Sumo Logic Notifications By Microsoft

Version: 1.0
Updated: Dec 04, 2024
Integration with Sumo Logic platform for monitors and Microsoft (Outlook) notification.
Actions
- Assess Alert Status (Scheduled) - Periodically monitor status of a Sumo Logic alert and notify a Outlook user about an unresolved alert.
Sumo Logic Notifications By Microsoft configuration
Register an application
Registering your application establishes a trust relationship between your app and the Microsoft identity platform. The trust is unidirectional: your app trusts the Microsoft identity platform, and not the other way around.
Follow these steps to create the app registration:
- Sign in to the Azure portal.
- If you have access to multiple tenants, use the Directory + subscription filter
 in the top menu to select the tenant in which you want to register an application.
in the top menu to select the tenant in which you want to register an application. - Search for and select the Azure Active Directory.
- Under Manage, select App registrations > New registration.
- Enter a Name for your application. Users of your app might see this name, and you can change it later.
- Select Register to complete the initial app registration.
- Don't enter anything for Redirect URI (optional).
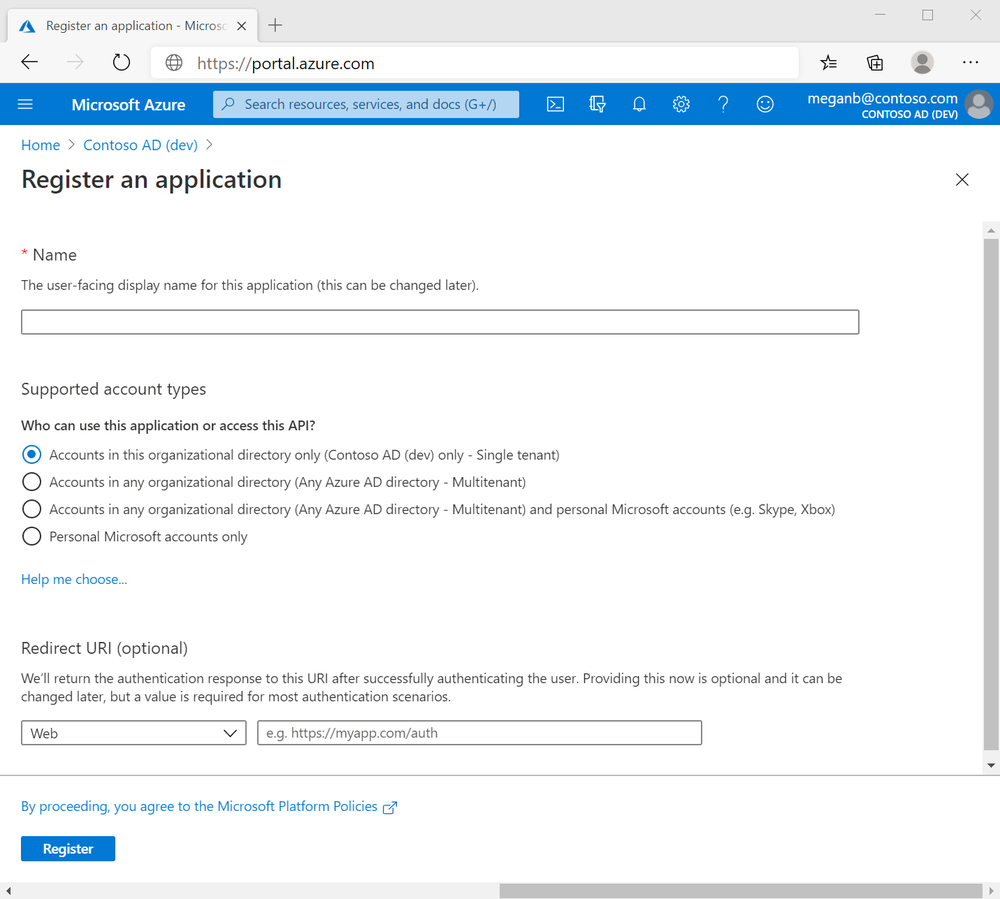
When registration completes, the Azure portal displays the app registration's Overview pane, which includes its Application (client) ID. Also referred to as just client ID, this value uniquely identifies your application in the Microsoft identity platform.
The client ID as one aspect in validating the security tokens it receives from the identity platform.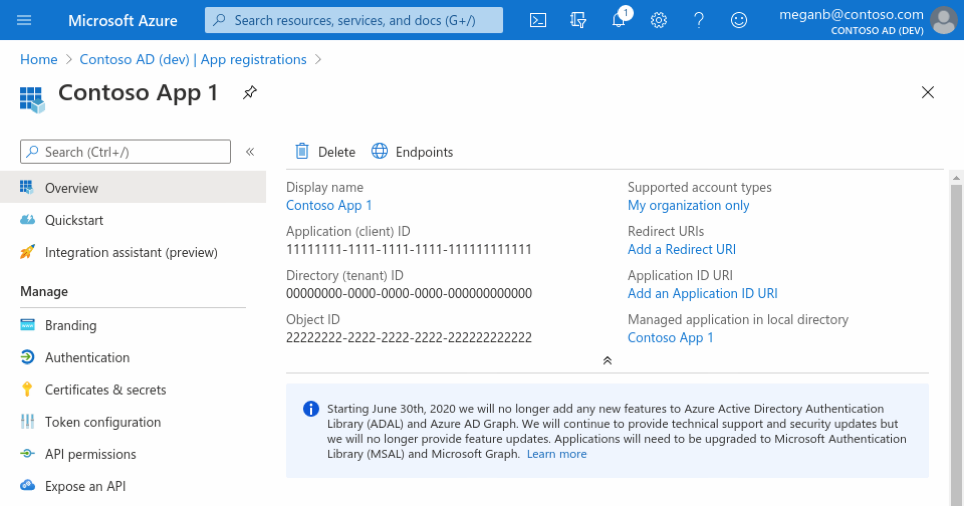
Add credentials
Credentials are used by confidential client applications that access an API. Examples of confidential clients are web apps, or service- and daemon-type applications. Credentials allow your application to authenticate as itself, requiring no interaction from a user at runtime.
You can add client secrets (a string) as credentials to your confidential client app registration.
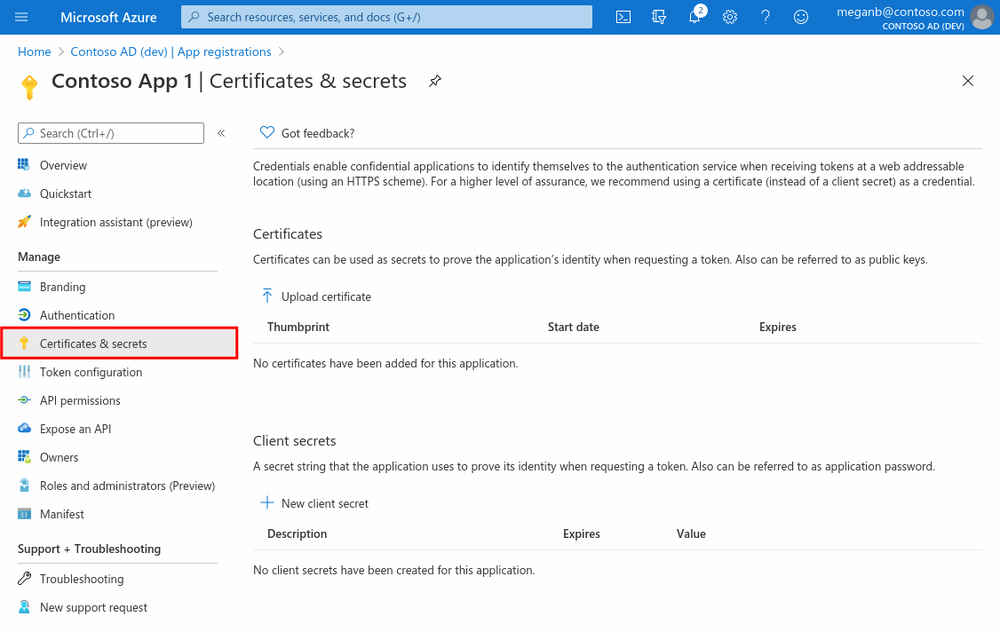
Add a client secret
The client secret, known also as an application password, is a string value of your app.
- Select your application in App registrations in the Azure portal.
- Select Certificates & secrets > New client secret.
- Add a description for your client secret.
- Select a duration.
- Click Add.
- Record the secret's value for use in your client application code - it's never displayed again after you leave this page.
Add permissions to API
- Select your application in App registrations in the Azure portal.
- Select API permissions > Add a permission.
- Delegated permissions are selected by default. Delegated permissions are appropriate for client apps that access an API as the signed-in user, and whose access should be restricted to the permissions you select in the next step.
- Application permissions are for service- or daemon-type applications that need to access API as themselves, without user interaction for sign-in or consent. Unless you've defined application roles for your API.
- Select Add a permission, and add the following permissions (as shown in the screenshot).
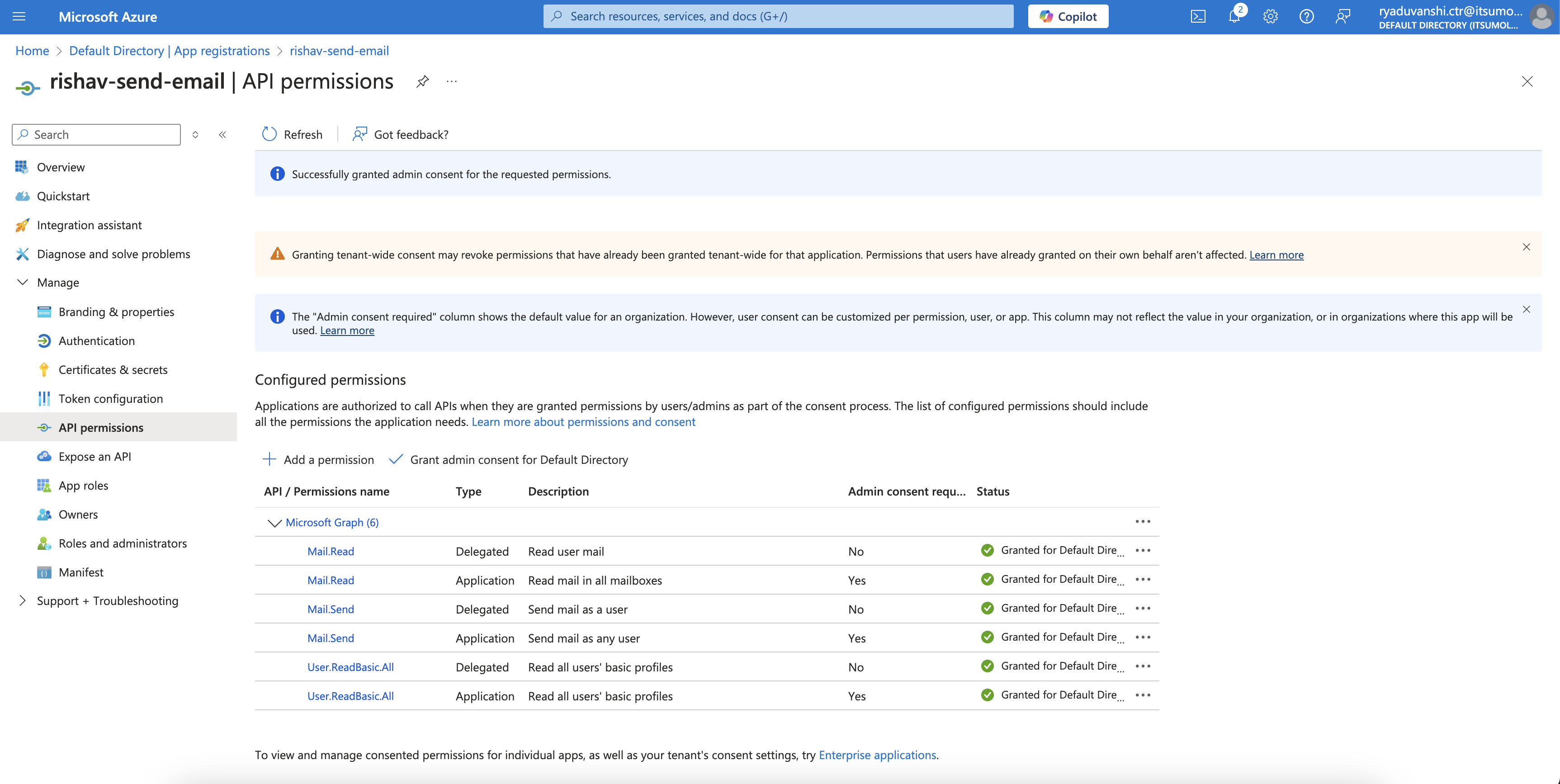
EWS API to be configured for these permissions
Applications are authorized to call APIs when they are granted permissions by users/admins as part of the consent process. The list of configured permissions should include all the permissions the application needs.
API / Permissions
Microsoft Graph (7)
- Mail.Read
- Type: Delegated
- Description: Read user mail
- Admin: -
- Mail.Read
- Type: Application
- Description: Read mail in all mailboxes
- Admin: Yes
- Mail.Send
- Type: Delegated
- Description: Send mail as a user
- Admin: Yes
- Mail.Send
- Type: Application
- Description: Send mail as any user
- Admin: Yes
- User.ReadBasic.All
- Type: Delegated
- Description: Read basic profiles of all users
- Admin: Yes
- User.ReadBasic.All
- Type: Application
- Description: Read basic profiles of all users
- Admin: Yes
Create an access key in Sumo Logic
- In the main Sumo Logic menu, select your username and then Preferences.
- From the preferences screen, in the section My Access Keys, click Add Access Key.

- Populate the name and click Create Key.
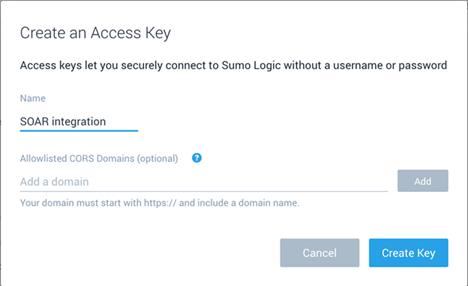
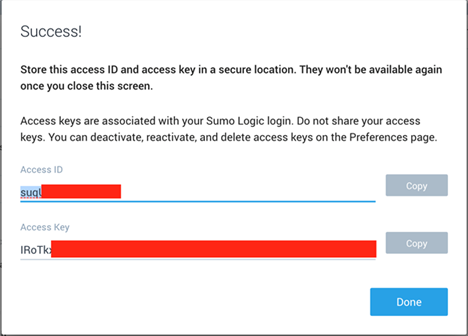
- Copy the Access ID and Access Key and store them (temporally) into a text editor.
note
They won't be available again once you close this screen.
- Click Done after you copied the Access ID and Access Key.
Configure Sumo Logic Notifications by Microsoft in Automation Service and Cloud SOAR
Before you can use this automation integration, you must configure its authentication settings so that the product you're integrating with can communicate with Sumo Logic. For general guidance, see Configure Authentication for Automation Integrations.
How to open the integration's configuration dialog
- Access App Central and install the integration. (You can configure at installation, or after installation with the following steps.)
- Go to the Integrations page.
Classic UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, select Automation and then select Integrations in the left nav bar.
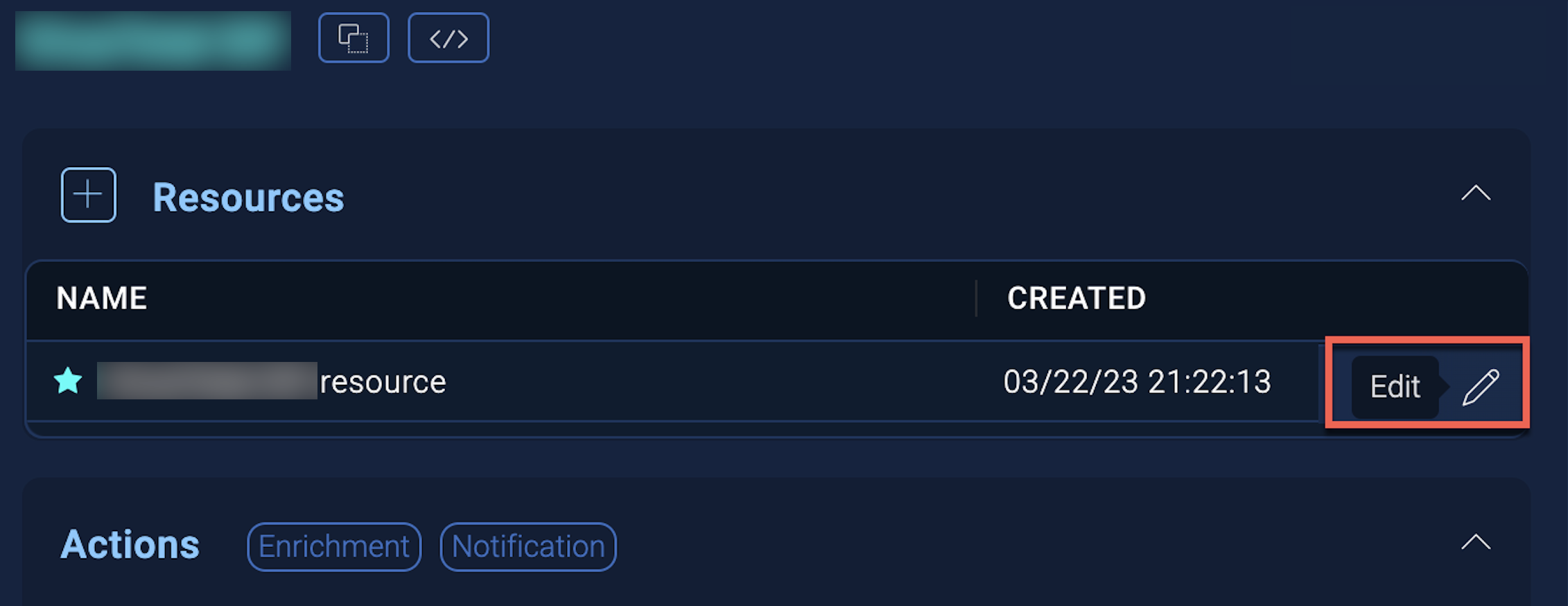
New UI. In the main Sumo Logic menu, select Automation > Integrations. You can also click the Go To... menu at the top of the screen and select Integrations. - Select the installed integration.
- Hover over the resource name and click the Edit button that appears.
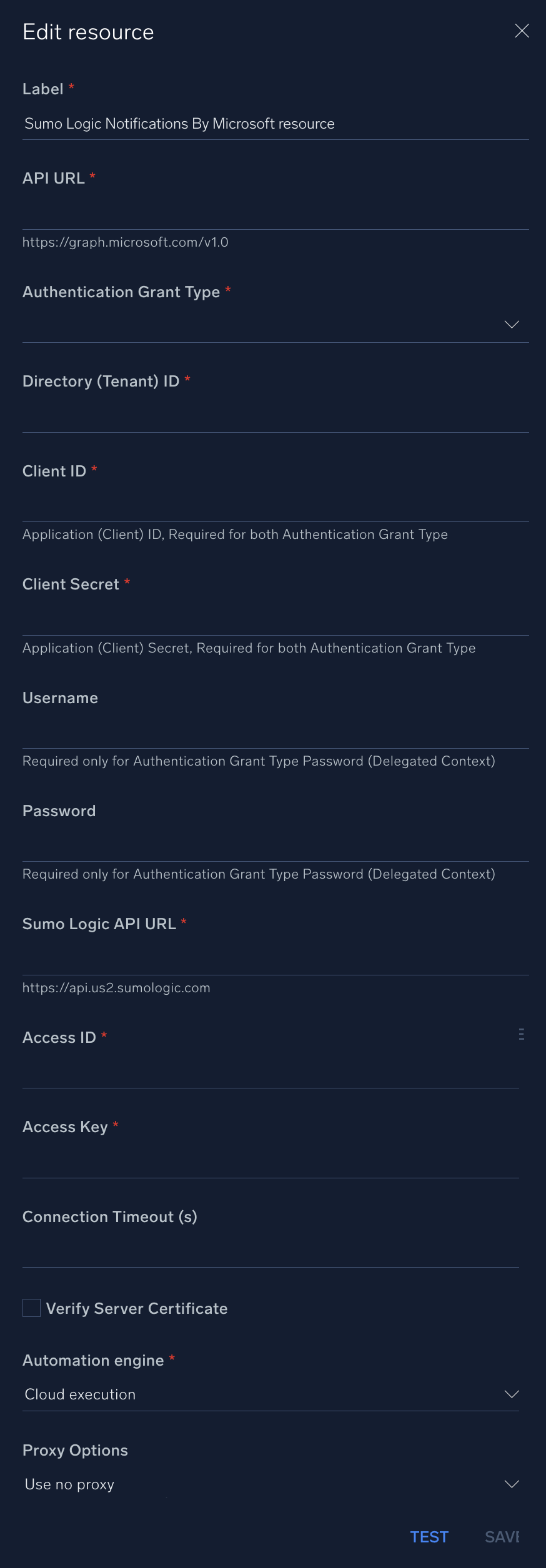
In the configuration dialog, enter information from the product you're integrating with. When done, click TEST to test the configuration, and click SAVE to save the configuration:
-
Label. Enter the name you want to use for the resource.
-
API URL. Enter your API URL for Microsoft, for example,
https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0. -
Authentication Grant Type. Choose one of the following according to the permissions you add to your app:
- Password (Delegated Context)
- Client Credentials (Application Context)
-
Directory (Tenant) ID. Enter the tenant ID of the AAD directory in which you created the application. (You can check from your app registration page).
-
Client ID. Enter your application ID. (You can check from your app registration page). This is required for both authentication grant types.
-
Client Secret. Enter your client secret. This is required for both authentication grant types.
-
Username. Enter the username of an admin user authorized to authenticate the integration. This is required only if you set the authentication grant type as Password (Delegated Context). Leave this field empty if you set the authentication grant type as Client Credentials (Application Context).
-
Password. Enter the password for the admin user. This is required only if you set the authentication grant type as Password (Delegated Context). Leave this field empty if you set the authentication grant type as Client Credentials (Application Context).
-
Sumo Logic API URL. Enter the API endpoint URL for your region (for example,
https://api.sumologic.com). -
Access ID. Enter the access ID for your Sumo Logic access key. Select Default as the scope when generating access keys.
-
Access Key. Enter the access key corresponding to your Sumo Logic access ID.
-
Connection Timeout (s). Set the maximum amount of time the integration will wait for a server's response before terminating the connection. Enter the connection timeout time in seconds (for example,
180). -
Verify Server Certificate. Select to validate the server’s SSL certificate.
-
Automation Engine. Select Cloud execution for this certified integration. Select a bridge option only for a custom integration. See Cloud or Bridge execution.
-
Proxy Options. Select whether to use a proxy. (Applies only if the automation engine uses a bridge instead of cloud execution.)
- Use no proxy. Communication runs on the bridge and does not use a proxy.
- Use default proxy. Use the default proxy for the bridge set up as described in Using a proxy.
- Use different proxy. Use your own proxy service. Provide the proxy URL and port number.
Change Log
- December 04, 2024 - First upload