Linux
The Sumo app for Linux allows you to view information about events, logins, and the security status of your Linux system. The app consists of predefined searches and three dashboards that provide visibility into your environment for real-time or historical analysis.
You may also be interested in the Sumo Logic App for Linux Cloud Security Monitoring and Analytics.
Collecting logs for Linux
This procedure describes how to collect logs from Linux into Sumo Logic.
Sumo apps gather data from the log messages collected from sources by collectors. The Sumo app for Linux requires specific Linux log types, which are set up during the collector and source configuration process.
Required logs for Ubuntu
The following logs, located in your Linux machine's /var/log folder, are required for using the Sumo app for Linux with Ubuntu:
- auth.log
- syslog
- daemon.log
- dpkg.log
- kern.log
Required logs for CentOS, Amazon Linux, and Red Hat
The following logs, located in your Linux machine's /var/log folder, are required for using the Sumo app for Linux with CentOS, Amazon Linux, and most Red Hat forks:
- audit/audit.log
- secure
- messages
- yum.log
Configure a Collector
Configure an Installed Collector.
Configure a Source
To configure a source for collecting Linux logs, you create a Local File Source. Following the instructions on Local File Source. When you define a Source Category for the source, we recommend something like: prod/os/linux. For more information about Source Categories, see Best Practices.
Sample log messages
Dec 16 20:26:23 ubuntu sshd[15533]: pam_unix(sshd:auth): authentication failure; logname= uid=0 euid=0 tty=ssh ruser= rhost=116.31.116.50 user=root
2016-12-16 19:23:13 startup packages remove
2016-12-16 19:23:13 remove tomcat7:all 7.0.68-1ubuntu0.1 <none>
Sample queries
See Suggested Searches for Linux OS.
Installing the Linux app
To install the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Install App.
note
Sometimes this button says Add Integration.
- Click Next in the Setup Data section.
- In the Configure section of your respective app, complete the following fields.
- Field Name. If you already have collectors and sources set up, select the configured metadata field name (eg _sourcecategory) or specify other custom metadata (eg: _collector) along with its metadata Field Value.
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-installation
Once your app is installed, it will appear in your Installed Apps folder, and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
Each panel slowly fills with data matching the time range query received since the panel was created. Results will not immediately be available but will be updated with full graphs and charts over time.
Viewing Linux dashboards
All dashboards have a set of filters that you can apply to the entire dashboard. Use these filters to drill down and examine the data to a granular level.
- You can change the time range for a dashboard or panel by selecting a predefined interval from a drop-down list, choosing a recently used time range, or specifying custom dates and times. Learn more.
- You can use template variables to drill down and examine the data on a granular level. For more information, see Filtering Dashboards with Template Variables.
- Most Next-Gen apps allow you to provide the scope at the installation time and are comprised of a key (
_sourceCategoryby default) and a default value for this key. Based on your input, the app dashboards will be parameterized with a dashboard variable, allowing you to change the dataset queried by all panels. This eliminates the need to create multiple copies of the same dashboard with different queries.
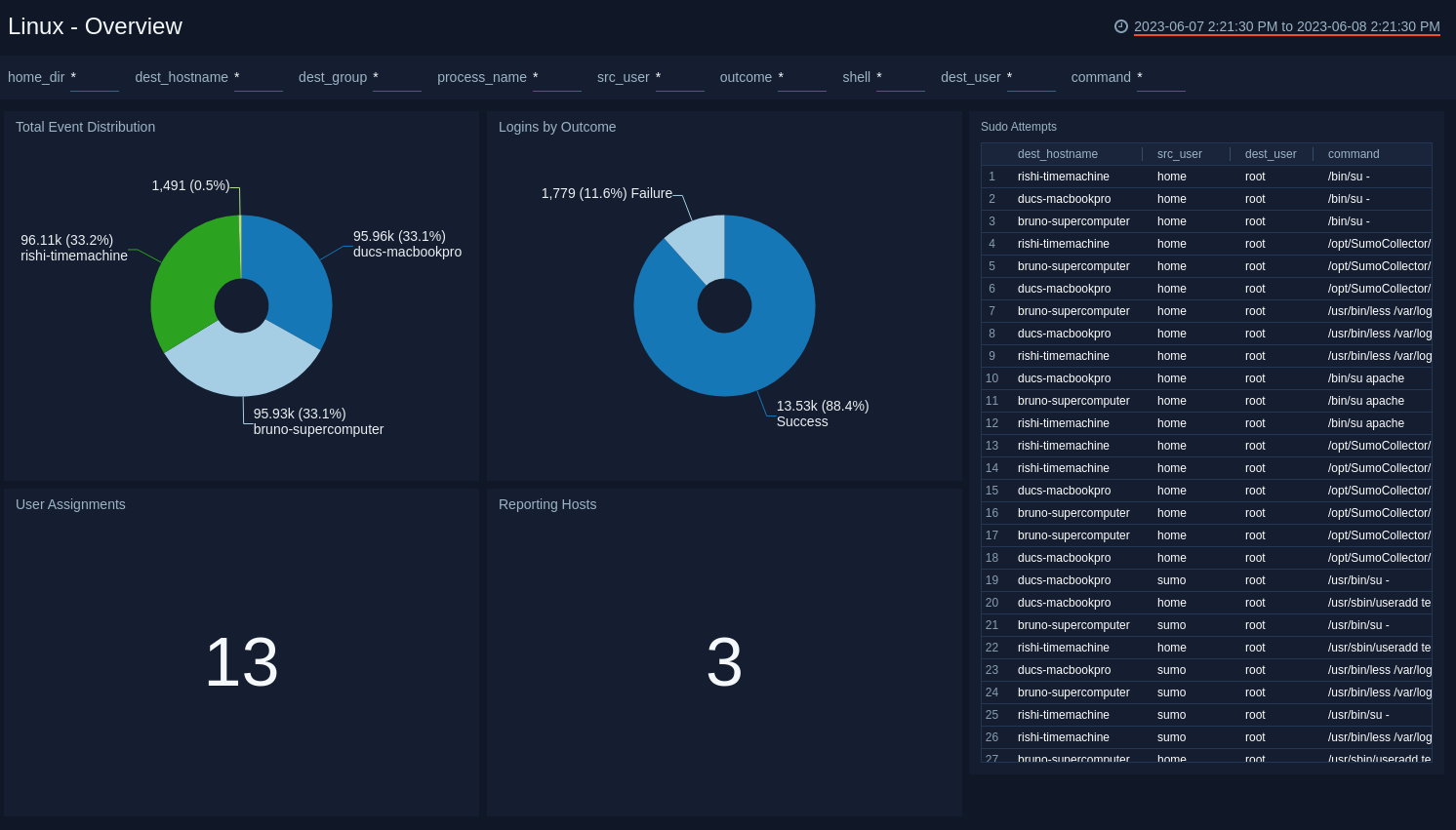
Overview
The Linux - Overview dashboard provides an overview of Linux activity, including the distribution of system events across hosts, group assignment changes, a breakdown of successful and failed logins, sudo attempts, and the count of reporting hosts.
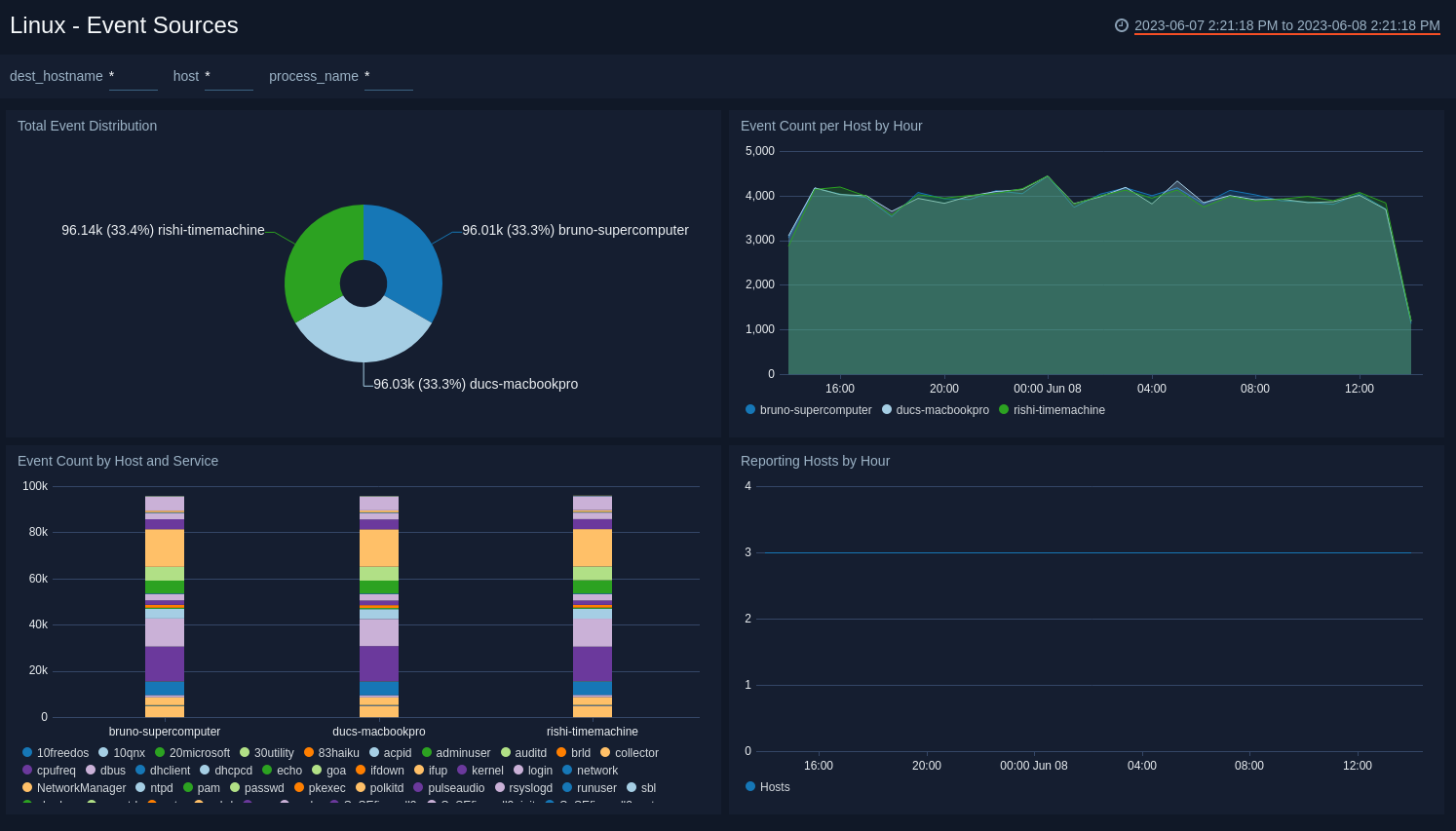
Event Sources
The Linux - Event Sources dashboard provides information about system events, including their distribution across hosts, event counts per host by hour, and even counts by host and service.
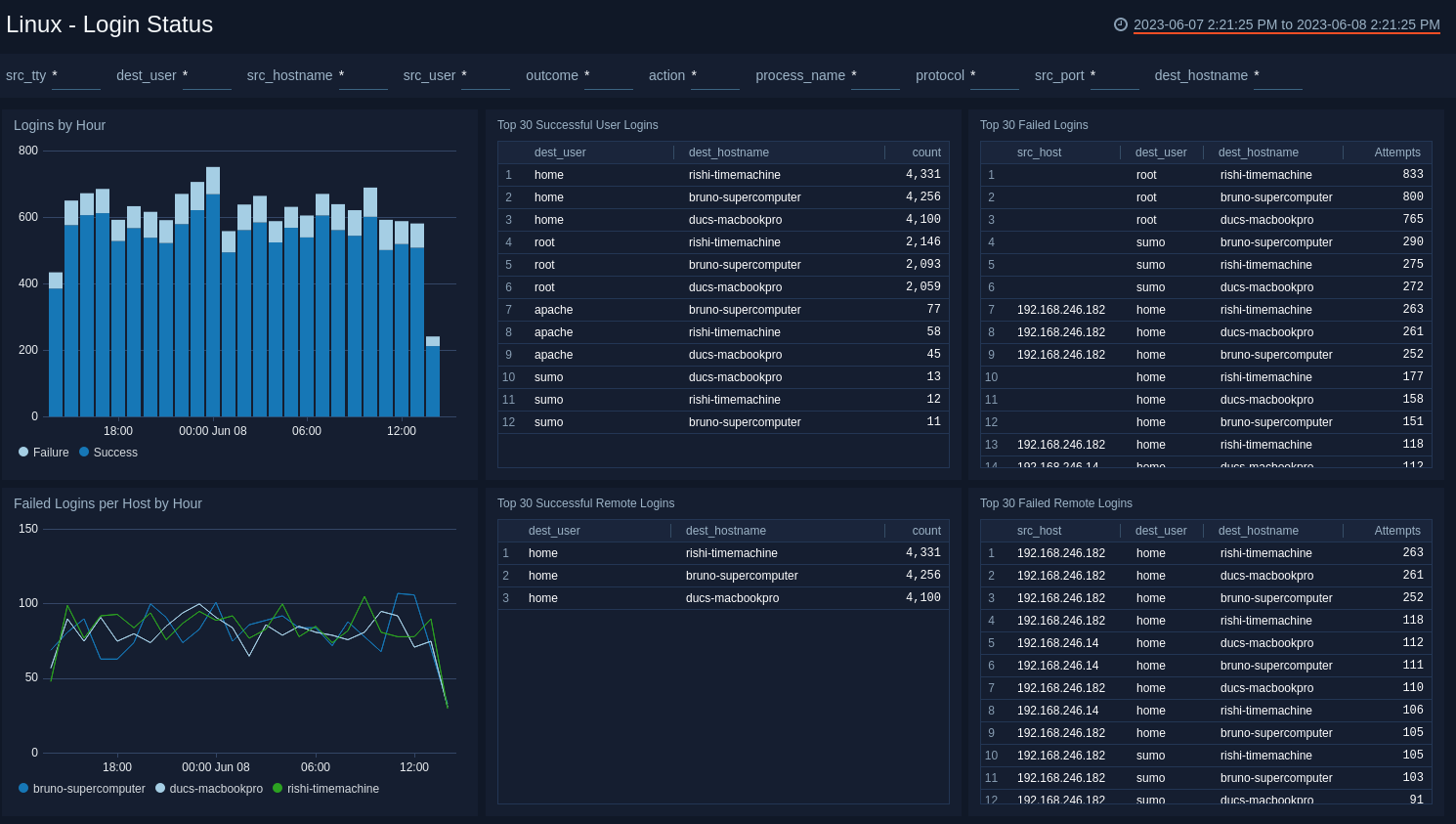
Login Status
The Linux - Login Status dashboard provides information about logins to Linux hosts; including logins by hour; failed logins per host; the top 30 successful and failed logins; and the top 30 successful and failed remote logins.
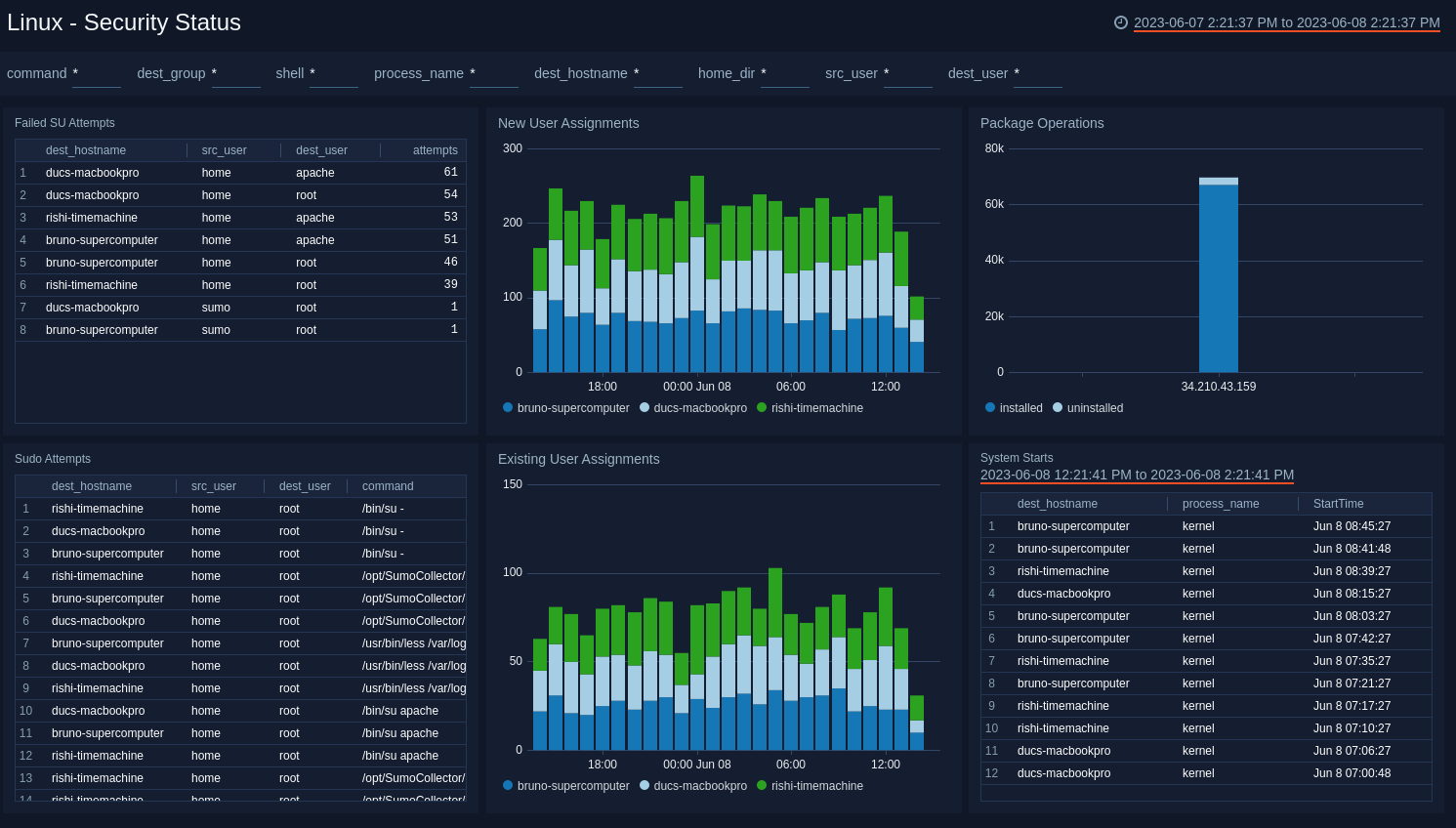
Security Status
The Linux - Security Status dashboard provides information about security on Linux hosts, including su, sudo attempts, new and existing user assignments, package operations, and system start events.
Suggested Searches for Linux OS
These suggested searches cover some of the most common scenarios for monitoring user activity and security activity on a Linux server. These searches work on RedHat, Debian, SuSe platforms, and their derivations (for example, CentOS, Ubuntu, OpenSuSe).
You can enter these queries into the Search box as a starting baseline, and then customize a query and time range for your system. Be sure to save your search queries if you plan to run them often.
It's assumed that common Linux OS logs are collected (for example: /var/log/*).
The _sourceCategory fields shown in these sample queries are based on the following Linux logs and their metadata:
- Generic system log: Typically named
/var/log/syslogor/var/log/messagesMeta field:SourceCategory = OS/Linux/System - Authentication log: Typically named
/var/log/author/var/log/auth.logMeta field:SourceCategory=OS/Linux/Security
These logs might have also been collected by the Collector (if selected during its installation).
User Activity
These searches are intended to help you understand how privileged and non-privileged users are authenticating to and using your Linux servers.
Successful User Login events
Returns all successful remote and local logins by a user. Suggested time range: -1 day.
_sourceCategory=OS/Linux* ("su:" or "sudo:" or "sshd:" or "sshd[" or "pam:") (("Accepted" and "pam") or "session" or ("to" and "on")) !"closed"
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<_sourceHost>\S*)\s" nodrop
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_host>\S*)\s(?:\w*):\s+(?<message>.*)$" nodrop
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_host>\S*)\s(?:\S*)\[\d+\]:\s+(?<message>.*)$" nodrop
| parse field=message "pam_unix(*:*):" as daemon, ltype nodrop | if (daemon="sshd", "ssh", "") as protocol | fields -daemon, ltype
| parse "session * for user * by *(uid=" as action, dest_user, src_user nodrop
| parse regex "session (?<action>\w*) for user (?<dest_user>\S*)" nodrop
| parse "rhost=* " as src_host nodrop
| parse "Accepted * for * from * port * *" as type, dest_user, src_host, src_port, protocol nodrop
| where dest_user!=""
| if (isEmpty(message),"Authentication successful",message) as message
| if (isEmpty(src_host),_sourceHost,src_host) as src_host | src_host as src_ip
| if (isEmpty(src_user),dest_user,src_user) as src_user
| timeslice 1s
| count as eventCount by _timeslice, dest_host, dest_user, message, protocol, src_host, src_ip, src_user
| sort by _timeslice, dest_host, dest_user, message, protocol, src_host, src_ip, src_user
All Failed authentication attempts
Returns all failed authentication attempts by either a user or a process. Suggested time range: -1 day.
_sourceCategory=*linux* ("authentication failure" or "FAILED SU" or "input_userauth_request: invalid user" or "Invalid user" or "Failed publickey" or "Failed password")
| parse regex "\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_hostname>\S+)\s(?<process_name>\w*)(?:\[|:)" nodrop
| parse " user = * " as dest_user nodrop
| parse "User *: Authentication failure" as dest_user nodrop
| parse " user=*" as dest_user nodrop
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s+(?<_sourceHost>\S*)\s+" nodrop
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s+(?<dest_hostname>\S*)\s+(?<message>[^;]+)" nodrop
| parse "ruser=* rhost=* user=*" as src_user, src_host, dest_user nodrop
| parse "ruser= rhost=* user=*" as src_host, dest_user nodrop
| parse " user=*\"" as dest_user nodrop
| parse "Authentication failure for * from *" as dest_user, src_host nodrop
| parse "FAILED SU (to *) * on" as dest_user, src_user nodrop
| parse regex "FAILED LOGIN (?:SESSION|\d+) FROM (?:\S+) FOR (?<dest_user>\S+)," nodrop
| parse "input_userauth_request: invalid user *" as dest_user nodrop
| parse "Invalid user * from * port *" as dest_user, src_host, src_port nodrop
| parse "Failed publickey for * from * port * *" as dest_user, src_host, src_port, protocol nodrop
| parse "Failed password for * from * port * *" as dest_user, src_host, src_port, protocol nodrop
| parse "Failed password for invalid user * from * port * *" as dest_user, src_host, src_port, protocol nodrop
| if (!isEmpty(protocol), protocol, if (message matches "sshd[*", "ssh", protocol)) as protocol
| where dest_user!=""
| if (src_user="", dest_user, src_user) as src_user
| if (src_host=" " or isEmpty(src_host), _sourceHost, src_host) as src_host | src_host as src_ip
Root Activities
Returns all sudo/su attempts, or activities by "root" user. Modify to include other privileged users that you want to track in your environment.
_sourceCategory=OS/Linux/Security ("sudo" or "root" or "su")
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_hostname>\S*)\s" nodrop
| extract "sudo:\s+(?<src_user>[^ ]+?)\s:.+?USER=(?<dest_user>[^ ]+?)\s+" nodrop
| parse regex "COMMAND=(?<command>[^$]*)$" nodrop
| parse " user * " as dest_user nodrop | parse " user *" as dest_user nodrop
| where command !="" or dest_user in ("root") or src_user in ("root")
Failed SU attempts
Returns all failed SU attempts.
_sourceCategory=*linux*("authentication failure" or "FAILED SU" or "input_userauth_request: invalid user" or "Invalid user" or "Failed publickey" or "Failed password") ("su:" or "su[")
| parse regex "\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_hostname>\S+)\s(?<process_name>\w*)(?:\[|:)" nodrop
| parse " user = * " as dest_user nodrop
| parse "User *: Authentication failure" as dest_user nodrop
| parse " user=*" as dest_user nodrop
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s+(?<_sourceHost>\S*)\s+" nodrop
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s+(?<dest_hostname>\S*)\s+(?<message>[^;]+)" nodrop
| parse "ruser=* rhost=* user=*" as src_user, src_host, dest_user nodrop
| parse "ruser= rhost=* user=*" as src_host, dest_user nodrop
| parse " user=*\"" as dest_user nodrop
| parse "Authentication failure for * from *" as dest_user, src_host nodrop
| parse "FAILED SU (to *) * on" as dest_user, src_user nodrop
| parse "FAILED su for * by *" as dest_user,src_user nodrop
| parse regex "FAILED LOGIN (?:SESSION|\d+) FROM (?<src_tty>\S+) FOR (?<dest_user>\S+)," nodrop
| parse "input_userauth_request: invalid user *" as dest_user nodrop
| parse "Invalid user * from * port *" as dest_user, src_host, src_port nodrop
| parse "Failed publickey for * from * port * *" as dest_user, src_host, src_port, protocol nodrop
| parse "Failed password for * from * port * *" as dest_user, src_host, src_port, protocol nodrop
| parse "Failed password for invalid user * from * port * *" as dest_user, src_host, src_port, protocol nodrop
| where dest_user!="" and src_user!=""
| count as attempts by dest_hostname, src_user, dest_user | sort - attempts
Security Activity Monitoring
New Users
Returns a list of all new users.
Suggested time range: -1 day
_sourceCategory=OS/Linux/S* "useradd" and (("new user") or ("new account"))
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_hostname>\S*)\s(?<process_name>\w*)(?:\[|:)" nodrop
| parse "name=*, UID=*, GID=*, home=*, shell=*" as dest_user,dest_uid,dest_gid,home_dir,shell nodrop
| parse "account=*, uid=*, gid=*, home=*, shell=*," as dest_user,dest_uid,dest_gid,home_dir,shell nodrop
New groups
Returns a list of all new groups.
Suggested time range: -1 day
_sourceCategory=OS/Linux/S* "new group"
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_hostname>\S*)\s(?<process_name>\w*)(?:\[|:)" nodrop
| parse "name=*, GID=*" as dest_group,dest_gid nodrop
| parse "group=*, gid=*," as dest_group,dest_gid nodrop
Existing users added to privileged groups
Returns all messages that indicate a user being added to an administrative group. Modify this query to include the IDs or names of the administrative groups in your environment.
Suggested time range: -1 day
_sourceCategory=OS/Linux/S* "to group" or "default group changed" or "change user"
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_hostname>\S*)\s(?<process_name>\w*)(?:\[|:)" nodrop
| parse "add '*' to group '*'" as dest_user,dest_group nodrop
| parse "account added to group - account=*, group=*, gid=*," as dest_user,dest_group,dest_gid nodrop
| parse "account=*, uid=*, gid=*, old gid=*," as dest_user,dest_uid, dest_gid,src_gid nodrop
| parse "change user '*' GID from '*' to '*'" as dest_user,src_gid, dest_gid nodrop
| where dest_gid in("10","0","4") or dest_group in ("root", "wheel", "adm")
Failed Password Changes
Returns all failed attempts to change a user password.
Suggested time range: -1 day
_sourceCategory=OS/Linux/* "Authentication failure"
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_hostname>\S*)\s(?<process_name>\w*)(?:\[|:)" nodrop
| parse "User *:" as dest_user nodrop
| parse " user=*" as dest_user nodrop
| where process_name="passwd"
System Start
Returns all incidents when the system starts (or restarts).
Suggested time range: -1 day
_sourceCategory=OS/Linux/System "Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset"
| parse regex "^(?<StartTime>\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+)\s(?<dest_hostname>\S*)\s(?<process_name>\w*)(?:\[\d+\]|):\s+" nodrop
Service Shutdown/Exiting
Returns all instances when a service is shutting down or exiting. Note that this query cannot capture the cases when there is no log when a service is down.
Suggested time range: -1 day
_sourceCategory=OS/Linux/System ("exiting" or "exited" or "terminating" or "terminated" or "shutting")
| parse regex "\S*\s+\d+\s+\d+:\d+:\d+\s(?<dest_hostname>\S*)\s(?<process_name>\w*)(?:\[\d+\]|):\s+"
| where process_name !=""
Upgrade/Downgrade the Linux app (Optional)
To update the app, do the following:
Next-Gen App: To install or update the app, you must be an account administrator or a user with Manage Apps, Manage Monitors, Manage Fields, Manage Metric Rules, and Manage Collectors capabilities depending upon the different content types part of the app.
- Select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
Optionally, you can identify apps that can be upgraded in the Upgrade available section. - To upgrade the app, select Upgrade from the Manage dropdown.
- If the upgrade does not have any configuration or property changes, you will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
- If the upgrade has any configuration or property changes, you will be redirected to the Setup Data page.
- In the Configure section of your respective app, complete the following fields.
- Field Name. If you already have collectors and sources set up, select the configured metadata field name (eg _sourcecategory) or specify other custom metadata (eg: _collector) along with its metadata Field Value.
- Click Next. You will be redirected to the Preview & Done section.
Post-update
Your upgraded app will be installed in the Installed Apps folder and dashboard panels will start to fill automatically.
See our Release Notes changelog for new updates in the app.
To revert the app to a previous version, do the following:
- Select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
- To version down the app, select Revert to < previous version of your app > from the Manage dropdown.
Uninstalling the Linux app (Optional)
To uninstall the app, do the following:
- Select App Catalog.
- In the 🔎 Search Apps field, run a search for your desired app, then select it.
- Click Uninstall.