Manage Organizations for MSSPs - Cloud SIEM
This article describes how to manage Cloud SIEM rules and rule tuning expressions in organizations for Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs). MSSP administrators must ensure that the content of their child organizations is properly configured. MSSPs often consist of a parent organization with child organizations that use Cloud SIEM.
Considerations
Roles
You must have the following organization role capabilities to create and manage organizations as an MSSP administrator:
- Organizations
- View Organizations
- Create Organizations
- Manage Organizations
Multi-insights list page in Cloud SIEM
If you are logged in to a parent organization with child organizations that also use Cloud SIEM, the insights list page in Cloud SIEM allows you to view insights in child organizations.
Manage Cloud SIEM rules
To ensure that content is consistent across child organizations, use the Manage Content tab to push content in target organizations with content from a source organization.
You can push the following:
- Cloud SIEM rules
- Cloud SIEM rule tuning expressions
- New UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, select Organizations. You can also click the Go To... menu at the top of the screen and select Organizations.
Classic UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, select Administration > Organizations. - Select the Manage Content tab.
- In the Source Org field, select the organization that will provide the source data to be pushed in other organizations.
- In the Content bar, select the content to be pushed:
- Cloud SIEM Rules. For more information about Cloud SIEM rules, refer to Cloud SIEM Rules.
- Cloud SIEM Rule Tuning. For more information about Cloud SIEM rule tuning expressions, refer to Rule Tuning Expressions.
- Select individual items to be pushed, or all items.
- Click Push to Orgs.
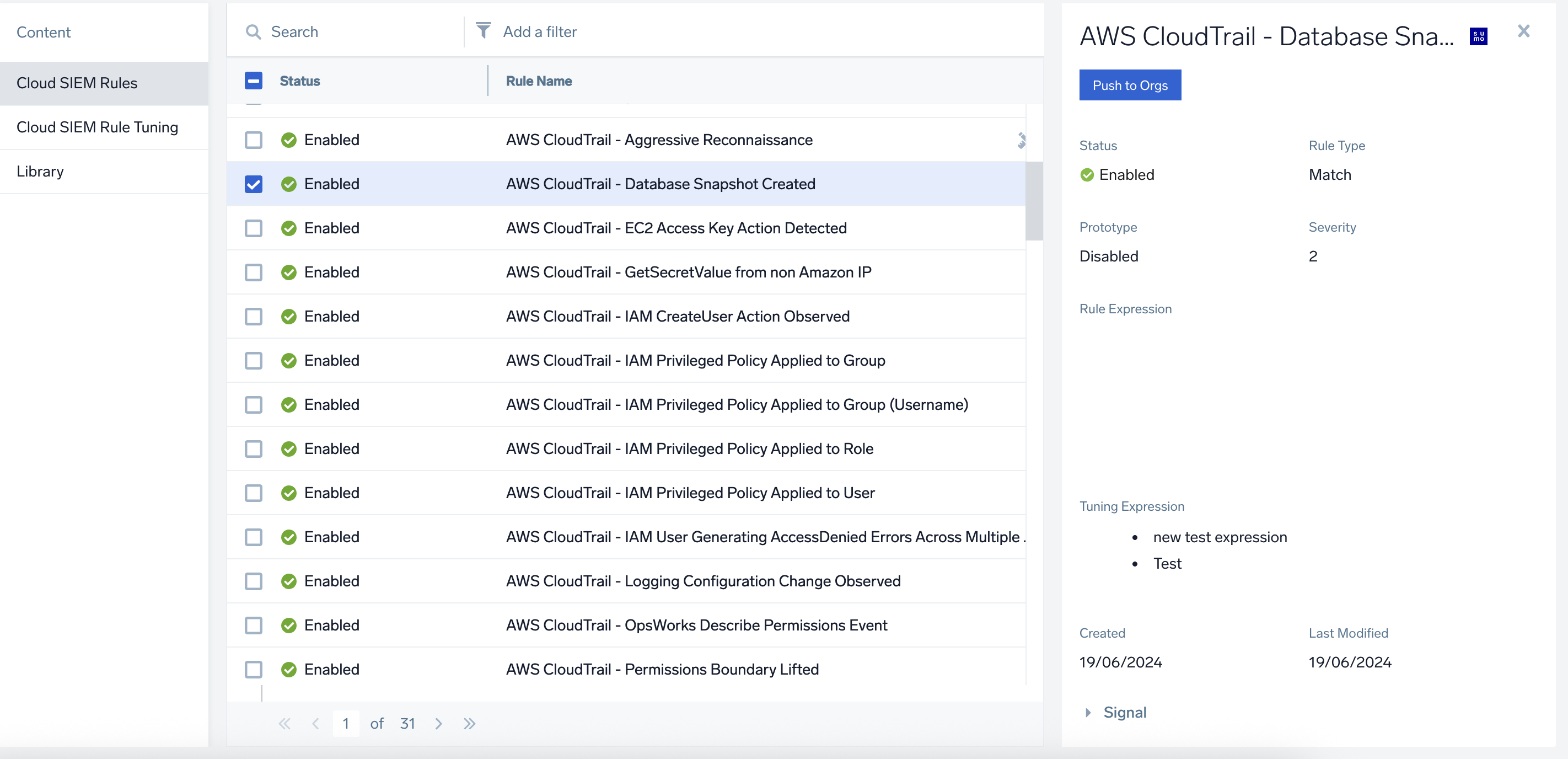
- On the Push Selected Items box, navigate to the Destinations section to select the organizations to push the selected items to. You can push to all organizations, a single child organization, or multiple child organizations.
- Click Push. A Pushing in progress dialog is displayed.
Tips
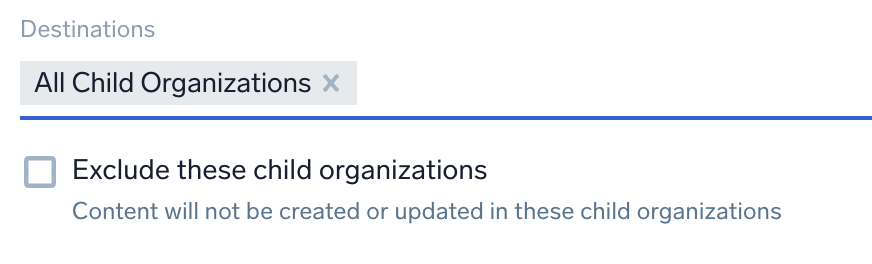
- If you select All Child Organizations, you can then select organizations to exclude, allowing you to push to all organizations except those you select:
- When you push rule tuning expressions, select Include Associated Cloud SIEM Rules to push all the Cloud SIEM rules that the expressions are used on:

Limitations
- If an item with the same name exists in the target organization, it will be replaced.
- Once a push is initiated, it cannot be reversed. Administrators should carefully review their selections before updating.
- If errors occur during the push, administrators must manually re-attempt the failed push. To see failed pushes, use View History.
- Push operations may take longer based on the volume of content being pushed.
- Rule tuning expressions must be pushed separately from rules.
- Cloud SIEM Legacy Rule Type is not supported for sync or push.
View history
- Click View History in the upper-right corner of the page. A query for push history displays:
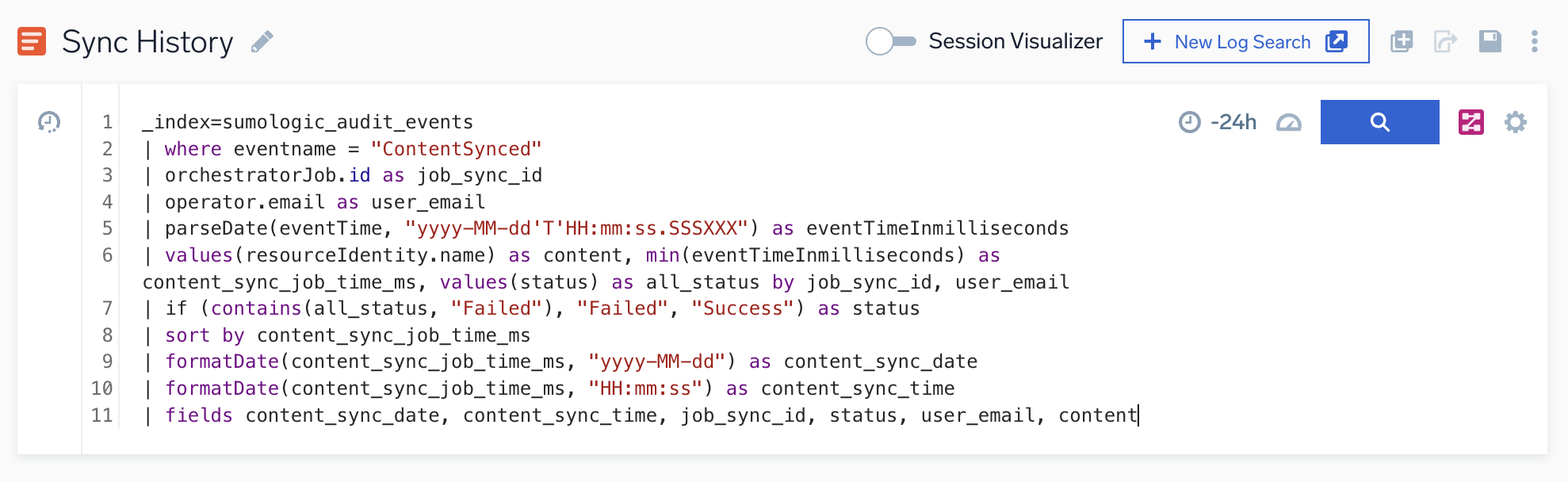
- Click the search button.

The push history displays. The email of the individual who performed the push appears in the user_email column, and the pushed items appear in the content column.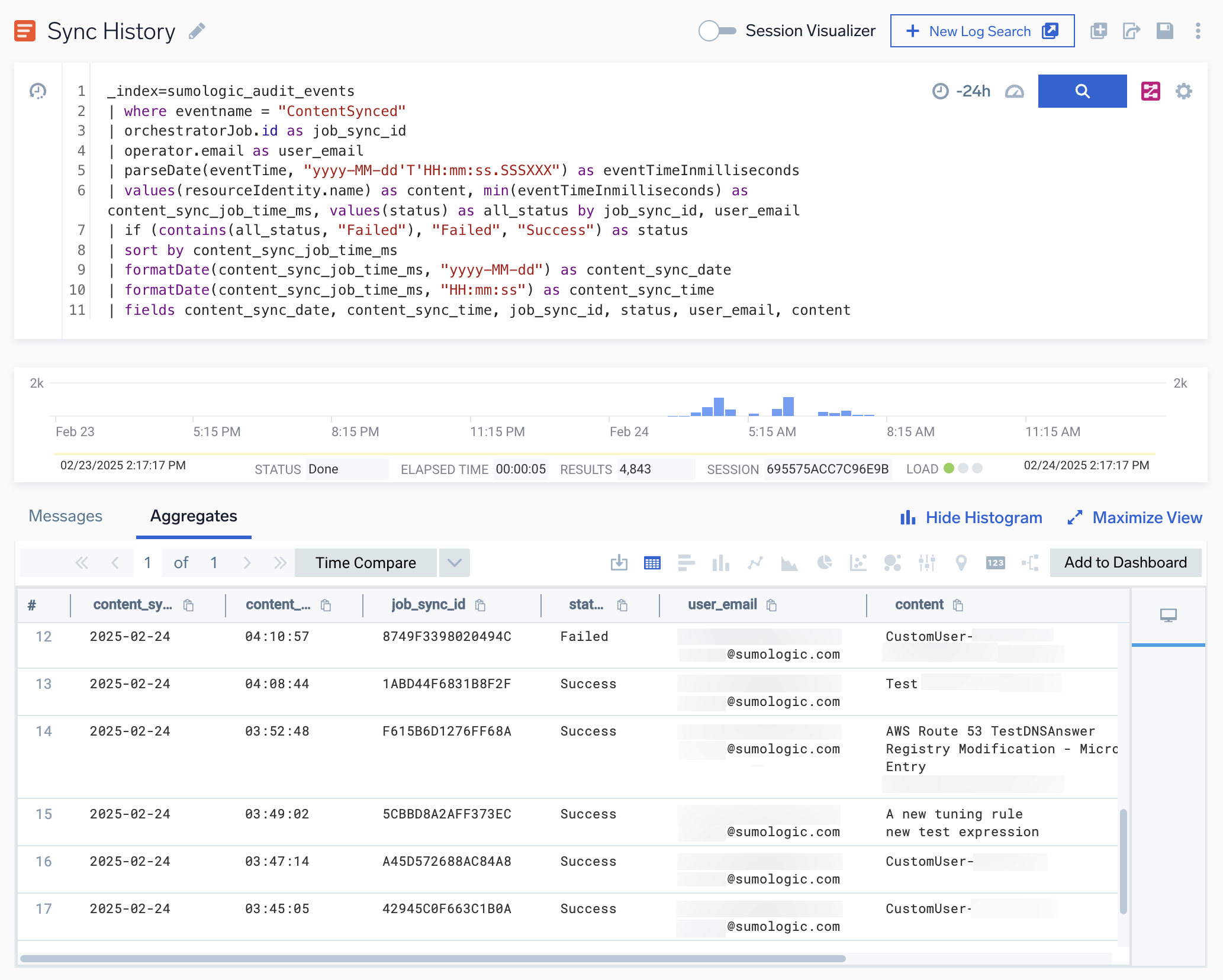
- Investigate any push that failed and re-run the push if needed.
View push in the audit log
You can view all content management push in the Audit Event Index by using the following query:
_index=sumologic_audit_events
| where eventname = "ContentSynced"
To see the results displayed the same as in View History, use the following query:
_index=sumologic_audit_events
| where eventname = "ContentSynced"
| orchestratorJob.id as job_sync_id
| operator.email as user_email
| parseDate(eventTime, "yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX") as eventTimeInmilliseconds
| values(resourceIdentity.name) as content, values(resourceIdentity.type) as content_type, min(eventTimeInmilliseconds) as content_sync_job_time_ms, values(status) as all_status by job_sync_id, user_email
| if (contains(all_status, "Failed"), "Failed", "Success") as status
| sort by content_sync_job_time_ms
| formatDate(content_sync_job_time_ms, "yyyy-MM-dd") as content_sync_date
| formatDate(content_sync_job_time_ms, "HH:mm:ss") as content_sync_time
| fields content_sync_date, content_sync_time, job_sync_id, status, user_email, content_type, content
FAQs
- What happens when an item with the same name already exists?
It will be replaced in the child organization. - What happens if an item selected for push doesn't already exist in the target organization?
The item will be created in the target organization. - What if errors occur during pushing?
Affected items will be skipped. Once the rest of the content is pushed, you can review errors in View History and retry. - Can I roll back changes after a push operation?
No, rollback is not supported. After a push operation is initiated, changes cannot be reversed. - How can I monitor push progress?
During a push, the system displays real-time status, including progress tracking, success or failure messages, and error logs. - How can I view push history?
Click View History in the upper-right corner of the page. A query for push history will display, showing the email of the individual who performed the push and the pushed items. - Who can I contact for additional questions or support?
Reach out to your Sumo Logic representative with any questions, issues, or feedback.
Pushing Cloud SIEM Rules
Are rule tuning expressions included?
No, they are not included, but can be pushed separately.
Pushing Cloud SIEM Rule tuning expressions
- What happens if the source tuning expression contains Cloud SIEM rules?
If the Include Linked Cloud SIEM Rules option is selected, existing rules with the same name in the destination organization will be linked to match the source tuning expression. - What if no matching Cloud SIEM rules are found in the destination organization?
Push will complete with a warning, and missing rules will be logged in the audit log. You can push those rules separately and re-run the tuning expression push.