Integrate Control Tower Accounts with AWS Observability
What is AWS Control Tower?
AWS Control Tower provides the easiest way to set up and govern a new, secure, multi-account AWS environment. With AWS Control Tower, you can provision new AWS accounts that are automatically set up so they conform to company policies and best practices in a few clicks.
For more information on AWS Control Tower, see AWS Control Tower on the AWS site.
Benefits of using the AWS Observability solution with Control Tower
The AWS Observability solution can be used with Control Tower-managed accounts to:
- Quickly identify and resolve issues in and across multiple accounts and services.
- Enable teams to seamlessly navigate and search logs and metrics data from across their AWS accounts, regions, and services. Unified service and account visibility greatly speeds troubleshooting and minimizes downtime to improve overall system availability.
- Eliminate data silos
- Unified logs and metrics data across AWS accounts and services eliminates data silos and makes it easier for teams to quickly identify root causes.
- Accelerate time-to-value
- Streamlined setup and pre-built dashboards provide instant insights into AWS accounts and services enabling visibility into the most important data out of the box.
For more information on the AWS Observability solution, see About AWS Observability.
Prerequisites
To integrate the AWS Observability solution with Control Tower, you collect CloudTrail audit logs from each AWS account that is managed by AWS Control Tower, and store the audit logs in a S3 bucket in a Log Archive AWS account.
We recommend you familiarize yourself with the AWS Observability Solution. For more information, see:
CloudTrail must be enabled for EventBridge to capture CreateManagedAccount, UpdateManagedAccount events, since these events are recorded and delivered through CloudTrail.
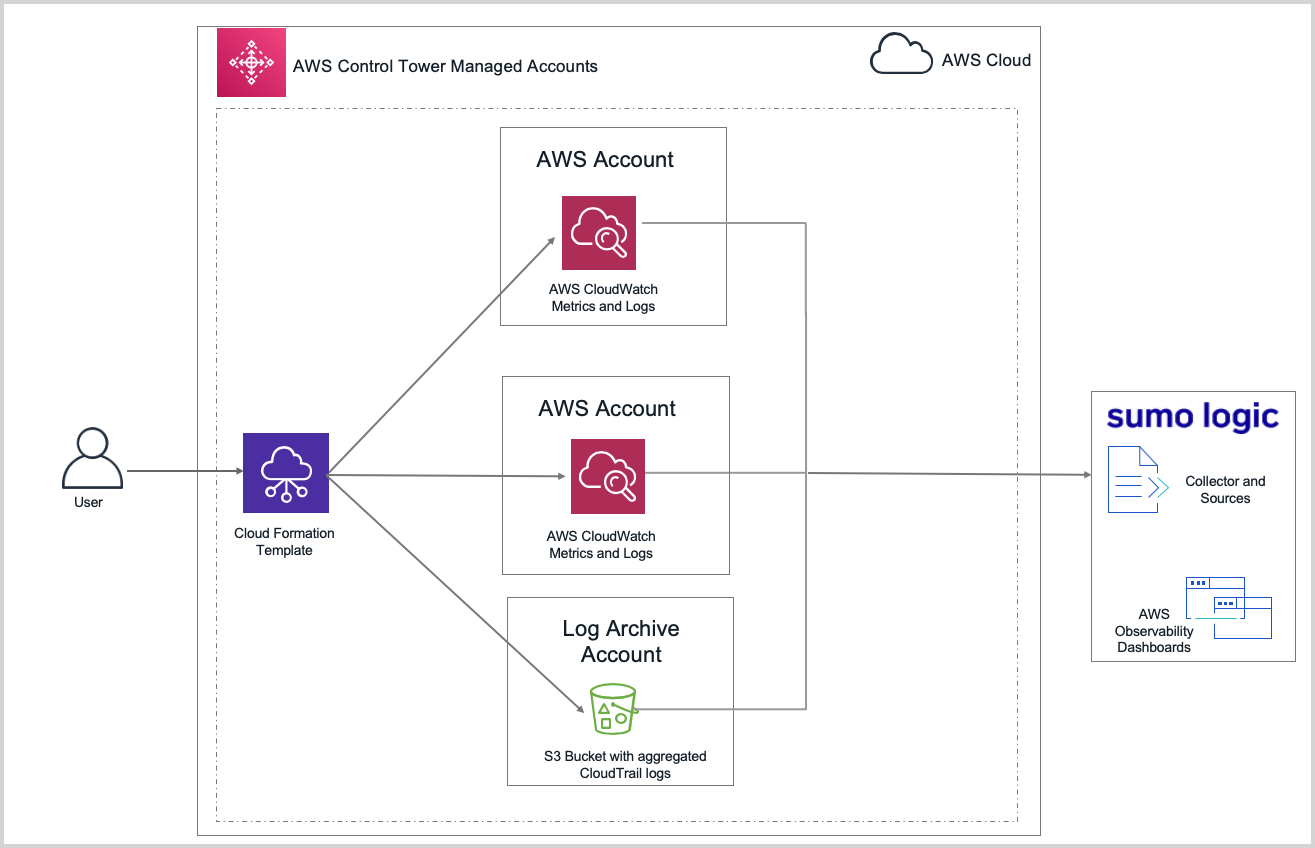
Integrate AWS Control Tower-managed accounts with the AWS Observability solution
Integrating with AWS Control Tower is a two-step process:
- Step 1: Set up collection for non-CloudTrail logs and all metrics by creating a CloudFormation stack in individual AWS accounts managed by Control Tower. In this step, you also install the apps in the Sumo Logic Observability app.
- Step 2: Set up collection of AWS CloudTrail logs that are aggregated from all Control Tower-managed accounts in a centralized log archive account.
- Step 3: Create a Field Extraction Rule (FER) that will tag logs with the account aliases you set up for each child account in the previous step.
Step 1: Set up collection from AWS accounts and install apps
In this step, you configure the collection of logs and metrics for all AWS accounts managed by Control Tower, and install the apps in the solution. To do so, follow these steps for each AWS account that is managed by AWS Control Tower.
-
Log in to the AWS Management Console as the AWS account user.
-
Follow steps 1 through 10 of the instructions in the Deploy AWS Observability to configure the AWS Observability CloudFormation template.
-
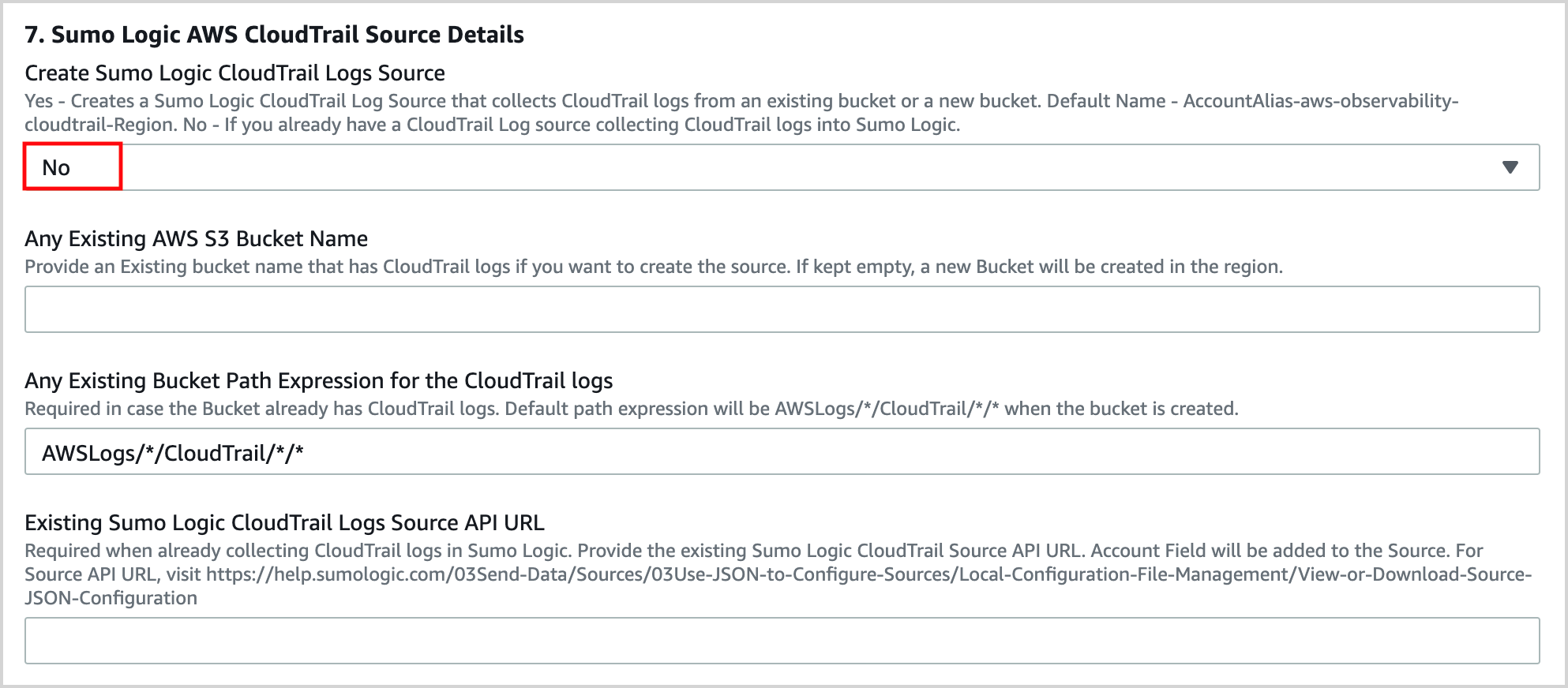
In the Sumo Logic AWS CloudTrail Source Details section of the template, select No for Create Sumo Logic CloudTrail Logs Source and keep the default values for all other options.
Step 2: Collect from the Log Archive account
In the instructions below, we assume the Log Archive AWS account is being used only for centralizing logs across AWS Control Tower-managed accounts. If this is not the case and you want to monitor AWS services in these accounts, follow the instructions in AWS Observability Solution to set up the relevant services.
-
Log in to the AWS Management Console as the Log Archive AWS account user.
-
steps 1 through 10 of the instructions in the Deploy AWS Observability to configure the AWS Observability CloudFormation template.
-
In the Sumo Logic Access Configuration section of the template, fill in as required by the template.
-
In the AWS Resources Tag Configuration section of the template, select None for Auto Enable Tagging and enter
logarchiveas the account alias. -
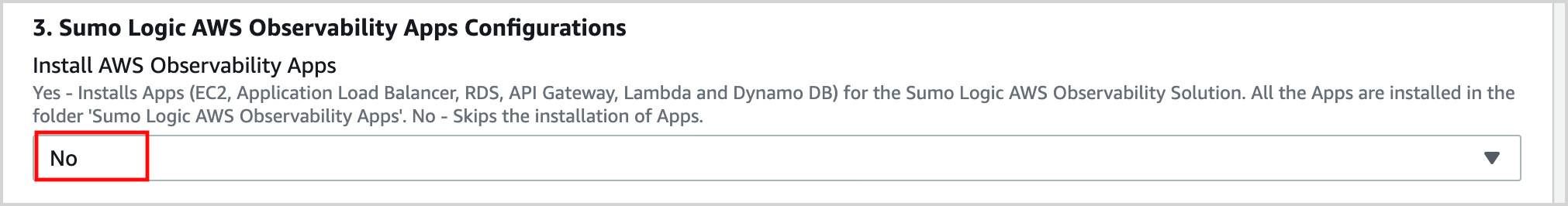
In the Sumo Logic AWS Observability Apps Configuration section of the template, select No for “Install AWS Observability Apps”, as they were installed in Step 1, above.
-
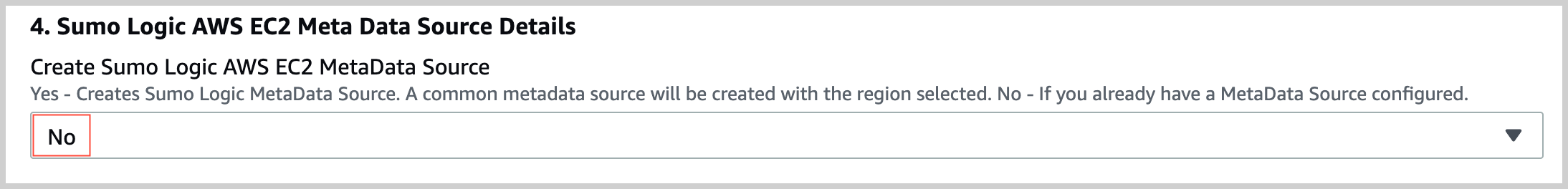
In the Sumo Logic AWS EC2 Meta Data Source Details section of the template, select No for Create Sumo Logic AWS EC2 MetaData Source.
-
In the Sumo Logic AWS CloudWatch Metrics and Inventory Source Details section of the template, select None for Select the Sumo Logic Metrics Sources to create, and leave the other options blank.
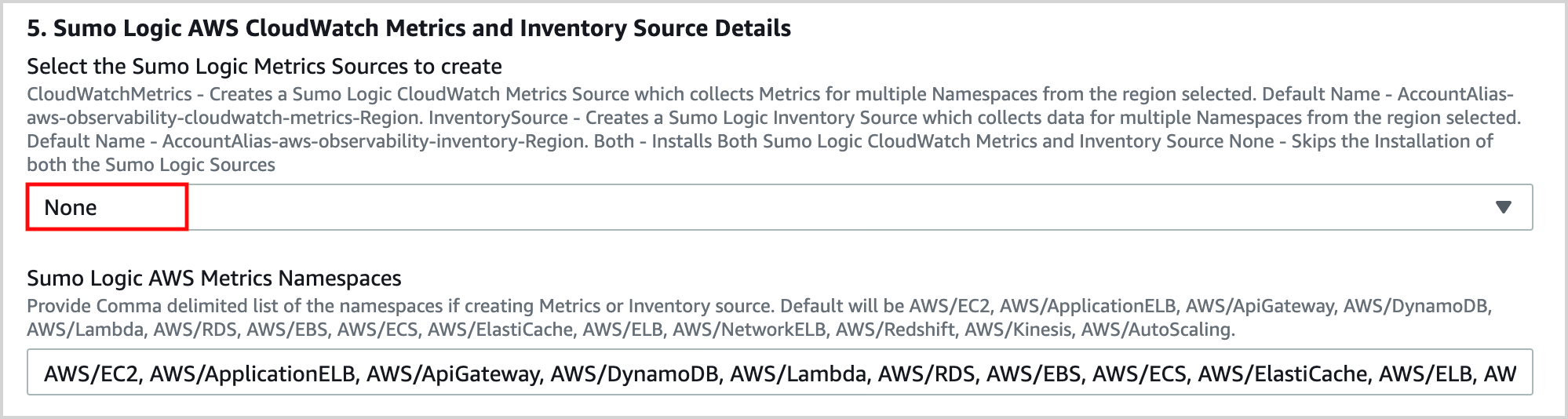
-
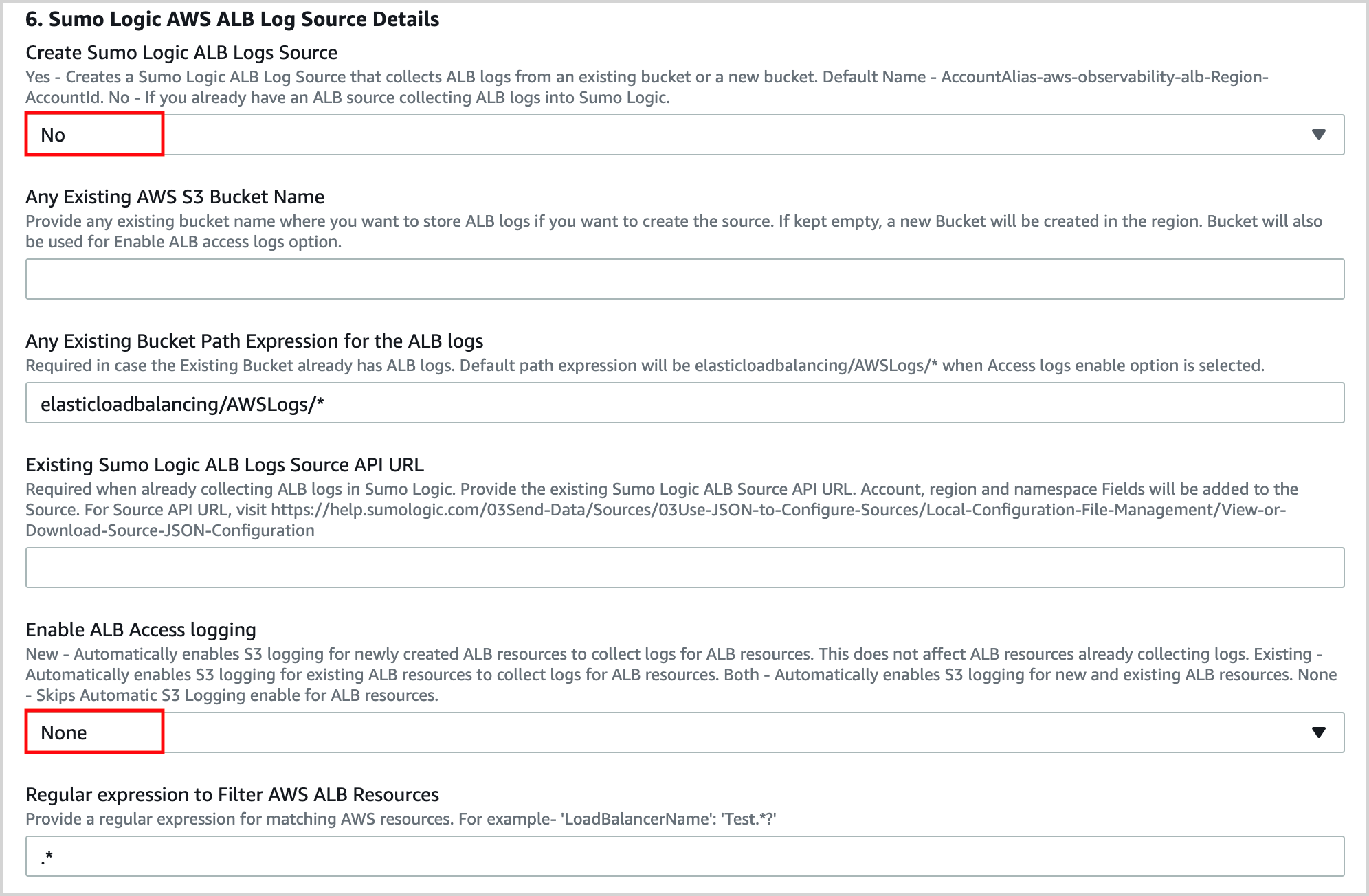
In the Sumo Logic AWS ALB Log Source Details section of the template:
-
Select No for Create Sumo Logic ALB Logs Source.
-
Select No for Enable ALB Access logging.
-
Keep the default values for all the other options.
-
-
In the Sumo Logic AWS CloudTrail Source Details section of the template:
Case 1: Set up Sumo Logic CloudTrail Source to collect data in Sumo Logic.
- Select Yes for Create Sumo Logic CloudTrail Logs Source.
- Enter the name of the CloudTrail Bucket in Any Existing AWS S3 Bucket Name.
- Provide apath expression for the Logs in “Any Existing Bucket Path Expression for the CloudTrail logs.
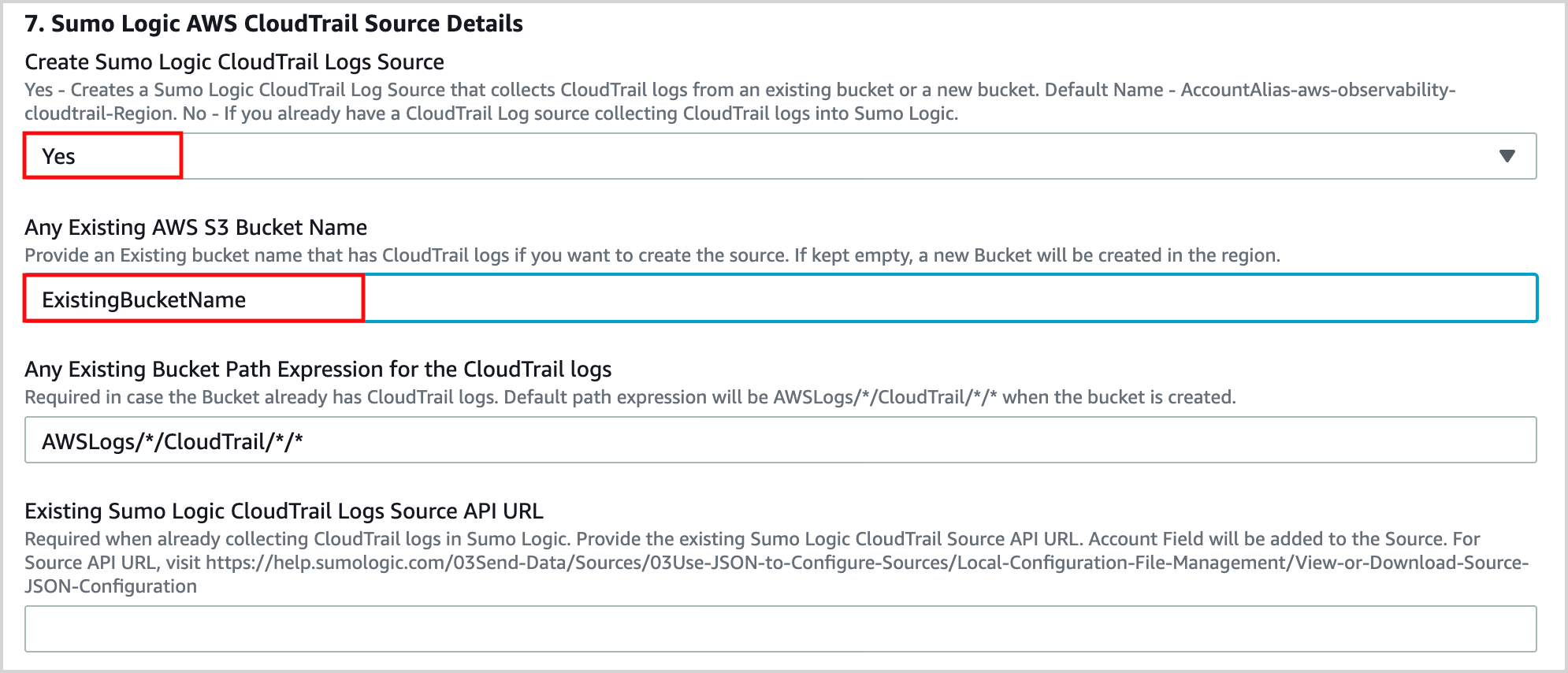
Case 2 : Already collecting CloudTrail Data in Sumo Logic
- Select No for Create Sumo Logic CloudTrail Logs Source and keep the default values for all the other options.
-
In the Sumo Logic AWS Lambda CloudWatch Logs Details section of the template:
- Select No for Create Sumo Logic CloudWatch Logs Source if you don’t plan to collect CloudWatch logs from this account.
- If you want to monitor Lambda CloudWatchALB logs, fill in the details required by the template.
-
Run through the prompts and click Create the stack.
Step 3: Create Field Extraction Rule
In this step, you create a Field Extraction Rule (FER) that will tag logs with the account aliases you set up for each child account in the previous step.
You must have a role that grants you the Manage Field Extractions capability to create an FER.
-
Log in to the Sumo Logic web UI and and follow the instructions in Create a Field Extraction Rule using the following values:
-
Rule Name. AWS Accounts
-
Applied At. Ingest Time
-
Scope. Specific Data
-
Metadata. _sourceCategory
-
Value. aws/observability/cloudtrail/logs
-
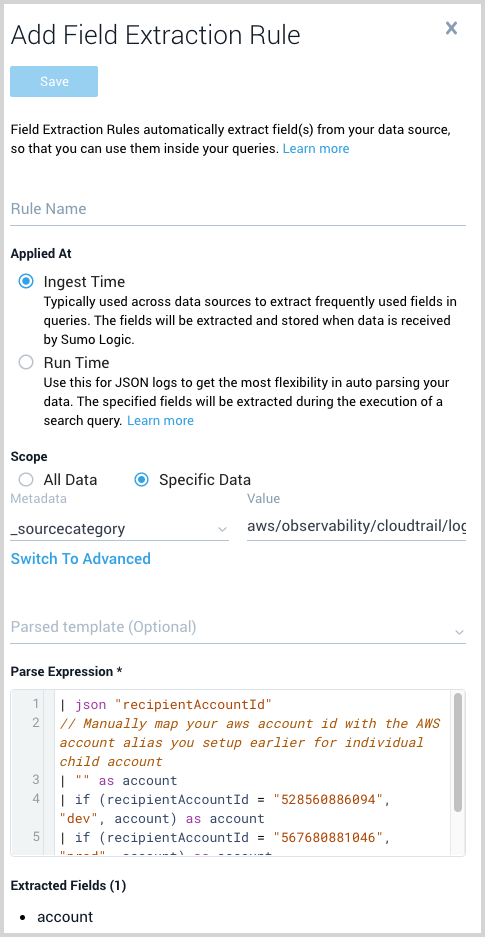
Parse Expression. Enter a parse expression to create an “account” field that maps to the alias you set for each child account in the previous step. For example, if you used the “dev” alias for an AWS account with ID "528560886094" and the “prod” alias for an AWS account with ID "567680881046", your parse expression would look like:
| json "recipientAccountId"
// Manually map your aws account id with the AWS account alias you setup earlier for individual child account
| "" as account
| if (recipientAccountId = "528560886094", "dev", account) as account
| if (recipientAccountId = "567680881046", "prod", account) as account
| fields account
This screenshot shows what this would look in Sumo Logic:
-
Step 4: View the AWS Observability dashboards
Now you can start monitoring your AWS services in AWS Control Tower managed accounts. For information about the solution dashboards, see View the AWS Observability Dashboards.