HAProxy - OpenTelemetry Collector
The HAProxy app is a unified logs and metrics app designed to help you monitor the availability, performance, health, and resource utilization of HAProxy server farms. It provides preconfigured dashboards and searches that offer visibility into your environment for real-time and historical analysis: visitor locations, HTTP error codes percentage, backend and frontend server statistics, traffic patterns, errors, server operations, and access from known malicious sources.
The OpenTelemetry collector runs on the same host as HAProxy, where it uses the HAProxy Receiver and the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Exporter to send the metrics to Sumo Logic. HAProxy logs are sent to Sumo Logic through the OpenTelemetry filelog receiver.
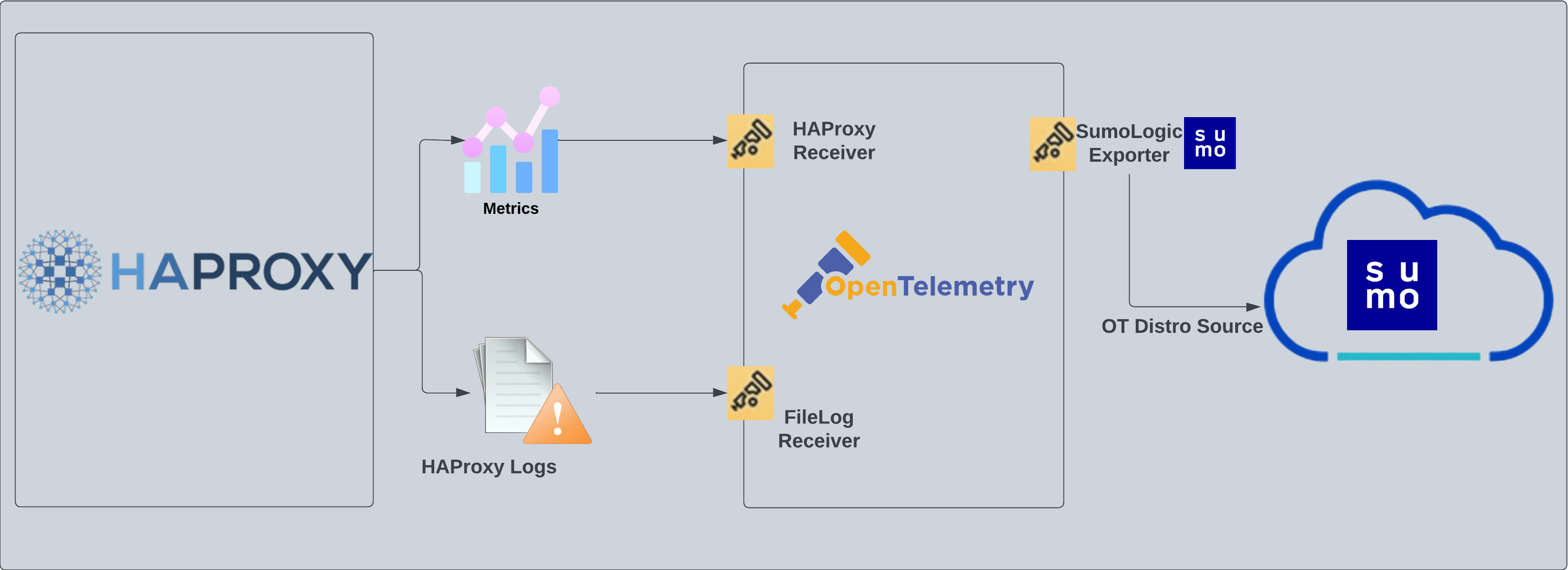
HAProxy log types
The app supports logs from the open source version of HAProxy. This app is tested on the 2.3.9 version of HAProxy.
The HAProxy logs are generated in files as configured in the configuration file /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg (learn more).
This app includes built-in monitors. For details on creating custom monitors, refer to the Create monitors for HAProxy app.
Fields Create in Sumo Logic for HAProxy
Following are the Fields which will be created as part of HAProxy App install if not already present.
sumo.datasource. Has fixed value of haproxy.webengine.system. Has fixed value of haproxy.webengine.cluster.name. User configured. Enter a name to identify the HAProxy cluster. This cluster name will be shown in the Sumo Logic dashboards.webengine.node.name. Has the value of host name of the machine which is being monitored.deployment.environment. User configured. This is the deployment environment where the Memcache cluster resides. For example: dev, prod, or qa.
Prerequisites
For metrics collection
The receiver used gets stats from an HAProxy instance using the stats endpoint. This receiver supports HAProxy version 2.3.9 and later.
Receive server statistics by configuring the server's haproxy.cfg file to enable stats support.
For logs collection
This section provides instructions for configuring log collection for HAProxy running on a non-Kubernetes environment for the Sumo Logic app for HAProxy.
By default, HAProxy logs are forwarded to Syslog. This needs to be changed to send the logs to files. Configuration in the file /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg is needed to be modified to send logs to files.
-
HAProxy logs have several levels of verbosity. To select a level, set your loglevel to one of the following:
- emerg. Errors such as running out of operating system file descriptors.
- alert. Some rare cases where something unexpected has happened, such as being unable to cache a response.
- info. TCP connection and http request details and errors.
- err. Errors such as being unable to parse a map file, being unable to parse the HAProxy configuration file, and when an operation on a stick table fails.
- warning. Certain important, but non-critical, errors such as failing to set a request header or failing to connect to a DNS nameserver.
- notice. Changes to a server's state, such as being UP or DOWN or when a server is disabled. Other events at startup, such as starting proxies and loading modules are also included. Health check logging, if enabled, also uses this level.
- debug. Complete information, useful for development/testing.
All logging settings are located in Haproxy.conf. For the dashboards to work properly, you'll need to set the log format.
%ci:%cp\ [%tr]\ %ft\ %b/%s\ %TR/%Tw/%Tc/%Tr/%Ta\ %ST\ %B\ %CC\ %CS\ %tsc\ %ac/%fc/%bc/%sc/%rc\ %sq/%bq\ %hr\ %hs\ %{+Q}r -
You can enable HAProxy logs to syslog by adding the following line in the global section of
/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfgfile. This means that HAProxy will send its messages to rsyslog on 127.0.0.1.global
log 127.0.0.1 local2 -
Create an
etc/rsyslog.d/haproxy.conffile containing below lines.local2.* /var/log/haproxy.log- You can, of course, be more specific and create separate log files according to the level of messages:
local2.=info /var/log/haproxy-info.log
local2.=notice /var/log/haproxy-notice.log -
Restart HAProxy and rsyslog server to enforce configuration changes.
sudo service rsyslog restart
sudo service haproxy reload
For Linux systems with ACL Support, the otelcol install process should have created the ACL grants necessary for the otelcol system user to access default log locations. You can verify the active ACL grants using the getfacl command. Install the ACL in your Linux environment, if not installed.
The required ACL may not be supported for some rare cases, for example, Linux OS Distro, which is officially not supported by Sumo Logic. In this case, you can run the following command to explicitly grant the permissions.
sudo setfacl -R -m d:u:otelcol-sumo:r-x,d:g:otelcol-sumo:r-x,u:otelcol-sumo:r-x,g:otelcol-sumo:r-x <PATH_TO_LOG_FILE>
Run the above command for all the log files in the directory that need to be ingested, which are not residing in the default location.
If Linux ACL Support is not available, traditional Unix-styled user and group permission must be modified. It should be sufficient to add the otelcol system user to the specific group that has access to the log files.
Collection configuration and app installation
As part of data collection setup and app installation, you can select the App from App Catalog and click on Install App. Follow the steps below.
Step 1: Set up Collector
If you want to use an existing OpenTelemetry Collector, you can skip this step by selecting the Use an existing Collector option.
To create a new Collector:
- Select the Add a new Collector option.
- Select the platform where you want to install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector.
This will generate a command that you can execute in the machine environment you need to monitor. Once executed, it will install the Sumo Logic OpenTelemetry Collector.
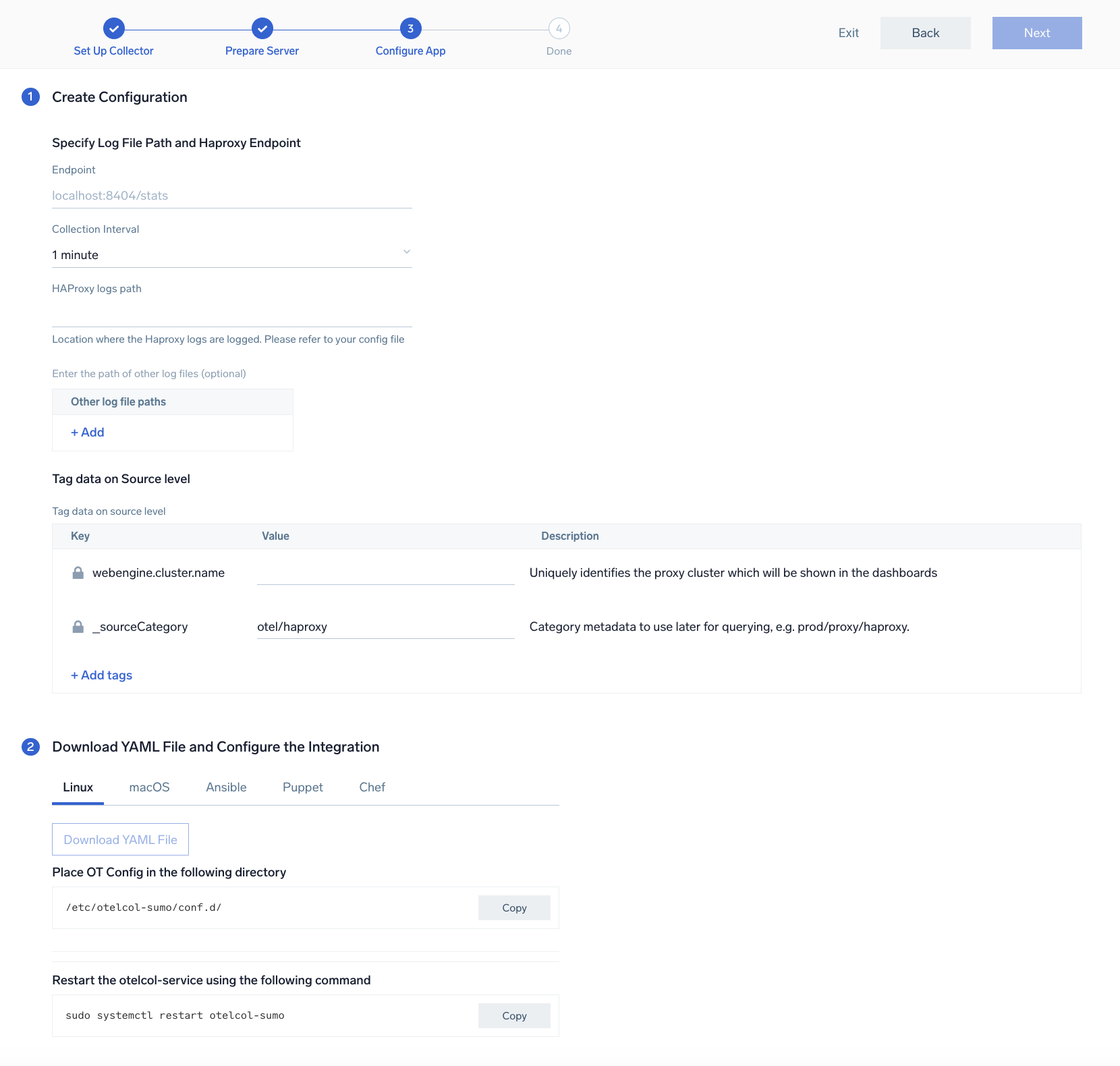
Step 2: Configure integration
In this step, you will configure the yaml required for HAProxy Collection.
Below are the inputs required:
- Endpoint. The URL of the httpd status endpoint (default:
http://localhost:8404/stats). - HAProxy logs Path. Enter the path to the log file for your HAProxy instance.
The path of the log file configured to capture haproxy logs is needed to be given here. The files are typically located in /var/log/haproxy*.log. If you're using a customized path, check the haproxy.conf file for this information. You can add any custom fields which you want to tag along with the data ingested in Sumo Logic. Click on the Download YAML File button to get the yaml file.
Step 3: Send logs and metrics to Sumo Logic
Once you have downloaded the YAML file as described in the previous step, follow the below steps based on your platform.
- Linux
- macOS
- Chef
- Ansible
- Puppet
- Copy the yaml file to
/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/folder in the Haproxy instance which needs to be monitored. - Restart the collector using:
sudo systemctl restart otelcol-sumo
- Copy the yaml file to
/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/folder in the Haproxy instance which needs to be monitored. - Restart the otelcol-sumo process using:
otelcol-sumo --config /etc/otelcol-sumo/sumologic.yaml --config "glob:/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/*.yaml"
- Copy the yaml file into your Chef cookbook files directory
files/<downloaded_yaml_file>. - Use a Chef file resource in a recipe to manage it.
cookbook_file '/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/<downloaded_yaml_file>' do mode 0644 notifies :restart, 'service[otelcol-sumo]', :delayed end - Add the recipe to your collector setup to start collecting the data. Every team typically has their established way of applying the Chef recipe. The resulting Chef recipe should look something like:
cookbook_file '/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/<downloaded_yaml_file>' do
mode 0644
notifies :restart, 'service[otelcol-sumo]', :delayed
end
- Place the file into your Ansible playbook files directory.
- Run the Ansible playbook.
ansible-playbook -i inventory install_sumologic_otel_collector.yaml
-e '{"installation_token": "<YOUR_TOKEN>", "collector_tags": {<YOUR_TAGS>}, "src_config_path": "files/conf.d"}'
- Place the file into your Puppet module files directory
modules/install_otel_collector/files/<downloaded_yaml>. - Use a Puppet file resource to manage it.
file { '/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/<downloaded_yaml_file>':
ensure => present,
source => 'puppet:///modules/install_otel_collector/<downloaded_yaml_file>',
mode => '0644',
notify => Service[otelcol-sumo],
} - Apply the Puppet manifest. Every team typically has their established way of applying the Puppet manifest. The resulting Puppet manifest should look something like:
node 'default' {
class { 'install_otel_collector'
installation_token => '<YOUR_TOKEN>',
collector_tags => { <YOUR_TAGS> },
}
service { 'otelcol-sumo':
provider => 'systemd',
ensure => running,
enable => true,
require => Class['install_otel_collector'],
}
file { '/etc/otelcol-sumo/conf.d/<downloaded_yaml_file>':
ensure => present,
source => 'puppet:///modules/install_otel_collector/<downloaded_yaml_file>',
mode => '0644',
notify => Service[otelcol-sumo],
}
}
After successfully executing the above command, Sumo Logic will start receiving data from your host machine.
Click Next. This will install the app (dashboards and monitors) to your Sumo Logic Org.
Dashboard panels will start to fill automatically. It's important to note that each panel fills with data matching the time range query and received since the panel was created. Results won't immediately be available, but within 20 minutes, you'll see full graphs and maps.
Sample log messages
May 13 08:24:43 localhost haproxy[21813]:
27.2.81.92:64274 [13/May/2021:08:24:43.921] web-edupia.vn-4
Sample metrics
{
"Query": "A",
"metric": "avg",
"haproxy.proxy_name": "stats",
"webengine.cluster.name": "haproxy_otel_cluster",
"webengine.node.name": "node1",
"min": 3385124.8,
"max": 3553632,
"latest": 3553632,
"avg": 3469494.86851211,
"sum": 1002684017.0,
"count": 289,
}
Sample queries
Logs
This query example is from the HAProxy - Overview dashboard > Top 5 URLs with Errors panel:
webengine.cluster.name=* %"sumo.datasource"=haproxy
| json "log" as _rawlog nodrop
| if (isEmpty(_rawlog), _raw, _rawlog) as haproxy_log_message
| parse regex field=haproxy_log_message "(?<syslog_host>.*)\]:\s+" nodrop
| parse regex field=haproxy_log_message ":\s+(?<c_ip>[\w\.]+):(?<c_port>\d+)\s+" nodrop
| parse regex field=haproxy_log_message "\s+\[(?<accept_date>.+)\]\s+" nodrop
| parse regex field=haproxy_log_message "\s+\[(?<accept_date>.+)\]\s+(?<frontend_name>\S+)\s+(?<backend_name>\S+)/(?<server_name>\S+)\s+" nodrop
| parse regex field=haproxy_log_message "\s+(?<tq>-?\d+)/(?<tw>-?\d+)/(?<tc>-?\d+)/(?<tr>-?\d+)/(?<tt>\+?\d+)\s+" nodrop
| parse regex field=haproxy_log_message "\s+(?<status_code>\d+)\s+(?<bytes_read>[\d-]+)\s+(?<tsc>.*)\s+(?<act>\d+)/(?<fe>\d+)/(?<be>\d+)/(?<srv>\d+)/(?<retries>\+?\d+)\s+" nodrop
| parse regex field=haproxy_log_message "\s+(?<queue_server>\d+)/(?<queue_backend>\d+)\s+" nodrop
| parse regex field=haproxy_log_message "\s+\{(?<request_headers>.*)\}\s+" nodrop
| parse regex field=haproxy_log_message "\s+\"(?<http_request>.*)\"" nodrop
| parse regex field=request_headers "(?<referer>\S+)\|(?<user_agent>[^\"]*)"
| parse regex field=http_request "(?<method>\w+)\s+(?<request>[^\"]*)\s+(?<http_version>\w+)"| where status_code matches "4*" or status_code matches "5*" and !isEmpty(c_ip) |count by status_code,request
| sort by _count
| limit 5
Metrics
Here is a sample metrics query from the Http Response Codes dashboard > HAProxy - Backend Metrics panel:
sumo.datasource=haproxy metric=haproxy.requests.total status_code=* haproxy.service_name=backend deployment.environment=* webengine.cluster.name=* webengine.node.name=* haproxy.proxy_name=*
| parse field=status_code * as code
| avg by webengine.cluster.name,webengine.node.name,haproxy.proxy_name,code
Viewing the HAProxy dashboards
Overview
The HAProxy - Overview dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of HAProxy visitor location, response over time and url with errors.
Use this dashboard to:
- Gain insights into originated traffic location by region. This can help you allocate computer resources to different regions according to their needs.
- Gain insights into Client, Server Responses on HAProxy Server. This helps you identify errors in HAProxy Server.
Backend
The HAProxy - Backend dashboard provides an at-a-glance view for the number of backend active servers, backend weight, respond code from backend, and throughput http.
Frontend
The HAProxy - Frontend dashboard provides details of HAProxy Frontend. It provides information such as number request to frontend, number of error requests, and current session.
Server
The HAProxy - Server dashboard provides details of HAProxy Server. This dashboard helps you monitor the uptime and error request by proxy.
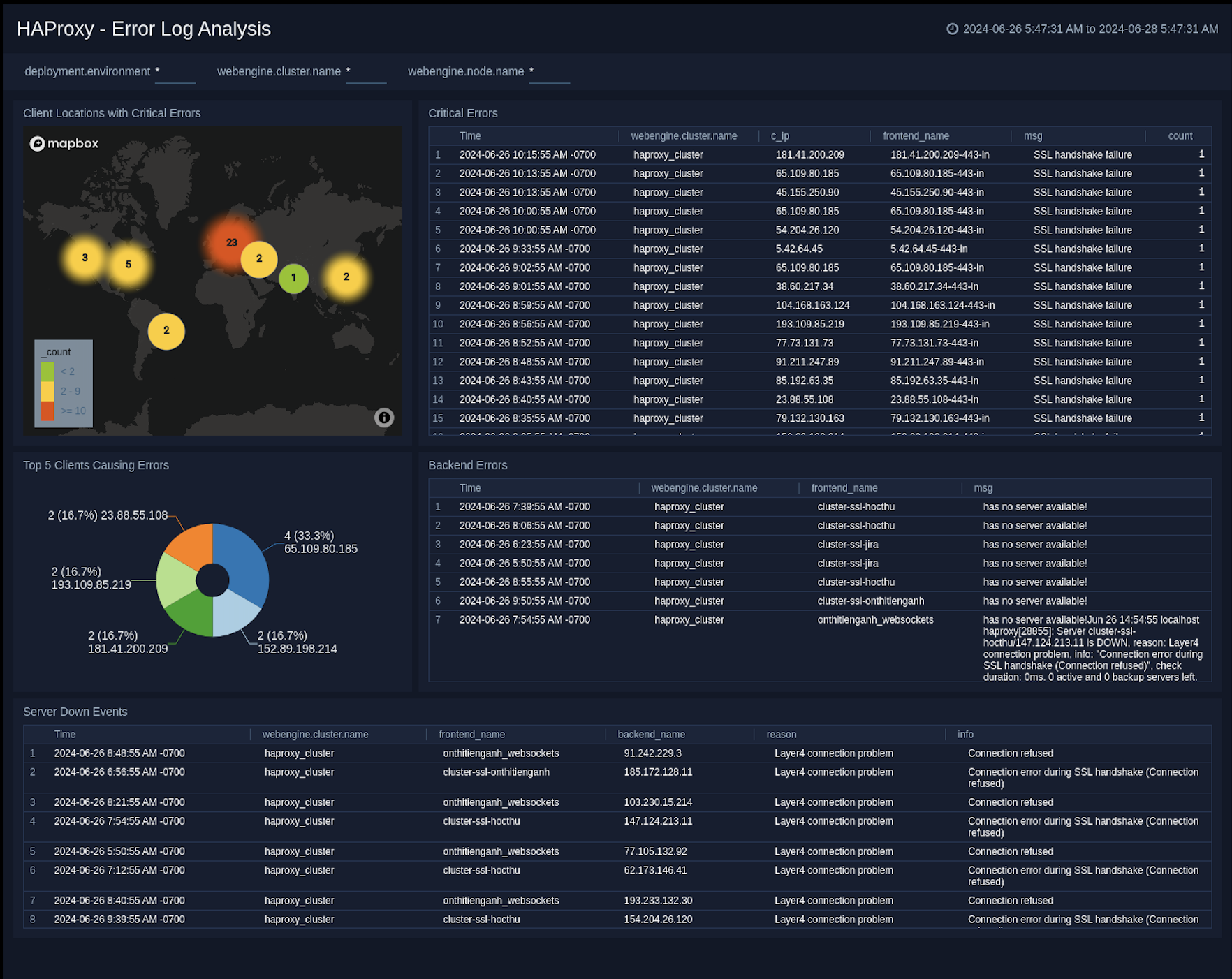
Error Log Analysis
The HAProxy - Error Logs Analysis dashboard provides a high-level view of log level breakdowns, comparisons, and trends. The panels also show the geographic locations of clients and clients with critical messages, new connections and outliers, client requests, request trends, and request outliers.
Use this dashboard to:
- Track requests from clients. A request is a message asking for a resource, such as a page or an image.
- To track and view client geographic locations generating errors.
- Track critical alerts and emergency error alerts.
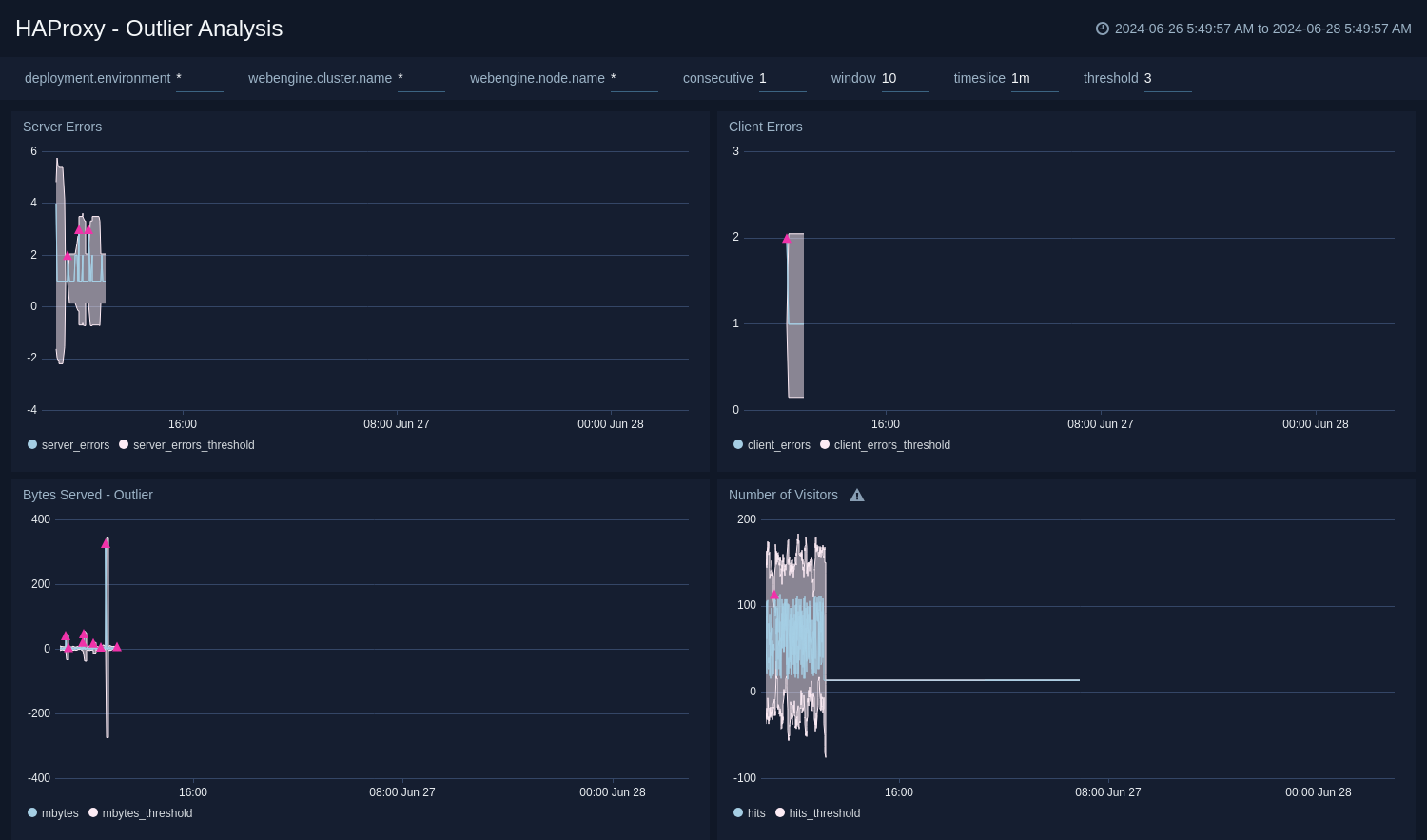
Outlier Analysis
The HAProxy - Outlier Analysis dashboard provides a high-level view of HAProxy server outlier metrics for bytes served, number of visitors, and server errors. You can select the time interval over which outliers are aggregated, then hover the cursor over the graph to display detailed information for that point in time.
Use this dashboard to:
- Detect the outliers in your infrastructure with Sumo Logic's machine learning algorithm.
- To identify outliers in incoming traffic and the number of errors encountered by your servers.
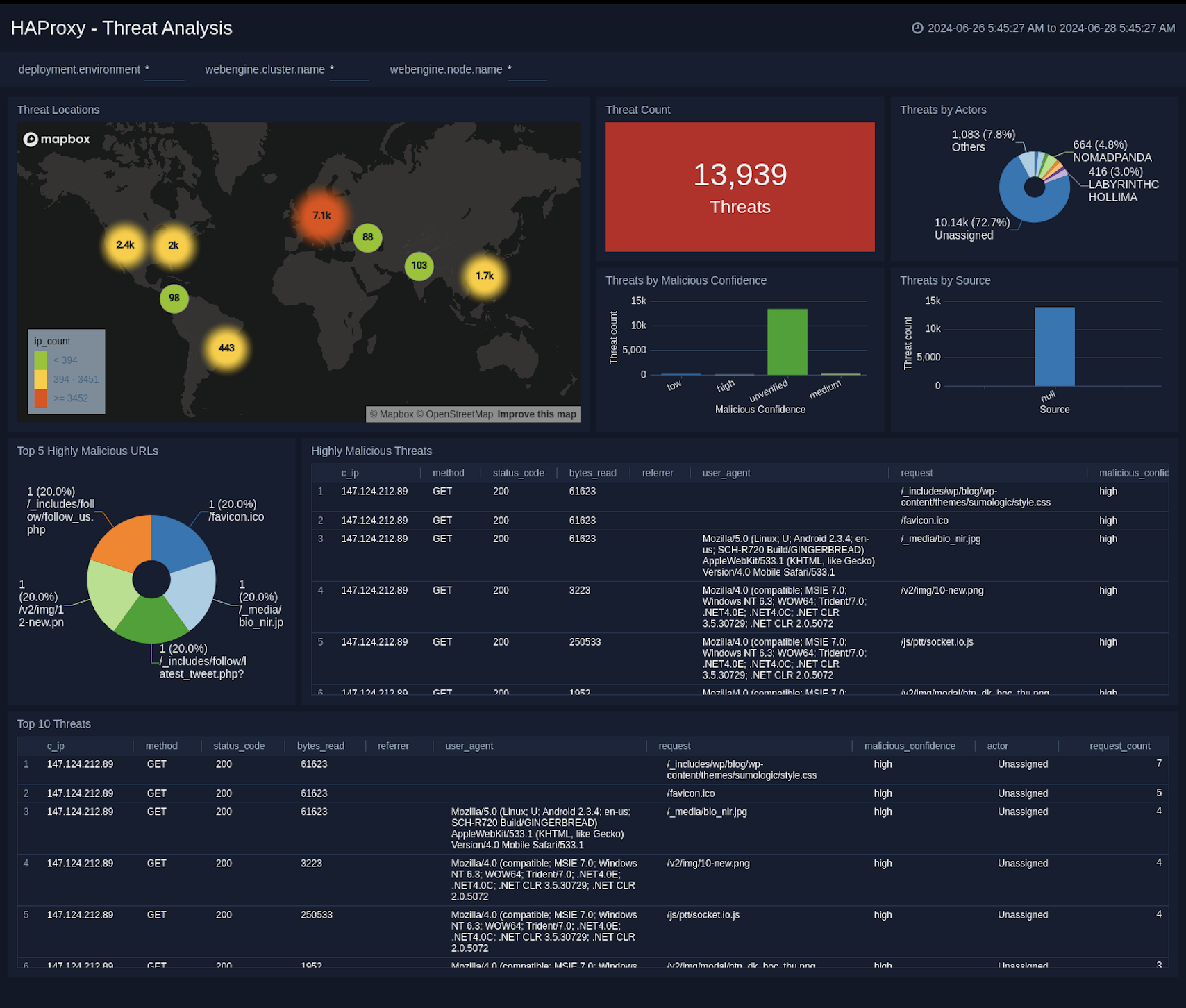
Threat Analysis
The HAProxy - Threat Analysis dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of threats to HAProxy servers on your network. Dashboard panels display the threat count over a selected time period, geographic locations where threats occurred, source breakdown, actors responsible for threats, severity, and a correlation of IP addresses, method, and status code of threats.
Use this dashboard to:
- To gain insights and understand threats in incoming traffic and discover potential IOCs. Incoming traffic requests are analyzed using Sumo Logic threat intelligence.
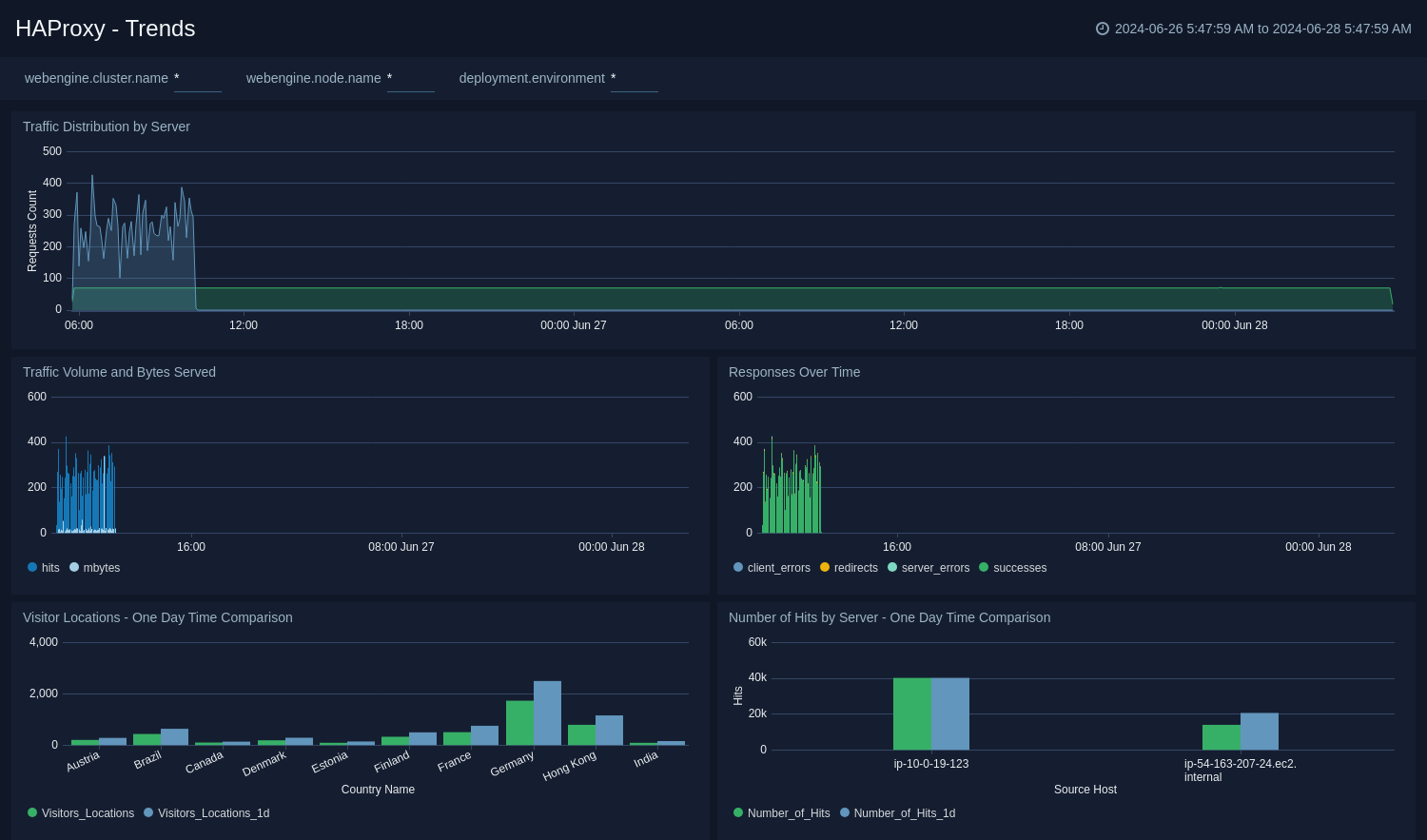
Trends
The HAProxy - Trends dashboard provides an at-a-glance view of traffic to HAProxy servers on your network. Dashboard panels display the traffic count over one day time period, locations where traffic trends for visits by country one days time.
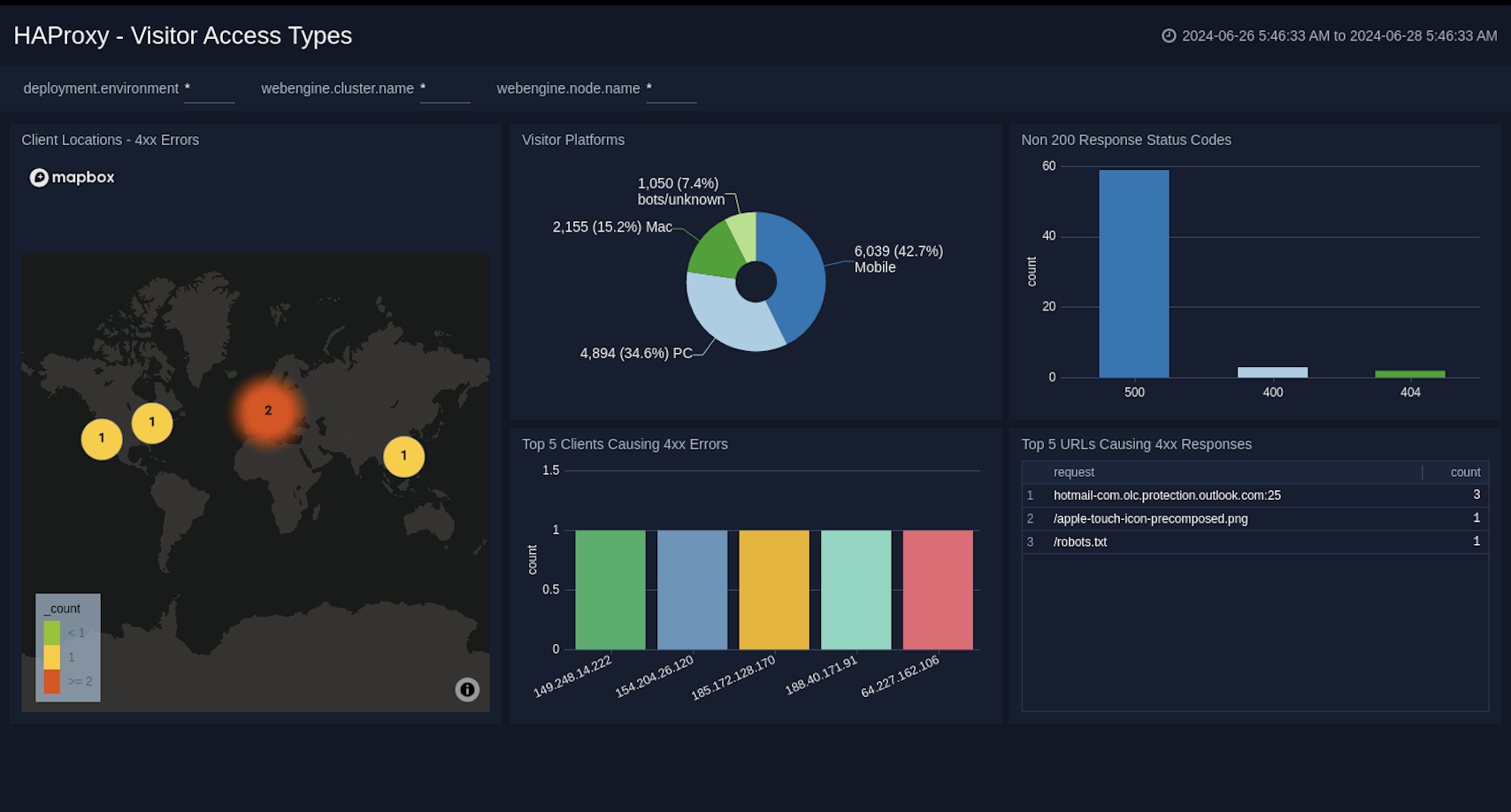
Visitor Access Types
The HAProxy - Visitor Access Types dashboard provides insights into visitor platform types, browsers, and operating systems, as well as the most popular mobile devices, PC and Mac versions used.
Use this dashboard to:
- Understand which platform and browsers are used to gain access to your infrastructure. These insights can be useful for planning in which browsers, platforms, and operating systems (OS) should be supported by different software services.
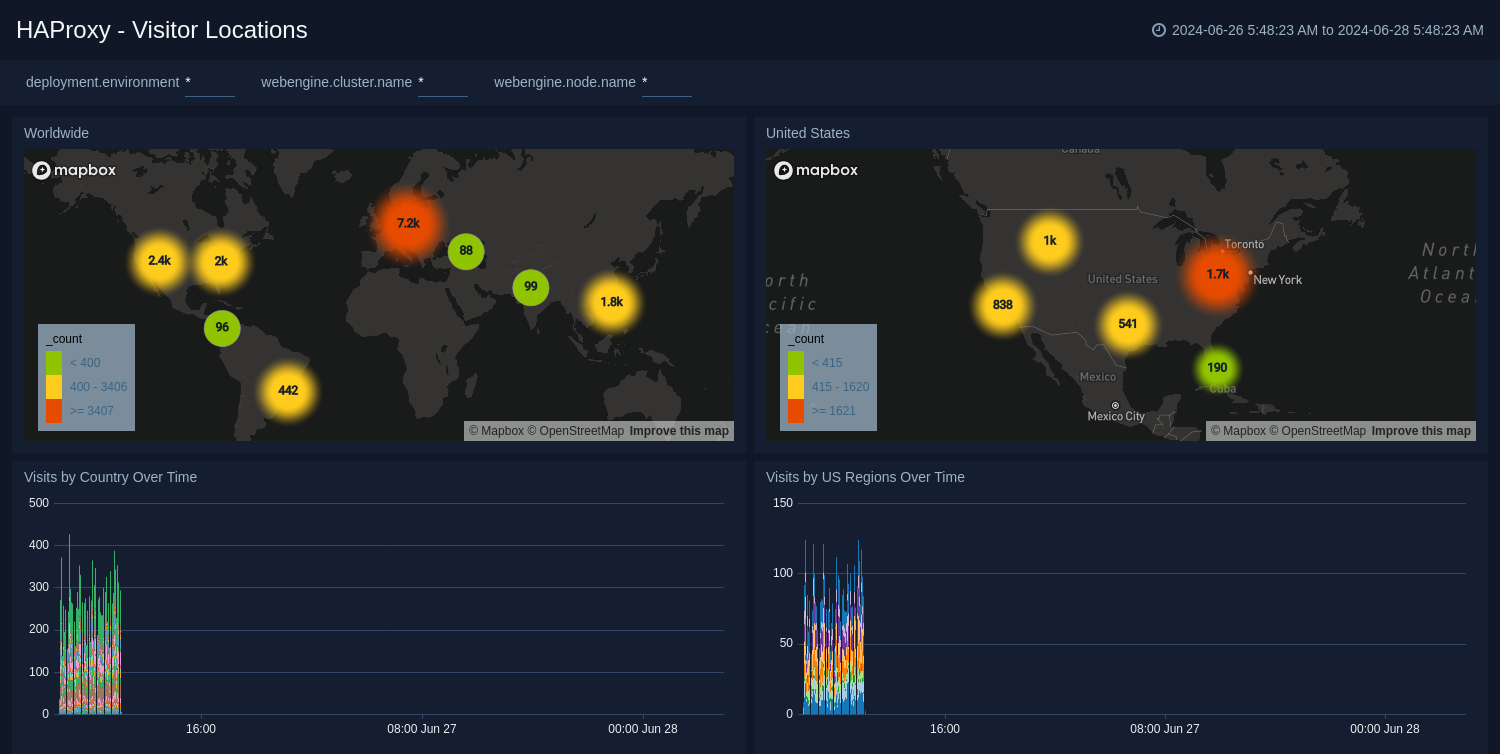
Visitor Locations
The HAProxy - Visitor Locations dashboard provides a high-level view of HAProxy visitor geographic locations both worldwide and in the United States. Dashboard panels also show graphic trends for visits by country over time and visits by US region over time.
Use this dashboard to:
- Gain insights into geographic locations of your user base. This is useful for resource planning in different regions across the globe.
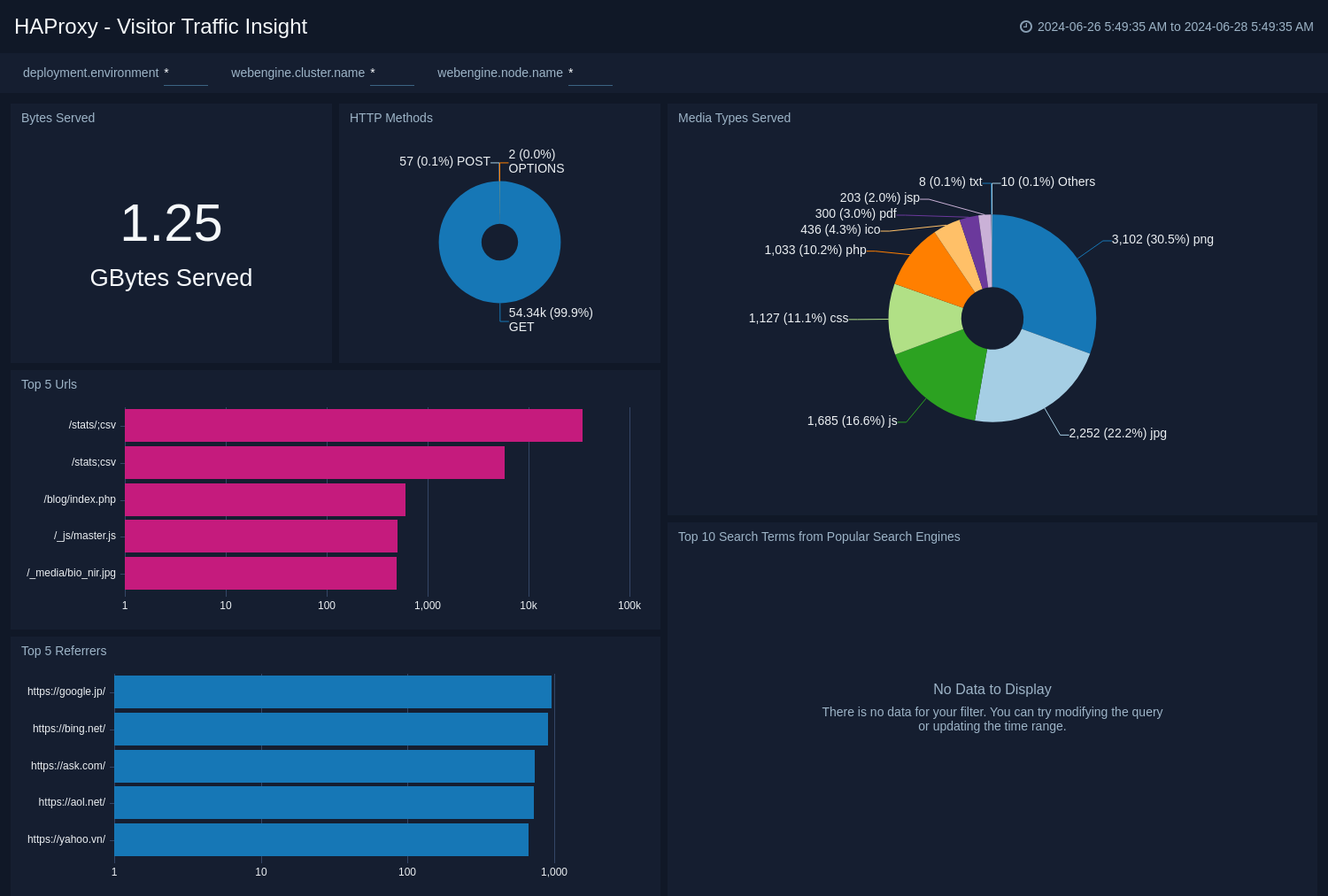
Visitor Traffic Insight
The HAProxy - Visitor Traffic Insight dashboard provides detailed information on the top documents accessed, top referrers, top search terms from popular search engines, and the media types served.
Use this dashboard to:
- To understand the type of content that is frequently requested by users.
- It helps in allocating IT resources according to the content types.
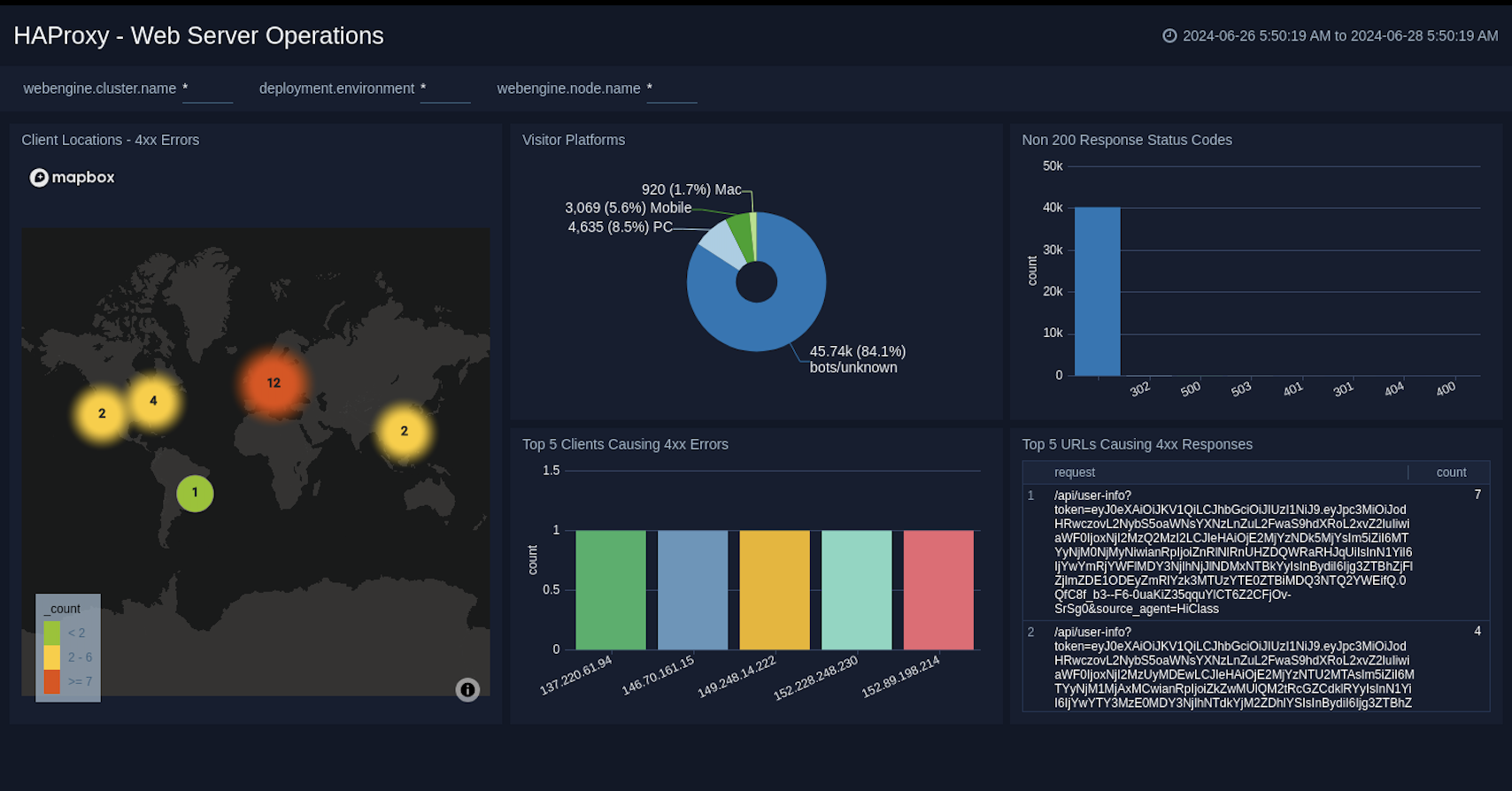
Web Server Operations
The HAProxy - Web Server Operations dashboard provides a high-level view combined with detailed information on the top ten bots, geographic locations, and data for clients with high error rates, server errors over time, and non 200 response code status codes. Dashboard panels also show information on server error logs, error log levels, error responses by a server, and the top URIs responsible for 404 responses.
Use this dashboard to:
- Gain insights into Client, Server Responses on HAProxy Server. This helps you identify errors in HAProxy Server.
- To identify geo locations of all Client errors. This helps you identify client location causing errors and helps you to block client IPs.
Create monitors for HAProxy app
From your App Catalog:
- From the Sumo Logic navigation, select App Catalog.
- In the Search Apps field, search for and then select your app.
- Make sure the app is installed.
- Navigate to What's Included tab and scroll down to the Monitors section.
- Click Create next to the pre-configured monitors. In the create monitors window, adjust the trigger conditions and notifications settings based on your requirements.
- Scroll down to Monitor Details.
- Under Location click on New Folder.
note
By default, monitor will be saved in the root folder. So to make the maintenance easier, create a new folder in the location of your choice.
- Enter Folder Name. Folder Description is optional.
tip
Using app version in the folder name will be helpful to determine the versioning for future updates.
- Click Create. Once the folder is created, click on Save.
HAProxy alerts
| Name | Description | Alert Condition | Recover Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
HAProxy - Access from Highly Malicious Sources | This alert is triggered when an HAProxy is accessed from highly malicious IP addresses. | Count > 0 | Count < = 0 |
HAProxy - Backend Error | This alert is triggered when backend server error is detected. | Count > 0 | Count < = 0 |
HAProxy - Backend Server Down | This alert is triggered when a backend server for a given HAProxy server is down. | Count > 0 | Count < = 0 |
HAProxy - High Client (HTTP 4xx) Error Rate | This alert is triggered when there are too many HTTP requests (>5%) with a response status of 4xx. | Count > 0 | Count < = 0 |
HAProxy - High Server (HTTP 5xx) Error Rate | This alert fires when there are too many HTTP requests (>5%) with a response status of 5xx. | Count > 0 | Count < = 0 |
Additional resources
- Blog: Everything you need to know about HAProxy log format
- App description: HAProxy App for Sumo Logic