Google App Engine

Google App Engine is a platform to build web and mobile apps that scale automatically. The Sumo Logic App for Google App Engine helps you monitor the activities in your App Engine. The pre-configured dashboards provide insight into the requests, applications, HTTP status codes, latency, and response time in your App Engine.
Log types
The App uses:
- Google Cloud Audit Logs — These logs track events on multiple GCP services, including Compute Engine, IAM and App Engine
- App Engine Request Logs — These logs provide information about each request in App Engine, including the external IP address making the request
Sample log messages
Click to expand
{
"message": {
"data": {
"httpRequest": {
"status": 200
},
"insertId": "5a0e593e000d3494692375e0",
"labels": {
"clone_id": "00c61b117c27a4ec1f60970fdd9db838ca7ce717bfea65f950122a708e22eff25699065ba561"
},
"logName": "projects/bmlabs-loggen/logs/appengine.googleapis.com%2Frequest_log",
"operation": {
"first": true,
"id": "5a0e593e00ff07071f75c6d2240001737e776b2d6465760001626967736b7966343a363932382d30333566343662000100",
"last": true,
"producer": "appengine.googleapis.com/request_id"
},
"protoPayload": {
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/google.appengine.logging.v1.RequestLog",
"appEngineRelease": "1.9.54",
"appId": "s~bmlabs-loggen",
"cost": 9.957699999999999e-8,
"endTime": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC",
"finished": true,
"first": true,
"host": "bigskyf4.bmlabs-loggen.appspot.com",
"httpVersion": "HTTP/1.1",
"instanceId": "00c61b117c27a4ec1f60970fdd9db838ca7ce717bfea65f950122a708e22eff25699065ba561",
"instanceIndex": -1,
"ip": "0.1.0.2",
"latency": "0.404415s",
"line": [
{
"logMessage": "Setting in-memory RuntimeSettings:6928-035f46b.",
"severity": "DEBUG",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/base/runtime_settings.py",
"functionName": "_get_data",
"line": "180"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
{
"logMessage": "TASK-INFO: {\"gae_latency_seconds\": 0.16422700881958008, \"task_eta\": 1510889790.3144629, \"execution_count\": 0, \"ran\": 1510889790.4786899, \"expected_eta\": 1510889790.3136301, \"retry_count\": 0, \"latency_seconds\": 0.16505980491638184}",
"severity": "DEBUG",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/base/deferred/deferred.py",
"functionName": "_log_task_info",
"line": "752"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
{
"logMessage": "Deferred 8a3a365c-4ed3-40ae-8a1c-faff06a9464c running function audit.actions._write with args = () and kwargs = {'account': <authmodel.auth.Account object at 0xf46cae50>, 'entity_keys': [datastore_types.Key.from_path(u'Membership', 4674727938359296L, _app=u's~bmlabs-loggen')], 'timestamp': datetime.datetime(2017, 11, 17, 3, 36, 30, 307040), 'audit_type': 'account_deactivated', 'user': <authmodel.auth.WFUser object at 0xf41fd730>, 'message': u'Service Docs exited the service_docs account.', 'ip_address': '52.4.205.181'}.",
"severity": "INFO",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/base/deferred/deferred.py",
"functionName": "_run_function",
"line": "574"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
{
"logMessage": "TASK-DONE: {\"queue_name\": \"audit-log\", \"worker_id\": \"8a3a365c-4ed3-40ae-8a1c-faff06a9464c\", \"task_name\": \"27563511594509108661\"}",
"severity": "INFO",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/base/deferred/deferred.py",
"functionName": "_run_deferred",
"line": "921"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
{
"logMessage": "gstats: ['event'] messages are disabled by default.",
"severity": "DEBUG",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/external_libs/gstats/client.py",
"functionName": "__init__",
"line": "424"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
{
"logMessage": "gstats: statsd sent 16 metric keys with 18 metric values in 2 udp packets in [17, 15] ms",
"severity": "DEBUG",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/external_libs/gstats/listeners/statsd.py",
"functionName": "send",
"line": "362"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
{
"logMessage": "GSTATSDATA: eJytlU1v2zAMhv9KofPqWHJkOQF6G7Dr2u60oRAEm0uM+iOTqLRBkP8+Sh3W2d3QOPPNskTx4cvX9JFh3YJ2YGtwbH11ZHZXauzRNLrsfYfx3d40Pm5/O8bzDk27oyUTKVfXnF9z9SXN1lm+ztKk4ELl6Vf24eoljs6p08OJlmjc4w8PHhILaA+XJ5CKDxOkpwdatYCmMmjilTuDW3rofNOcQnJ4BiqM7o67vqsx5GOt+33PhAKFGubPlvItQSz1T4Sw47C3oPeZ/uxRV94arPtuBqSlSIdIXL2DRHtjjV4bFNTyAe3yJuViepNaaEtTbkF/glnVyfhyyCIo23mRMhvpem6kHOec3o+BYe58d+uBPps5XSNHrhF/adLZptkY0I1B6MoDTZSy7yo3ZLwEMc/FyEYJQReF4lLKTBRZvuITjHU/s7EKNTbWfzX5IzSAMGuLi5F+fDUNMfb43TxSqF9KlE0NcWKwDYWgu7lJk1WiIgJY91IVC+9S9i8OZnxVo276DXvFYQtttot4ZFHBd7AWqkU8mJgyqOUS/WRrhBCz7V1kcPrpUVewZ7GMwy7ejqRyG35BkTcMOAKLAIHYOxp6FSQ0US+Ze3z89yN7koo/AQ4fOc0=",
"severity": "DEBUG",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/external_libs/gstats/listeners/log.py",
"functionName": "send",
"line": "190"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
{
"logMessage": "gstats: .send() took 36 ms",
"severity": "DEBUG",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/external_libs/gstats/client.py",
"functionName": "send",
"line": "678"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
{
"logMessage": "PROFILE: eJyt0U9rwjAYBvCvUnL2YFpj586C180eZZSQPmKxaSB5WxTpd1+6DdY2sFXx9v6BXx7e3BguUDmVGuw1Sl7Wi4iZFvYEWfjB0rdKVpXz9eHGisZKKk3tu/hn40u2A2VXR9AZSXLMbxxsW6qeZO5r0w/N8ehAvdotoqdhyT/YRNDQSqoTRkY6Nfj9Bv8zSDYTEUGSVAyYt2bKFJKkI2ORt8mI2sRBnuVA2jf1ewN7ncvFafBrfDPwtqhAmK2F6cT9J0/Cm3MxOnpdTBwLbQi5M+r8/cYvJlYBtnoYS3n30X0CIfoHPA==",
"severity": "INFO",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/external_libs/appstats_logger/middleware.py",
"functionName": "_stop_recording",
"line": "119"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
{
"logMessage": "appstats: http://bigskyf4.bmlabs-loggen.appspot.com/stats/details?time=1510889790466",
"severity": "INFO",
"sourceLocation": {
"file": "/base/data/home/apps/s~bmlabs-loggen/bigskyf4:6928-035f46b.405569666796645761/lib/appstats/recording.py",
"functionName": "save",
"line": "739"
},
"time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
}
],
"megaCycles": "196",
"method": "POST",
"moduleId": "bigskyf4",
"referrer": "https://bmlabs-loggen.wdesk.org/auth/logout/",
"requestId": "5a0e593e00ff07071f75c6d2240001737e776b2d6465760001626967736b7966343a363932382d30333566343662000100",
"resource": "/_ah/queue/deferred/audit.actions._write",
"responseSize": "117",
"startTime": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC",
"status": 200,
"taskName": "27563511594509108661",
"taskQueueName": "audit-log",
"traceId": "a736a2573bd0d51cce823884cc2b3460",
"urlMapEntry": "main.app",
"userAgent": "AppEngine-Google; (+http://code.google.com/appengine)",
"versionId": "6928-035f46b"
},
"receiveTimestamp": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC",
"resource": {
"labels": {
"module_id": "bigskyf4",
"project_id": "bmlabs-loggen",
"version_id": "6928-035f46b",
"zone": "us14"
},
"type": "gae_app"
},
"severity": "INFO",
"timestamp": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
"attributes": {
"logging.googleapis.com/timestamp": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
"message_id": "172694189887110",
"messageId": "172694189887110",
"publish_time": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC",
"publishTime": "2018-01-26T11:35:11.374UTC"
},
"subscription": "projects/bmlabs-loggen/subscriptions/sumo-test"
}
Sample queries
_collector="HTTP Source for GCP Pub/Sub" logName resource timestamp
| json "message.data.resource.type" as type
| parse regex "\"logName\":\"(?<log_name>[^\"]+)\""
| where type = "gae_app" | where log_name matches "projects/*/logs/appengine.googleapis.com%2Frequest_log"
| json "message.data.resource.labels" as labels
| json field=labels "module_id", "version_id", "zone", "project_id" as service, version, zone, project
| json "message.data.protoPayload.appId", "message.data.protoPayload.status" as app_id, status_code
| timeslice 30m
| if(status_code matches "20*", 1, 0) as resp_200
| if(status_code matches "30*", 1, 0) as resp_300
| if(status_code matches "40*", 1, 0) as resp_400
| if(status_code matches "50*", 1, 0) as resp_500
| if(!(status_code matches "20*" or status_code matches "30*" or status_code matches "40*" or status_code matches "50*"), 1, 0) as resp_others
| sum(resp_200) as tot_200, sum(resp_300) as tot_300, sum(resp_400) as tot_400, sum(resp_500) as tot_500, sum(resp_others) as tot_others by _timeslice
Collecting logs for the Google App Engine app
This section describes the Sumo pipeline for ingesting logs from Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services and provides instructions for configuring log collection for the Google App Engine App. A sample log message and query are also provided.
Collection Process for GCP Services
The key components in the collection process for GCP services are Google Logs Export, Google Cloud Pub/Sub, and Sumo’s Google Cloud Platform (GCP) source running on a hosted collector.
The GCP service generates logs which are exported and published to a Google Pub/Sub topic through Stackdriver. You will then set up a Sumo Logic Google Cloud Platform source that subscribes to this topic and receives the exported log data.
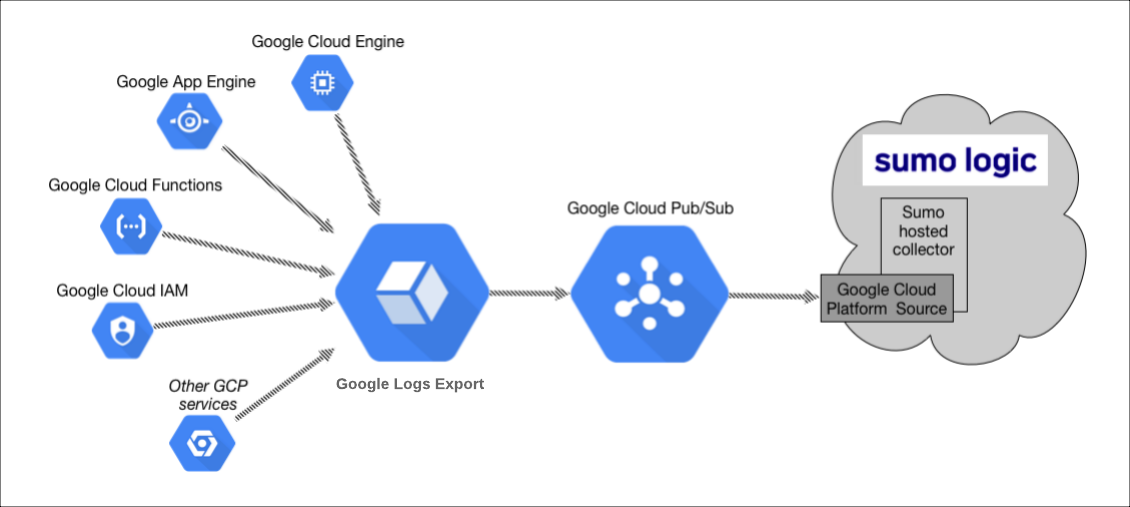
Configuring collection for GCP uses the following process:
- Configure a GCP source on a hosted collector. You'll obtain the HTTP URL for the source.
- Create a topic in Google Pub/Sub and subscribe the GCP source URL to that topic.
- Create an export of GCP logs from Google Stackdriver Logging. Exporting involves writing a filter that selects the log entries you want to export, and choosing a Pub/Sub as the destination. The filter and destination are held in an object called a sink.
See the following sections for configuration instructions.
Configure a Google Cloud Platform Source
The Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Source receives log data from Google Pub/Sub.
You can use the same GCP Source to receive log data from multiple GCP services. For example, you can send logs collected from Google Cloud Application Engine, Google Cloud IAM, and Google Cloud Audit.
However, this is not recommended since you cannot define specific Source Category values to each GCP service. If you create a GCP Source for each service you can define a specific Source Category to each service.
This Source will be a Google Pub/Sub-only Source, which means that it will only be usable for log data formatted as data coming from Google Pub/Sub.
- New UI. In the Sumo Logic main menu select Data Management, and then under Data Collection select Collection. You can also click the Go To... menu at the top of the screen and select Collection.
Classic UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, select Manage Data > Collection > Collection. - Select an existing Hosted Collector upon which to add the Source. If you do not already have a Collector you'd like to use, create one, using the instructions on Configure a Hosted Collector.
- Click Add Source next to the Hosted Collector and click Google Cloud Platform.
- Enter a Name to display for the Source. A Description is optional.
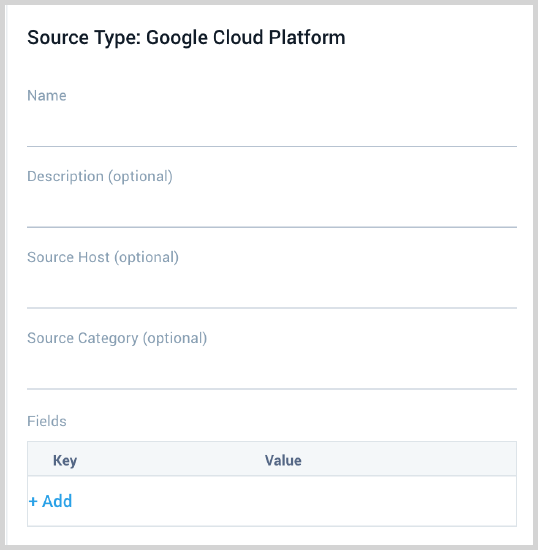
- Source Host (Optional). The Source Host value is tagged to each log and stored in a searchable metadata field called _sourceHost. Avoid using spaces so you do not have to quote them in keyword search expressions. This can be a maximum of 128 characters.
- Source Category (Optional). The Source Category value is tagged to each log and stored in a searchable metadata field called
_sourceCategory. See our Best Practices: Good Source Category, Bad Source Category. Avoid using spaces so you do not have to quote them in keyword search expressions. This can be a maximum of 1,024 characters. - Fields. Click the +Add Field link to add custom log metadata Fields, then define the fields you want to associate. Each field needs a name (key) and value. Look for one of the following icons and act accordingly:
 An orange triangle with an exclamation point is shown when the field doesn't exist, or is disabled in the fields table schema. In this case, you'll see an option to automatically add or enable the nonexistent fields to the Fields table schema. If a field is sent to Sumo Logic but isn’t present or enabled in the schema, it’s ignored and marked as Dropped.
An orange triangle with an exclamation point is shown when the field doesn't exist, or is disabled in the fields table schema. In this case, you'll see an option to automatically add or enable the nonexistent fields to the Fields table schema. If a field is sent to Sumo Logic but isn’t present or enabled in the schema, it’s ignored and marked as Dropped. A green circle with a check mark is shown when the field exists and is enabled in the Fields table schema. Proceed to the next step.
A green circle with a check mark is shown when the field exists and is enabled in the Fields table schema. Proceed to the next step.
- Advanced Options for Logs.
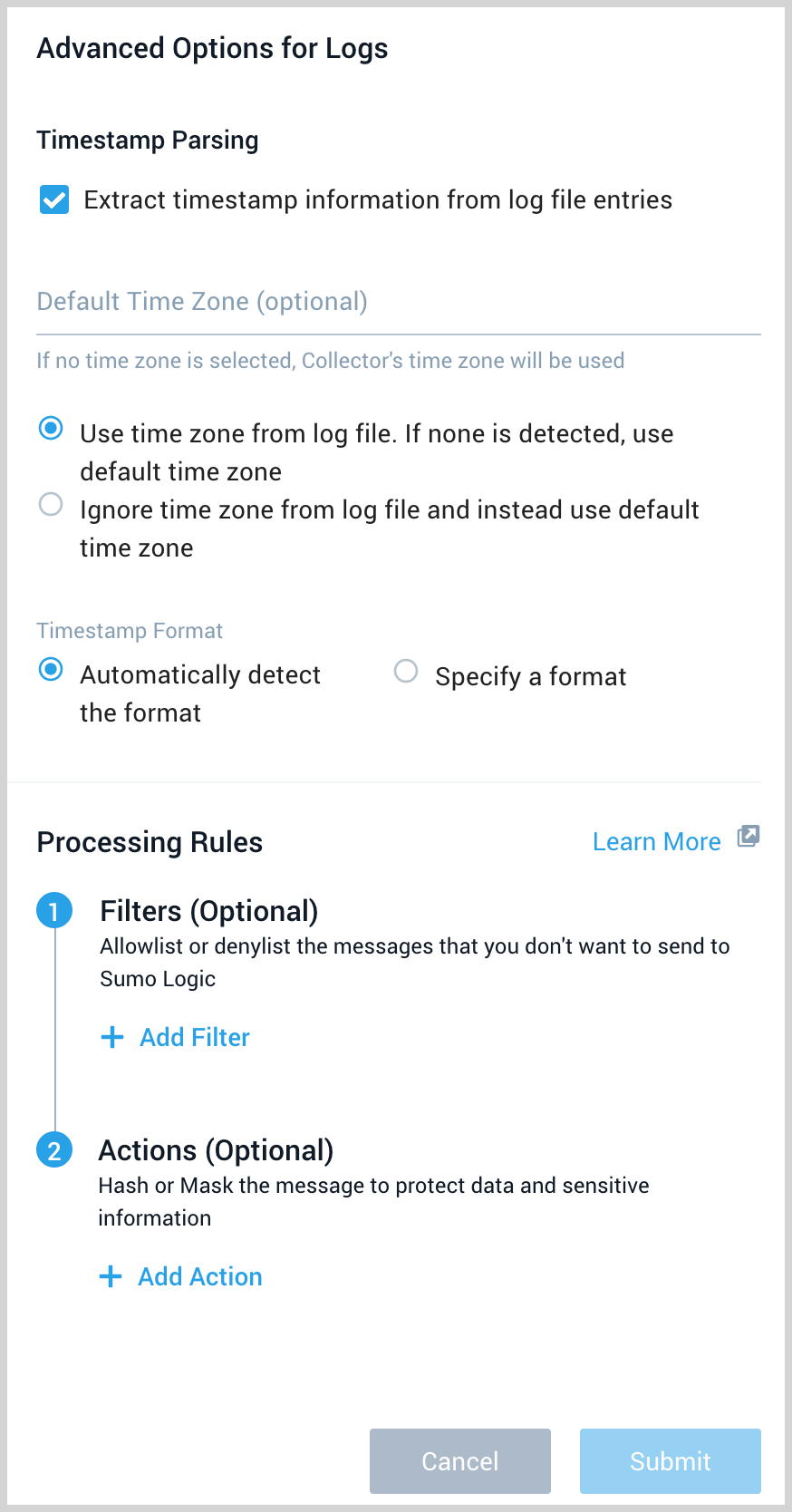
- Timestamp Parsing. This option is selected by default. If it's deselected, no timestamp information is parsed at all.
- Time Zone. There are two options for Time Zone. You can use the time zone present in your log files, and then choose an option in case time zone information is missing from a log message. Or, you can have Sumo Logic completely disregard any time zone information present in logs by forcing a time zone. It's very important to have the proper time zone set, no matter which option you choose. If the time zone of logs cannot be determined, Sumo Logic assigns logs UTC; if the rest of your logs are from another time zone your search results will be affected.
- Timestamp Format. By default, Sumo Logic will automatically detect the timestamp format of your logs. However, you can manually specify a timestamp format for a Source. See Timestamps, Time Zones, Time Ranges, and Date Formats for more information.
- Processing Rules. Configure any desired filters, such as allowlist, denylist, hash, or mask, as described in Create a Processing Rule.
- When you are finished configuring the Source, click Save.
Configure a Pub/Sub Topic for GCP
You need to configure a Pub/Sub Topic in GCP and add a subscription to the Source URL that belongs to the Sumo Logic Google Cloud Platform Source you created. Once you configure the Pub/Sub, you can export data from Google Logging to the Pub/Sub. For example, you can export Google App Engine logs, as described on Collect Logs for Google App Engine.
- Create a Pub/Sub Topic in GCP. See Google Cloud documentation for the latest configuration steps.
- Create a Pub/Sub subscription to the Source URL that belongs to the Sumo Logic Google Cloud Platform Source you created. See Google Cloud documentation for the latest configuration steps.
- Use a Push Delivery Method to the Sumo Logic Source URL. To determine the URL, navigate to the Source on the Collection page in Sumo Logic and click Show URL.
Limitations
Google limits the volume of data sent from a Topic. Our testing resulted in the following data limits:
| Topics | Megabytes per second | Payload size |
|---|---|---|
| One | 18 MBps (1.5 TB/day) | 100 KB |
| One | 6 MBps (0.5 TB/day) | 2.5 KB |
These limits may vary based on your setup and are based on our previous tests.
We recommend the following:
- Shard messages across topics within the above data limits.
- Ask GCP to increase the allowable capacity for the topic.
Create export of App Engine logs from Stackdriver
In this step you export logs to the Pub/Sub topic you created in the previous step.
- Go to Logging and click Logs Router.
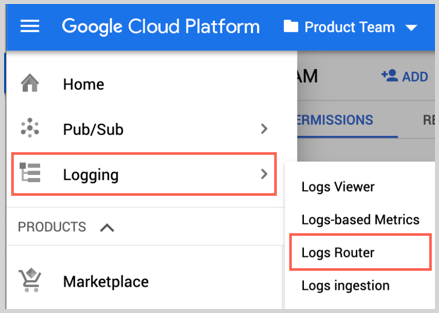
- Click Create Sink.
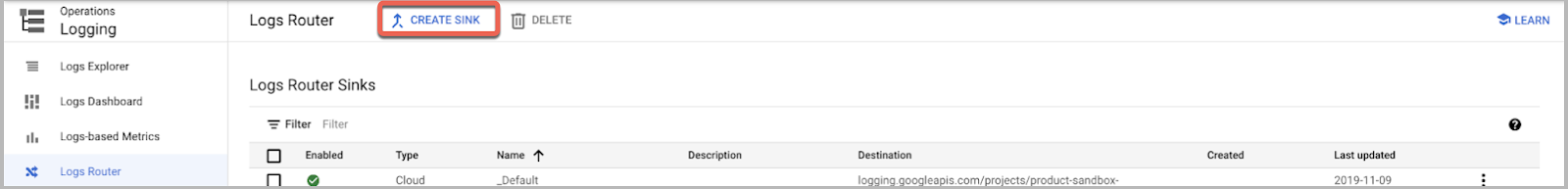
- In the Edit Export pane on the right:
- Set the Sink Name. For example, "gce-applications".
- Set Sink Service to “Cloud Pub/Sub”.
- Set Sink Destination to your Pub/Sub topic. For example, "pub-sub-logs".
- Click Create Sink.
- By default, GCP logs are stored within Stackdriver, but you can configure Stackdriver to exclude them as detailed here without affecting the export to Sumo Logic as outlined above. To understand how to exclude Stackdriver logs, please follow the instructions in this GCP document.
Installing the Google App Engine app
This section provides instructions for installing the Google App Engine App, as well as an example of each of the App dashboards.
Now that you have set up collection for Google App Engine, install the Sumo Logic App to use the pre-configured searches and dashboards that provide visibility into your environment for real-time analysis of overall usage.
To install the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Install App.
note
Sometimes this button says Add Integration.
- Click Next in the Setup Data section.
- In the Configure section of your respective app, complete the following fields.
- Field Name. If you already have collectors and sources set up, select the configured metadata field name (eg _sourcecategory) or specify other custom metadata (eg: _collector) along with its metadata Field Value.
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-installation
Once your app is installed, it will appear in your Installed Apps folder, and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
Each panel slowly fills with data matching the time range query received since the panel was created. Results will not immediately be available but will be updated with full graphs and charts over time.
Viewing Google App Engine dashboards
All dashboards have a set of filters that you can apply to the entire dashboard. Use these filters to drill down and examine the data to a granular level.
- You can change the time range for a dashboard or panel by selecting a predefined interval from a drop-down list, choosing a recently used time range, or specifying custom dates and times. Learn more.
- You can use template variables to drill down and examine the data on a granular level. For more information, see Filtering Dashboards with Template Variables.
- Most Next-Gen apps allow you to provide the scope at the installation time and are comprised of a key (
_sourceCategoryby default) and a default value for this key. Based on your input, the app dashboards will be parameterized with a dashboard variable, allowing you to change the dataset queried by all panels. This eliminates the need to create multiple copies of the same dashboard with different queries.
Overview
See the overview of your App Engine including the requests, applications, and status codes.
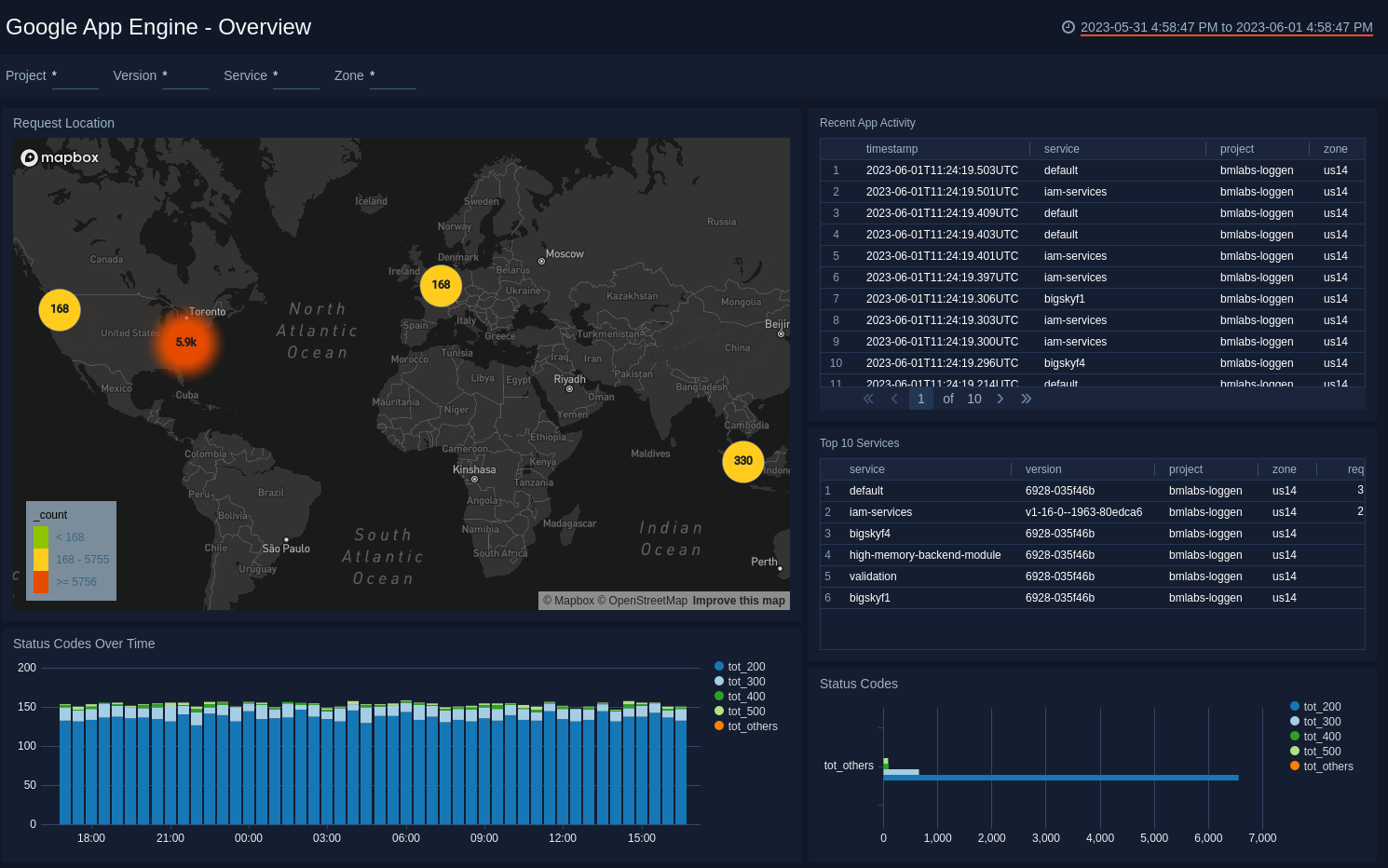
Request Location. See the location of requests in the last 24 hours on a world map.
Recent App Activity. See the details of app activities in the last three hours including the timestamp, app, project, zone, method, status, and latency.
Top Applications. See the details of top applications by requests in the last 24 hours including the app, version, project, zone, and count of requests.
Status Codes Over Time. See the count of 200, 300, 400, 500, and other status codes for every 30 minutes in the last 24 hours on a stacked column chart.
Status Codes. See the count of 200, 300, 400, 500, and other status codes in the last 24 hours on a bar chart.
Activity
See the details of App Engine activities including the projects, services, versions, and message severity.
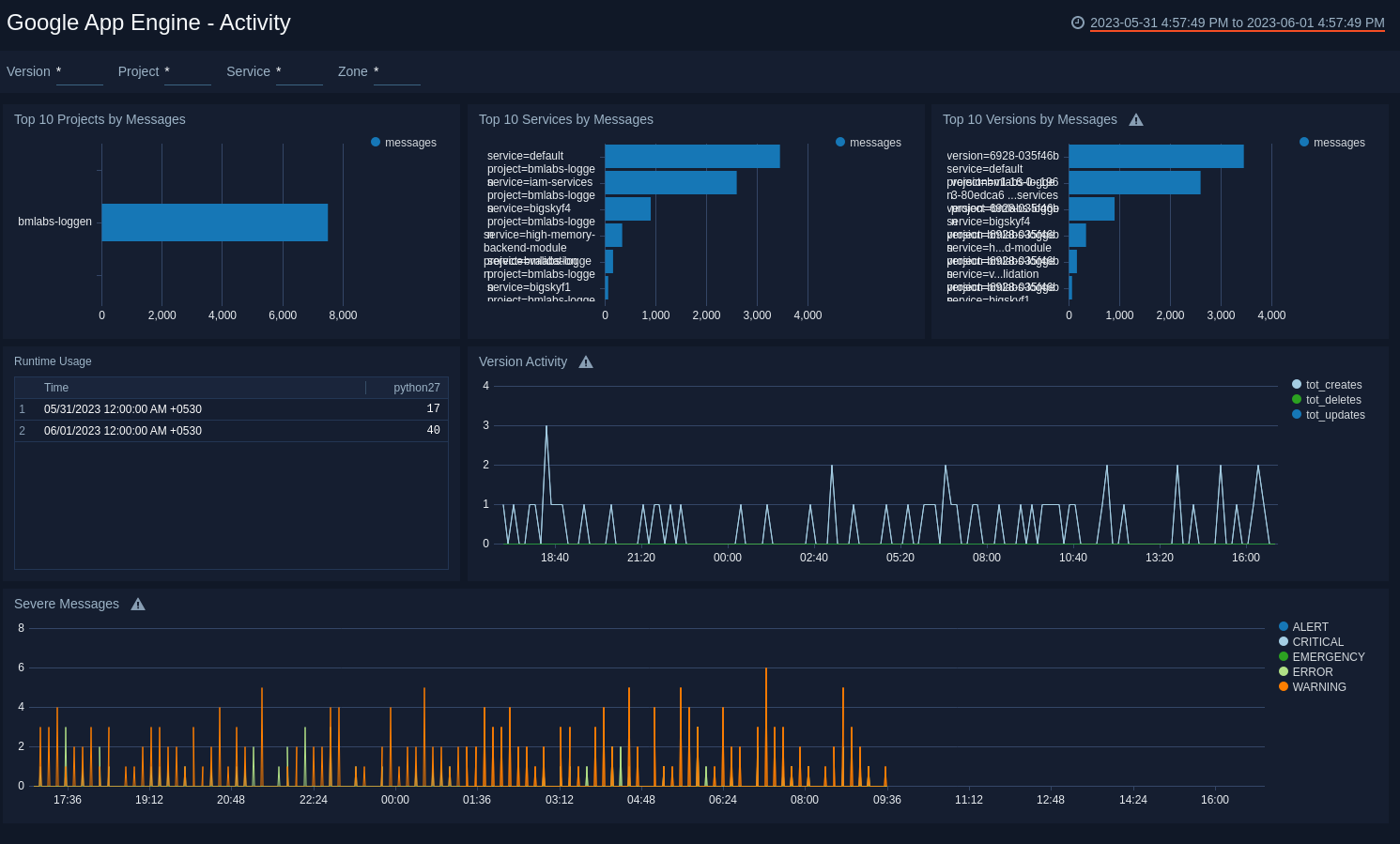
Top 10 Projects by Messages. See the top 10 projects by message count in the last hour on a bar chart.
Top 10 Services by Messages. See the top 10 services by message count in the last hour on a bar chart.
Top 10 Versions by Messages. See the top 10 versions by message count in the last hour on a bar chat.
Runtime Usage. See the count of runtimes in the last 24 hours displayed in a table.
Version Activity. See the count of version updates, deletes, and creation in the last hour on a line chart.
Severe Messages. See the count of messages by severity in the last hour on a line chart.
Request Activity
See the details of App Engine requests including the location, request methods, response status codes, latency, and response time.
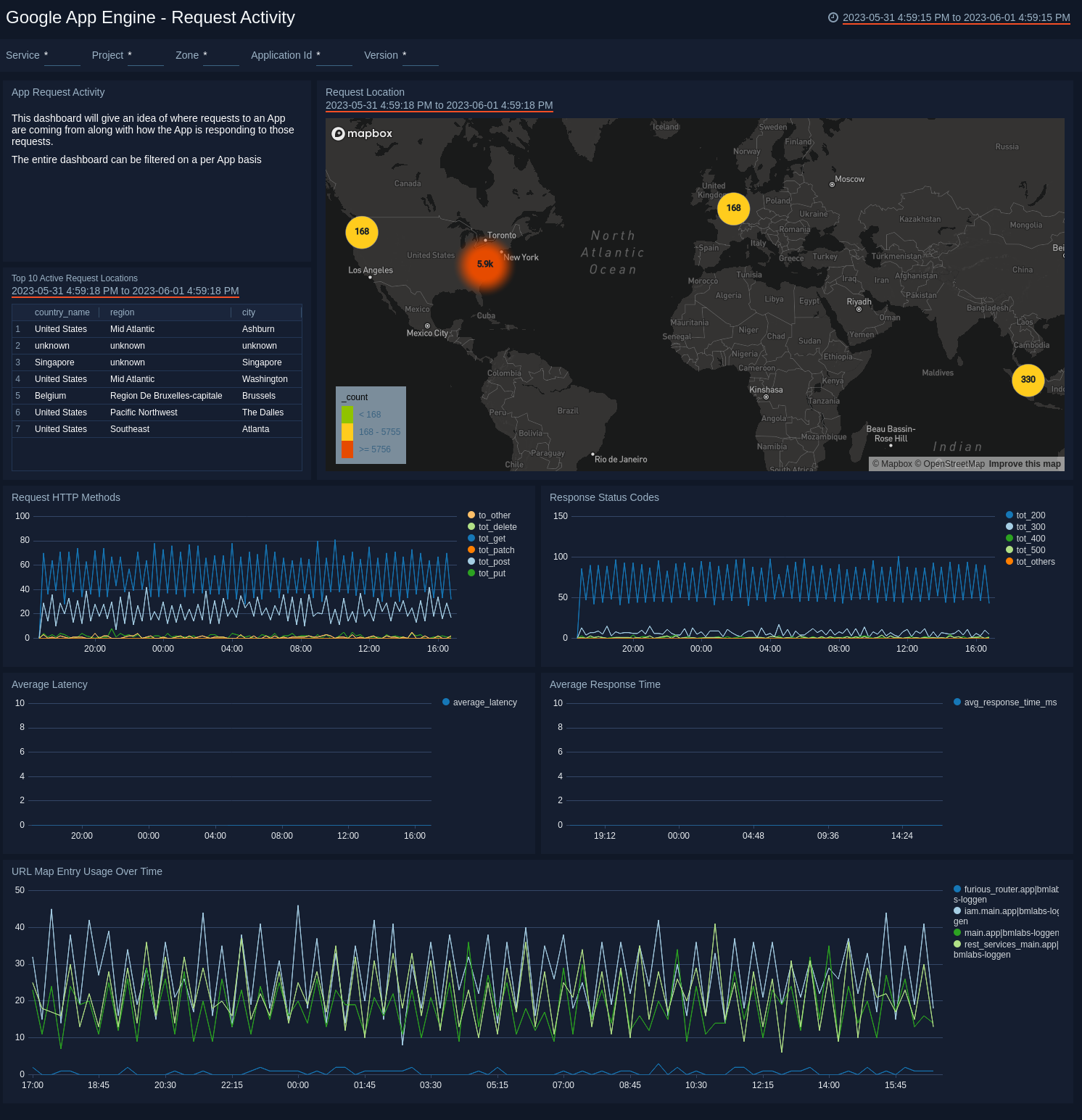
Request Location. See the location of requests in the last 24 hours on a world map.
Top 10 Active Request Locations. See the details of top 10 active requests by location in the last 24 hours including the country name, region, city, and count of requests in a table.
Request HTTP Methods. See the count and trend of HTTP request methods GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH and other methods in the last six hours on a line chart.
Response Status Codes. See the count and trend of 200, 300, 400, 500, and other response status codes in the last six hours on a line chart.
Average Latency. See the average and trend of latency in the last hour on a line chart.
Average Response Time. See the average and trend of response time in the last hour on a line chart.
Upgrade/Downgrade the Google App Engine app (Optional)
To update the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
Optionally, you can identify apps that can be upgraded in the Upgrade available section. - To upgrade the app, select Upgrade from the Manage dropdown.
- If the upgrade does not have any configuration or property changes, you will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
- If the upgrade has any configuration or property changes, you will be redirected to the Setup Data page.
- In the Configure section of your respective app, complete the following fields.
- Field Name. If you already have collectors and sources set up, select the configured metadata field name (eg _sourcecategory) or specify other custom metadata (eg: _collector) along with its metadata Field Value.
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-update
Your upgraded app will be installed in the Installed Apps folder and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
See our Release Notes changelog for new updates in the app.
To revert the app to a previous version, do the following:
- Select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
- To version down the app, select Revert to < previous version of your app > from the Manage dropdown.
Uninstalling the Google App Engine app (Optional)
To uninstall the app, do the following:
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Uninstall.