in Sumo Logic for ActiveMQ
Following are the fields which will be created as part of ActiveMQ app installation, if not already present.
messaging.cluster.name. User configured. Enter a name to uniquely identify your ActiveMQ cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.messaging.node.name. Has value ofhost name.messaging.system. Has fixed value ofactivemq.sumo.datasource. Has fixed value ofactivemq.
If process metrics are enabled it will also create fields for JMX metrics.
Prerequisites
Configure logging in ActiveMQ
- By default, ActiveMQ logs (
audit.logandactivemq.log) are stored in the directory called${ACTIVEMQ_HOME}/data/activemq.log. Make a note of this logs directory. - Enable auditing if not enabled by default.
ACTIVEMQ_OPTS="$ACTIVEMQ_OPTS -Dorg.apache.activemq.audit=true" - Ensure that below log formats are present in logging configuration. Also make sure appropriate log level is set.
- Audit Logs:
appender.auditlog.layout.pattern=%d | %-5p | %m | %t%n - ActiveMQ Logs:
appender.logfile.layout.pattern=%d | %-5p | %m | %c | %t%n%throwable{full}
For Linux systems with ACL Support, the otelcol install process should have created the ACL grants necessary for the otelcol system user to access default log locations. You can verify the active ACL grants using the getfacl command. Install the ACL in your Linux environment, if not installed.
The required ACL may not be supported for some rare cases, for example, Linux OS Distro, which is officially not supported by Sumo Logic. In this case, you can run the following command to explicitly grant the permissions.
sudo setfacl -R -m d:u:otelcol-sumo:r-x,d:g:otelcol-sumo:r-x,u:otelcol-sumo:r-x,g:otelcol-sumo:r-x <PATH_TO_LOG_FILE>
Run the above command for all the log files in the directory that need to be ingested, which are not residing in the default location.
If Linux ACL Support is not available, traditional Unix-styled user and group permission must be modified. It should be sufficient to add the otelcol system user to the specific group that has access to the log files.
For Windows systems, log files which are collected should be accessible by the SYSTEM group. Use the following set of PowerShell commands if the SYSTEM group does not have access.
$NewAcl = Get-Acl -Path "<PATH_TO_LOG_FILE>"
# Set properties
$identity = "NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM"
$fileSystemRights = "ReadAndExecute"
$type = "Allow"
# Create new rule
$fileSystemAccessRuleArgumentList = $identity, $fileSystemRights, $type
$fileSystemAccessRule = New-Object -TypeName System.Security.AccessControl.FileSystemAccessRule -ArgumentList $fileSystemAccessRuleArgumentList
# Apply new rule
$NewAcl.SetAccessRule($fileSystemAccessRule)
Set-Acl -Path "<PATH_TO_LOG_FILE>" -AclObject $NewAcl
Configure metrics in ActiveMQ
- Follow the instructions in JMX - OpenTelemetry's prerequisites section to download the JMX Metric Gatherer used by the JMX Receiver.
- Enable reads metrics from ActiveMQ servers via the JMX MBeans by setting
useJmx="true"in file config ActiveMQ.xml<broker useJmx="true" brokerName="BROKER1">
...
</broker> - Set the JMX port by changing the
ACTIVEMQ_SUNJMX_STARTparameter. Usually it is set in/opt/activemq/bin/envorC:\Program Files\apache-activemq\bin\activemq.batfile.ACTIVEMQ_SUNJMX_START="$ACTIVEMQ_SUNJMX_START -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=11099 -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.password.file=${ACTIVEMQ_CONF_DIR}/jmx.password -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.access.file=${ACTIVEMQ_CONF_DIR}/jmx.access"
Collection configuration and app installation
As part of data collection setup and app installation, you can select the App from App Catalog and click on Install App. Follow the steps below.
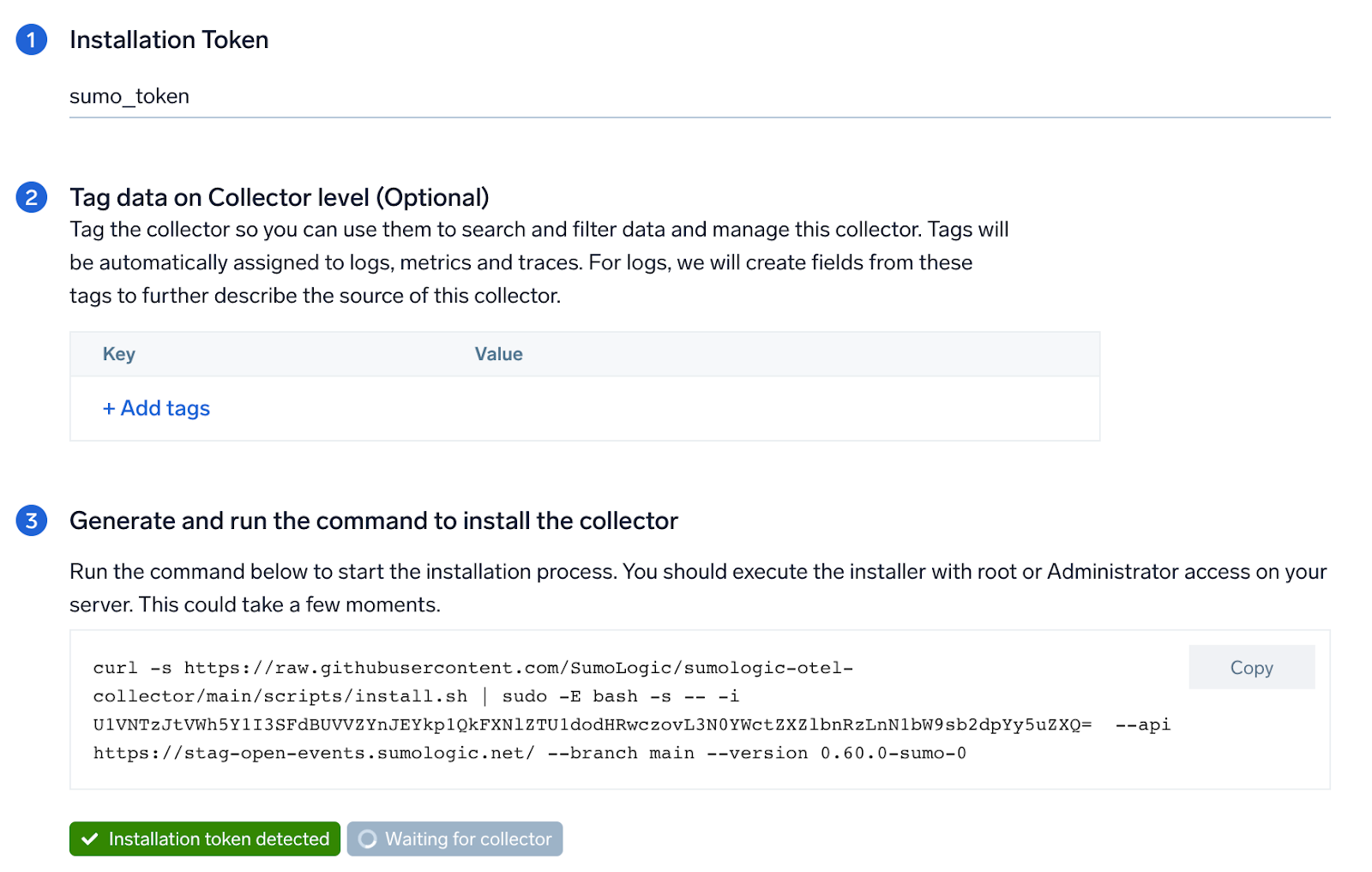
Step 1: Set up OpenTelemetry Collector
If you want to use an existing OpenTelemetry Collector, you can skip this step by selecting the Use an existing Collector option.
To create a new Collector:
- Select the Add a new Collector option.
- Select the platform where you want to install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector.
This will generate a command that you can execute in the machine environment you need to monitor. Once executed, it will install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector.
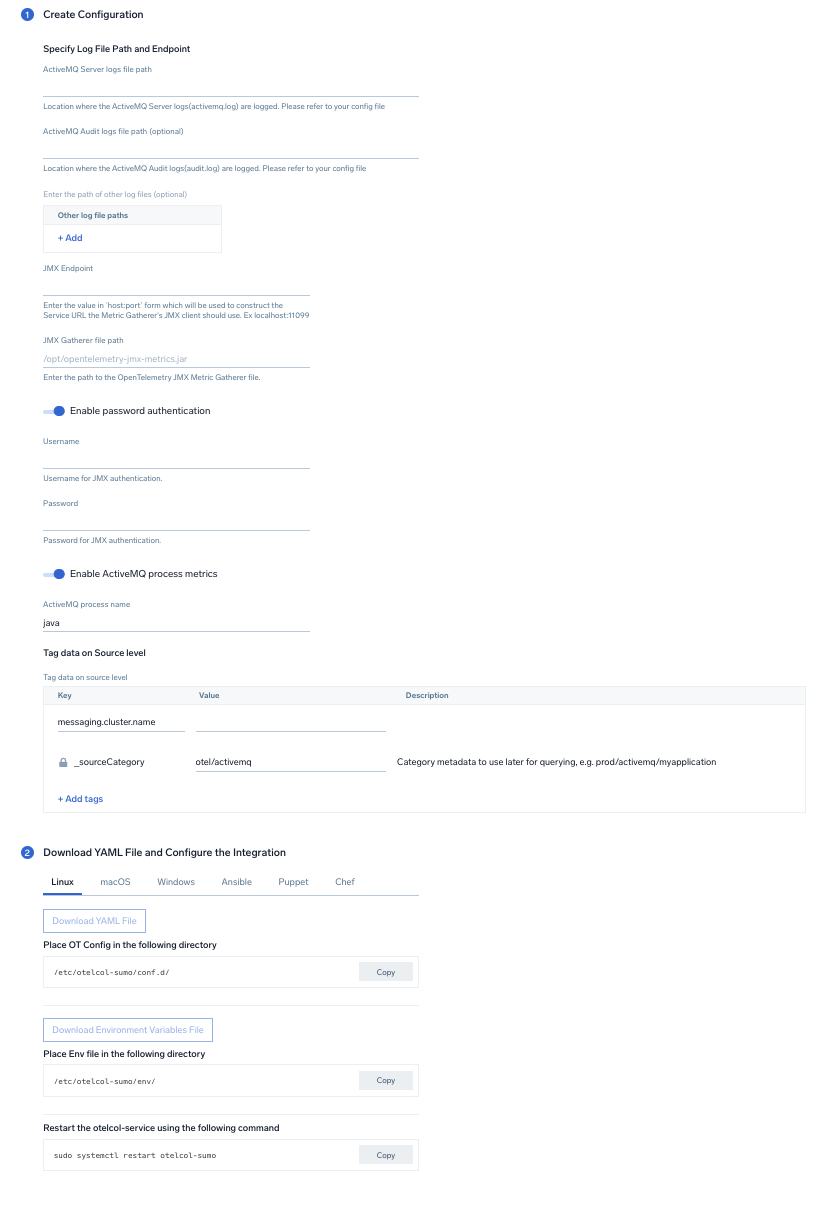
Step 2: Configure integration
In this step we will be configuring the YAML required for ActiveMQ Collection.
Below is the input required:
- ActiveMQ Server logs file path. Enter the path to the ActiveMQ log file for your ActiveMQ instance.
- ActiveMQ Audit logs file path. Enter the path to the Audit log file for your ActiveMQ instance.
- JMX Endpoint. Enter the value in
host:portform which will be used to construct the Service URL, the Metric Gatherer's JMX client should use. - JMX Gatherer file path. Enter the path to the OpenTelemetry JMX Metric Gatherer file configured in the prerequisites section.
- Enable password authentication. Toggle this if you are using password based jmx authentication.
- UserName. Username for JMX authentication, if applicable.
- Password. Password for JMX authentication, if applicable.
- Enable ActiveMQ process metrics. Toggle this to collect ActiveMQ Process metrics. Disable this if you are already collecting process metrics from the host.
- ActiveMQ process name. Enter the ActiveMQ process name.It will be used for filtering process metrics based on process name.
- Fields.
messaging.cluster.nameUser configured. Enter a name to identify this ActiveMQ cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.
Click on the Download YAML File button to get the YAML file.
For OpenTelemetry Collector version ≥ 0.104, we recommend using the downloaded config with an environment variable, for example: ${environment_variable}.
On Linux, click Download Environment Variables File to get a file that includes the password, which should be set as an environment variable (if you're using one).
Step 3: Send logs and metrics to Sumo Logic
Once you have downloaded the YAML file as described in the previous step, follow the below steps based on your platform.
- Linux
- Windows
- macOS
- Chef
- Ansible
- Puppet
- Copy the YAML file to
/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/folder in the ActiveMQ instance that needs to be monitored. - Restart the collector using:
sudo systemctl restart otelcol-sumo
- Copy the YAML file to
C:\ProgramData\Sumo Logic\OpenTelemetry Collector\config\conf.dfolder in the machine which needs to be monitored. - Restart the collector using:
Restart-Service -Name OtelcolSumo
- Copy the YAML file to
/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/folder in the ActiveMQ instance which needs to be monitored. - Restart the
otelcol-sumoprocess using the below command:
otelcol-sumo --config /etc/otelcol-sumo/sumologic.yaml --config "glob:/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/*.yaml"
- Copy the yaml file into your Chef cookbook files directory
files/<downloaded_yaml_file>.` - Use a Chef file resource in a recipe to manage it.
cookbook_file '/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/<downloaded_yaml_file>' do
mode 0644
notifies :restart, 'service[otelcol-sumo]', :delayed
end - Use a Chef file resource in a recipe to manage it.
cookbook_file '/etc/otelcol-sumo/env/<downloaded_env_file>' do
mode 0600
notifies :restart, 'service[otelcol-sumo]', :delayed
end - Add the recipe to your collector setup to start collecting. Every team typically has their established way of applying the Chef recipe. The resulting Chef recipe should look something like:
cookbook_file '/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/<downloaded_yaml_file>' do
mode 0644
notifies :restart, 'service[otelcol-sumo]', :delayed
end
cookbook_file '/etc/otelcol-sumo/env/<downloaded_env_file>' do
mode 0600
notifies :restart, 'service[otelcol-sumo]', :delayed
end
- Place the file into your Ansible playbook files directory.
- Run the Ansible playbook using:
ansible-playbook -i inventory install_sumologic_otel_collector.yaml
-e '{"installation_token": "<YOUR_TOKEN>", "collector_tags": {<YOUR_TAGS>}, "src_config_path": "files/conf.d", "src_env_path": "files/env"}'
- Place the file into your Puppet module files directory
modules/install_otel_collector/files/<downloaded_yaml>. - Use a Puppet file resource to manage it
file { '/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/<downloaded_yaml_file>':
ensure => present,
source => 'puppet:///modules/install_otel_collector/<downloaded_yaml_file>',
mode => '0644',
notify => Service[otelcol-sumo],
} - Use a Puppet file resource to manage it
file { '/etc/otelcol-sumo/env/<downloaded_env_file>'
ensure => present,
source => 'puppet:///modules/install_otel_collector/<downloaded_env_file>',
mode => '0600',
notify => Service[otelcol-sumo],
} - Apply the Puppet manifest. Every team typically has their established way of applying the Puppet manifes. The resulting Puppet manifest should look something like:
node 'default' {
class { 'install_otel_collector'
installation_token => '<YOUR_TOKEN>',
collector_tags => { <YOUR_TAGS> },
}
service { 'otelcol-sumo':
provider => 'systemd',
ensure => running,
enable => true,
require => Class['install_otel_collector'],
}
file { '/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/<downloaded_yaml_file>':
ensure => present,
source => 'puppet:///modules/install_otel_collector/<downloaded_yaml_file>',
mode => '0644',
notify => Service[otelcol-sumo],
}
file { '/etc/otelcol-sumo/env/<downloaded_env_file>':
ensure => present,
source => 'puppet:///modules/install_otel_collector/<downloaded_env_file>',
mode => '0600',
notify => Service[otelcol-sumo],
}
}
After successfully executing the above command, Sumo Logic will start receiving data from your host machine.
Click Next. This will install the app (dashboards and monitors) to your Sumo Logic Org.
Dashboard panels will start to fill automatically. It's important to note that each panel fills with data matching the time range query and received since the panel was created. Results won't immediately be available, but within 20 minutes, you'll see full graphs and maps.
Sample log messages
2021-06-22 15:00:41,922 | DEBUG | Stopping transport tcp:///192.168.100.8:36302@61616 | org.apache.activemq.transport.tcp.TcpTransport | ActiveMQ BrokerService[localhost] Task-15300
2010-12-22 12:12:07,225 | INFO | admin requested /admin/createDestination.action [JMSDestination='test' JMSDestinationType='queue' secret='4eb0bc3e-9d7a-4256-844c-24f40fda98f1' ] from 127.0.0.1 | qtp12205619-39
2010-12-22 12:12:14,512 | INFO | admin requested /admin/purgeDestination.action [JMSDestination='test' JMSDestinationType='queue' secret='eff6a932-1b58-45da-a64a-1b30b246cfc9' ] from 127.0.0.1 | qtp12205619-36
2010-12-22 12:12:17,802 | INFO | admin requested /admin/sendMessage.action [JMSTimeToLive='' JMSXGroupSeq='' AMQ_SCHEDULED_DELAY='' JMSType='' JMSMessageCountHeader='JMSXMessageCounter' JMSXGroupID='' JMSReplyTo='' JMSDestination='test' AMQ_SCHEDULED_PERIOD='' JMSText='Enter some text
here for the message body...' JMSDestinationType='queue' AMQ_SCHEDULED_CRON='' JMSCorrelationID='' AMQ_SCHEDULED_REPEAT='' JMSMessageCount='1' secret='a0e1df62-14d6-4425-82a2-17aa01a16e7d' JMSPriority='' ] from 127.0.0.1 | qtp12205619-37
Sample metrics
"Query","metric","deployment.environment","host.name","messaging.cluster.name","messaging.node.name","messaging.system","os.type","sumo.datasource","broker","destination","unit","latest"
"#A","activemq.message.wait_time.avg","testprod","ip-10-0-10-92","activemq_cluster","ip-10-0-10-92","activemq","linux","activemq","localhost","testtopic","ms","254.4"
Sample queries
Log query
This sample log query is from the Events by Severity panel of the ActiveMQ - Logs dashboard.
sumo.datasource=activemq deployment.environment={{deployment.environment}} messaging.cluster.name={{messaging.cluster.name}} messaging.node.name={{messaging.node.name}}
| json auto maxdepth 1 nodrop
| if (isEmpty(log), _raw, log) as raw_log_message
| parse field=raw_log_message "*|*|*|*|*" as timedate,severity,msg,class,address |trim(severity) as severity | count by severity
Metrics query
This sample metrics query from the Average Enqueue Latency panel of the ActiveMQ - Destinations dashboard.
sumo.datasource=activemq deployment.environment={{deployment.environment}} messaging.cluster.name={{messaging.cluster.name}} messaging.node.name={{messaging.node.name}} destination={{destination}} !(destination=activemq.*) metric=activemq.message.wait_time.avg | avg by destination,messaging.cluster.name
Viewing the ActiveMQ dashboards
All dashboards have a set of filters that you can apply to the entire dashboard. Use these filters to drill down and examine the data to a granular level.
- You can change the time range for a dashboard or panel by selecting a predefined interval from a drop-down list, choosing a recently used time range, or specifying custom dates and times. Learn more.
- You can use template variables to drill down and examine the data on a granular level. For more information, see Filtering Dashboards with Template Variables.
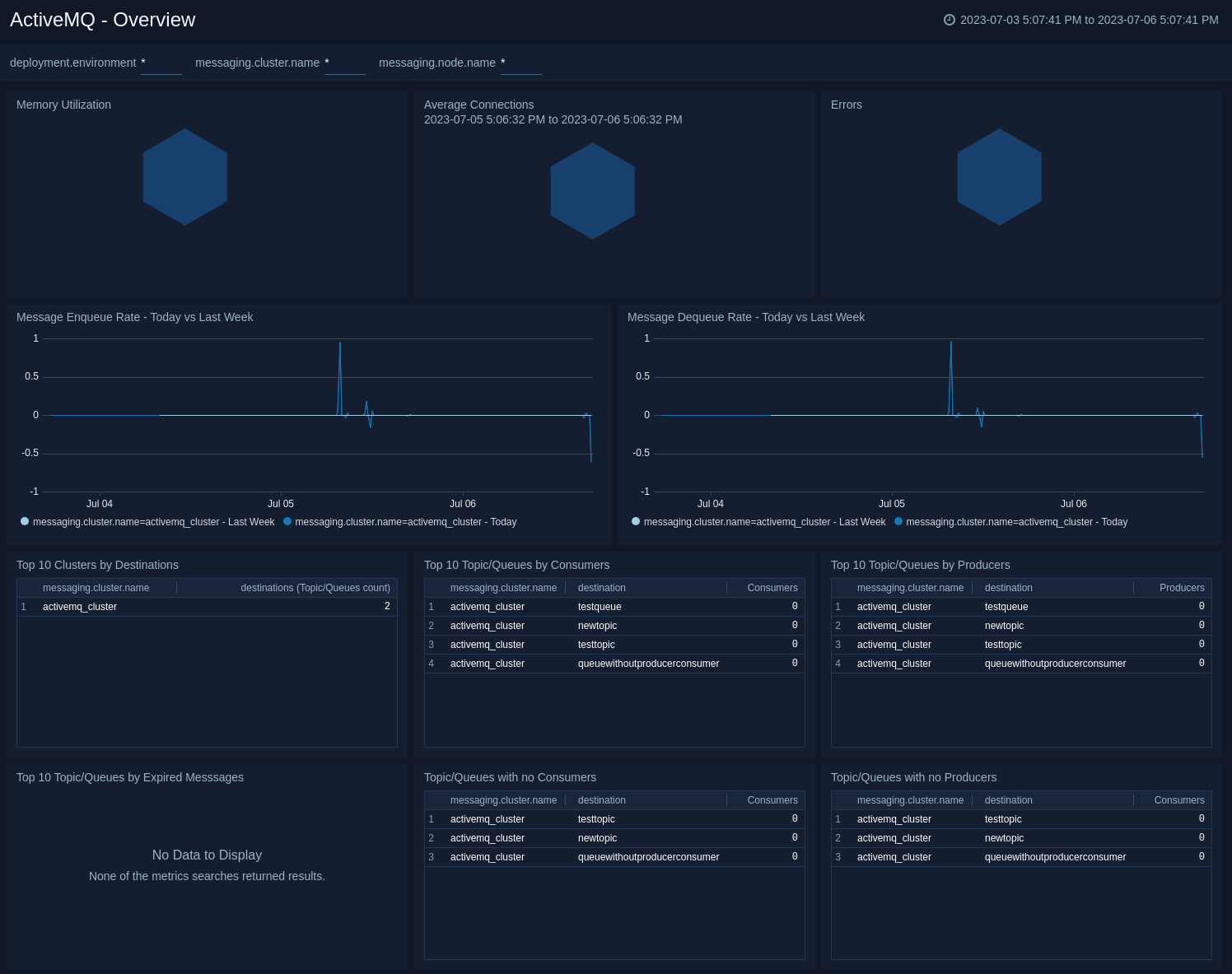
Overview
The ActiveMQ - Overview dashboard gives you an at-a-glance view of your ActiveMQ deployment across brokers, queues, topics, and messages.
Use this dashboard to:
- Analyze memory, errors and connections.
- Gain insights into Enqueue messages for your ActiveMQ server and compare it with last week's trend.
- Gain insights into Dequeue messages for your ActiveMQ server and compare it with last week's trend.
- Determine queues/topics with no producers and consumers.
- Determine queues/topics with expired messages.
Brokers
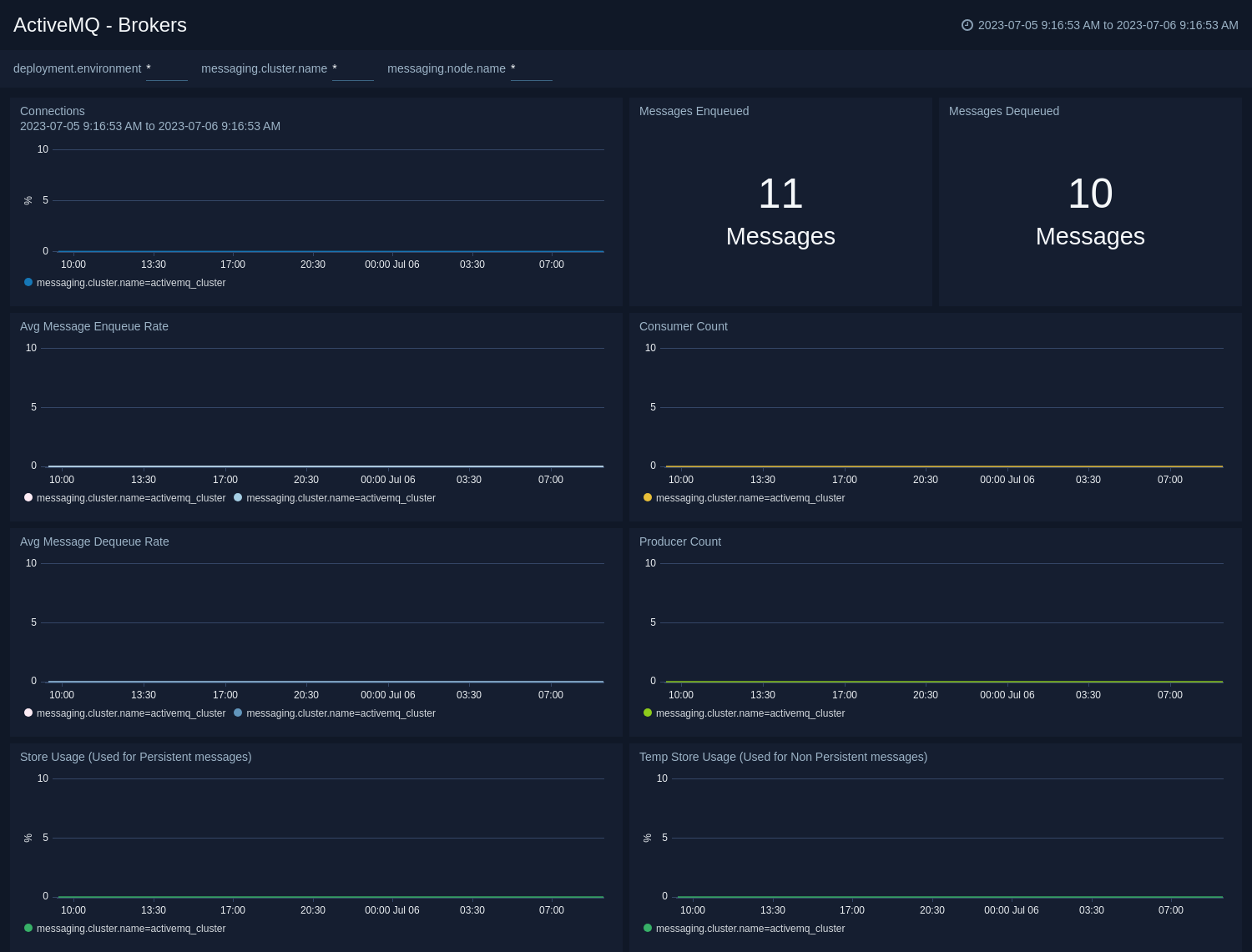
The ActiveMQ - Brokers dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of the state of your brokers in the ActiveMQ cluster.
Use this dashboard to:
- Gain insights into the storage and temp storage for your ActiveMQ brokers.
- Gain insights into enqueue rate, dequeue rate for your ActiveMQ brokers.
- Determine the amount of current connections, producers, and consumers for your ActiveMQ brokers.
Destinations
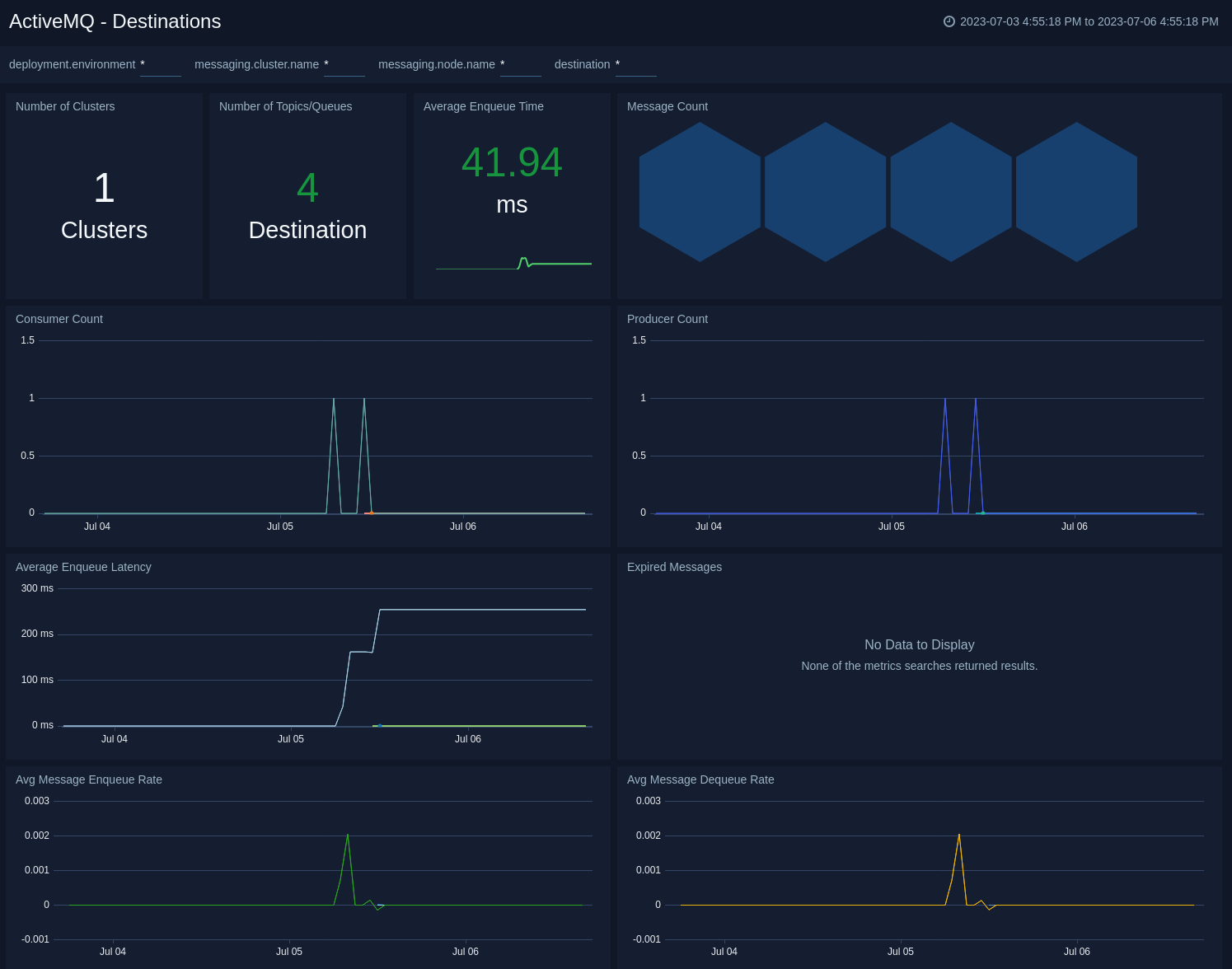
The ActiveMQ - Destinations dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of the state of your topics/queues in ActiveMQ clusters.
Use this dashboard to:
- Monitor enqueue latency across topics/queues.
- Gain insights into enqueue rate, dequeue rate across topics/queues.
- Monitor producers, consumers and expired messages on topics/queues.
- Determine the number of topics/queues.
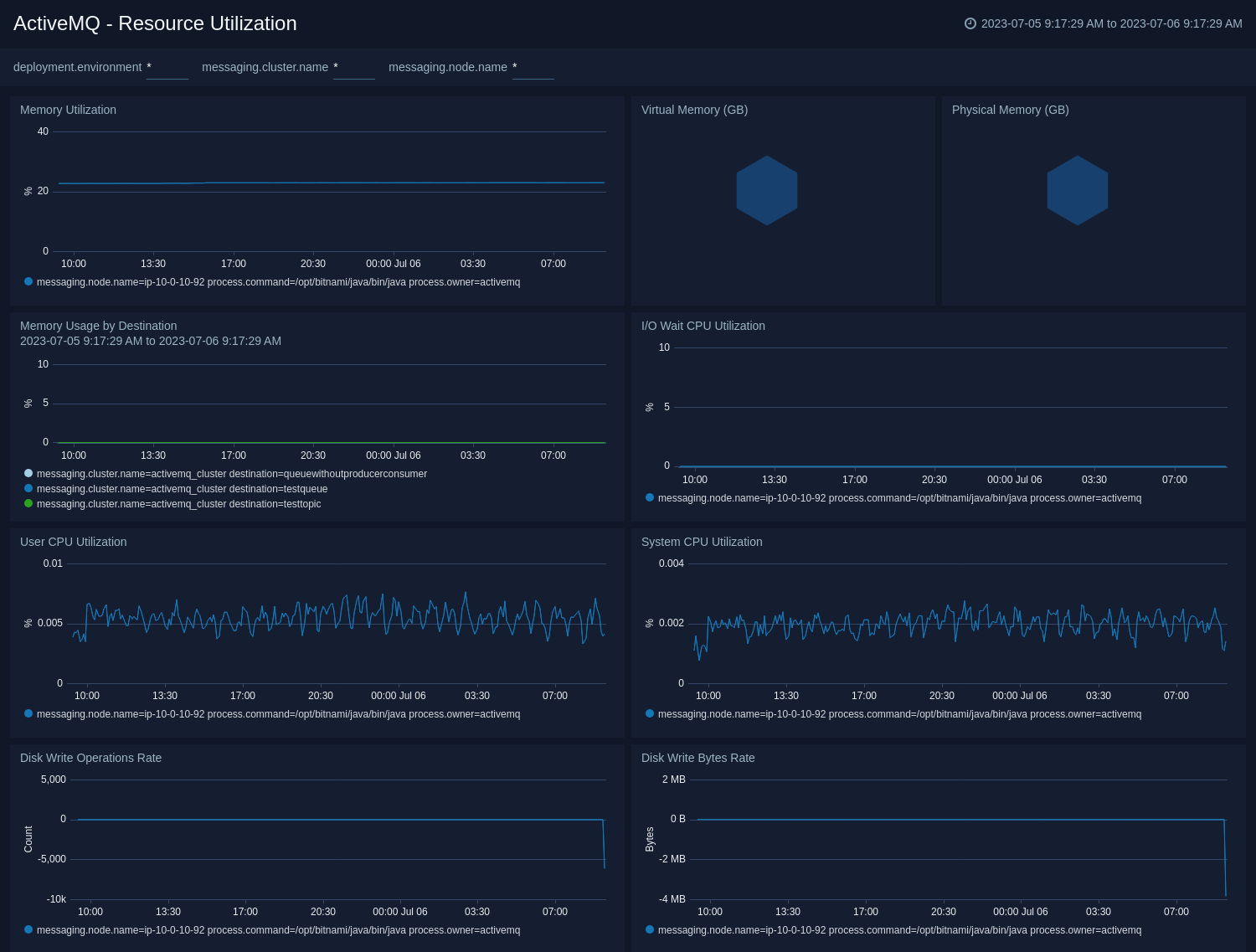
Resource utilization
The ActiveMQ - Resource Utilization dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of the state of system loads in clusters: Virtual memory usage, physical memory usage, CPU utilization, disk operations, disk writes, and I/O wait.
Use this dashboard to:
- Analyze memory and CPU utilization of activemq process.
- Gain insights into disk write operations and disk write bytes of activemq process.
- Gain insights into memory utilization by topics/queues.
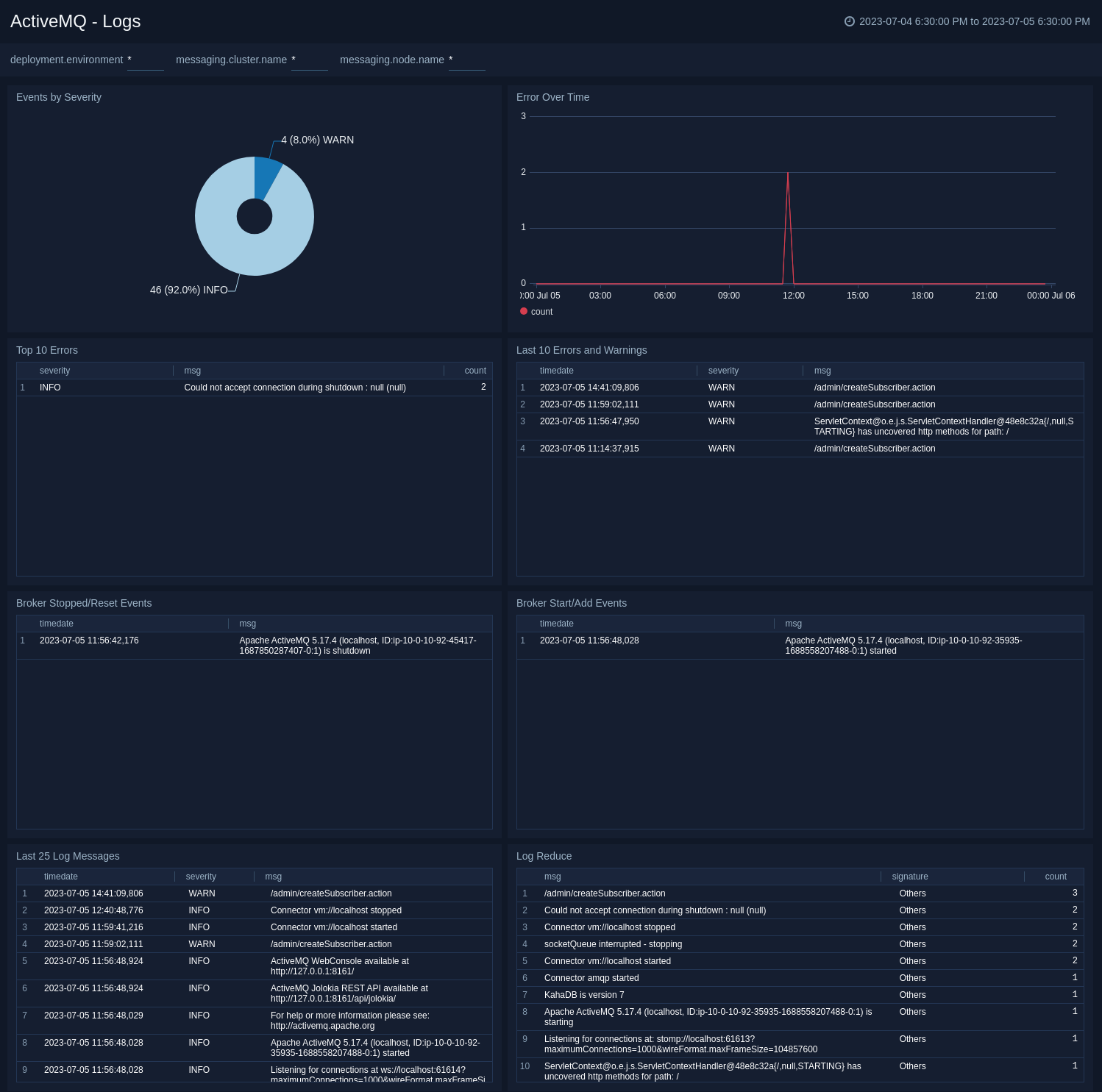
Logs
The ActiveMQ - Logs dashboard helps you quickly analyze your ActiveMQ error logs across all clusters.
Use this dashboard to:
- Identify critical events in your ActiveMQ cluster.
- Examine trends to detect spikes in error or fatal events
- Monitor Broker added/started and shutdown events in your cluster.
- Quickly determine patterns across all error logs in a given ActiveMQ cluster.
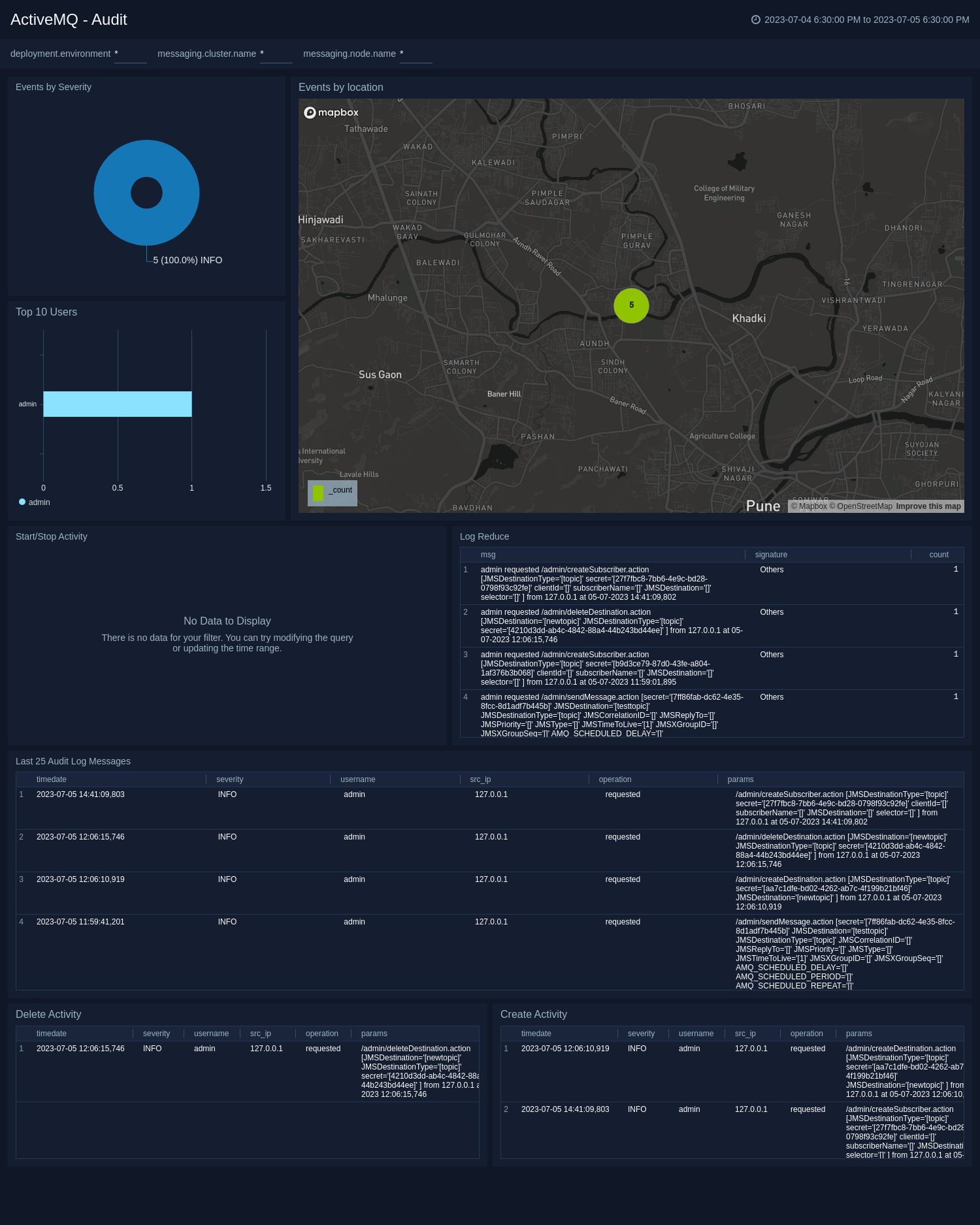
Audit
This ActiveMQ - Audit dashboard helps you quickly analyze your ActiveMQ audit logs across all clusters.
Use this dashboard to:
- Identify locations of users performing management action.
- Track username, operation, and IP address for each management level event.
- Monitor create and delete activity in your cluster.
- Quickly determine patterns across all audit logs in a given ActiveMQ cluster.
Create monitors for ActiveMQ app
From your App Catalog:
- From the Sumo Logic navigation, select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
- Make sure the app is installed.
- Navigate to What's Included tab and scroll down to the Monitors section.
- Click Create next to the pre-configured monitors. In the create monitors window, adjust the trigger conditions and notifications settings based on your requirements.
- Scroll down to Monitor Details.
- Under Location click on New Folder.
note
By default, monitor will be saved in the root folder. So to make the maintenance easier, create a new folder in the location of your choice.
- Enter Folder Name. Folder Description is optional.
tip
Using app version in the folder name will be helpful to determine the versioning for future updates.
- Click Create. Once the folder is created, click on Save.
ActiveMQ alerts
| Alert Name | Alert Description and conditions | Alert Condition | Recover Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
ActiveMQ - High CPU Usage Alert | This alert gets triggered when CPU usage on a node in a ActiveMQ cluster is high. | Count >= 80 | Count < 80 |
ActiveMQ - High Memory Usage Alert | This alert gets triggered when memory usage on a node in a ActiveMQ cluster is high. | Count >= 80 | Count < 80 |
ActiveMQ - High Storage Used Alert | This alert gets triggered when there is high store usage on a node in a ActiveMQ cluster. | Count >= 80 | Count < 80 |
ActiveMQ - Maximum Connection Alert | This alert gets triggered when one node in ActiveMQ cluster exceeds the maximum allowed client connection limit. | Count >= 1 | Count < 1 |
ActiveMQ - No Consumers on Queues Alert | This alert gets triggered when a ActiveMQ queue has no consumers. | Count < 1 | Count >= 1 |
ActiveMQ - Node Down Alert | This alert gets triggered when a node in the ActiveMQ cluster is down. | Count >= 1 | Count < 1 |
ActiveMQ - Too Many Connections Alert | This alert gets triggered when there are too many connections to a node in a ActiveMQ cluster. | Count >= 1000 | Count < 1000 |