About the Integration Framework
Integration file hierarchy
Integrations are defined using two types of text files. The first type, the integration definition file, is used to define the properties of the product which the integration connects. This includes information such as the name, logo, connection parameters, test code, and the Docker container used to execute the actions. One integration definition file is required for each integration and serves as a container for all the actions that the integration will perform.
The second type of file is an action definition file, which is used to define a single action that will be performed using the integration. Each integration action is defined in a separate action definition file, which will be associated with the appropriate integration definition. Action definition files are the files which contain the actual code which will be executed to perform the action. Supported languages include Perl, Python, PowerShell, and Bash. In addition to the action code, action definition files also contain information such as the name, required and optional fields, and the format in which the resulting information will be displayed.
The following diagram shows the integration file hierarchy:
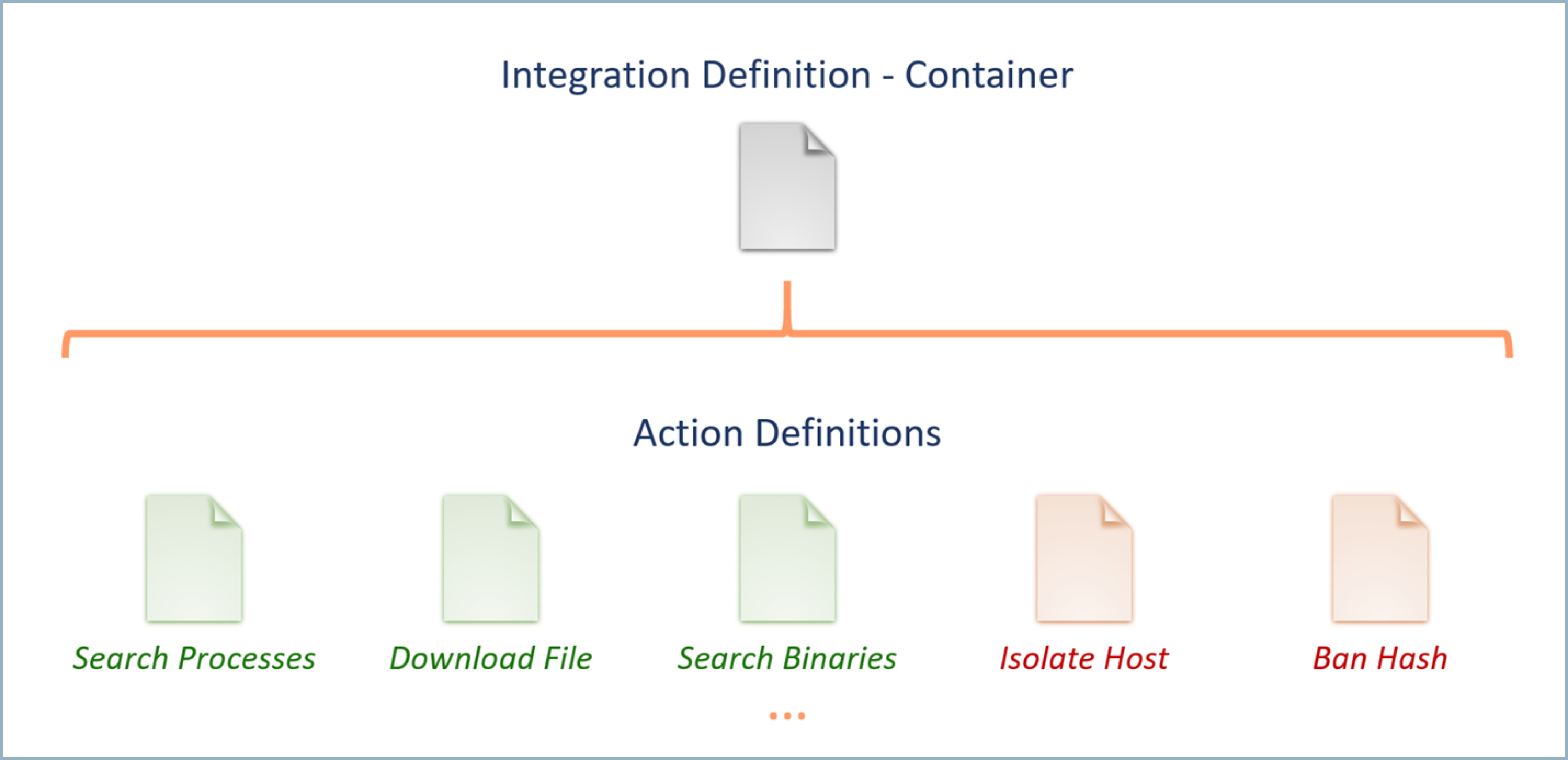
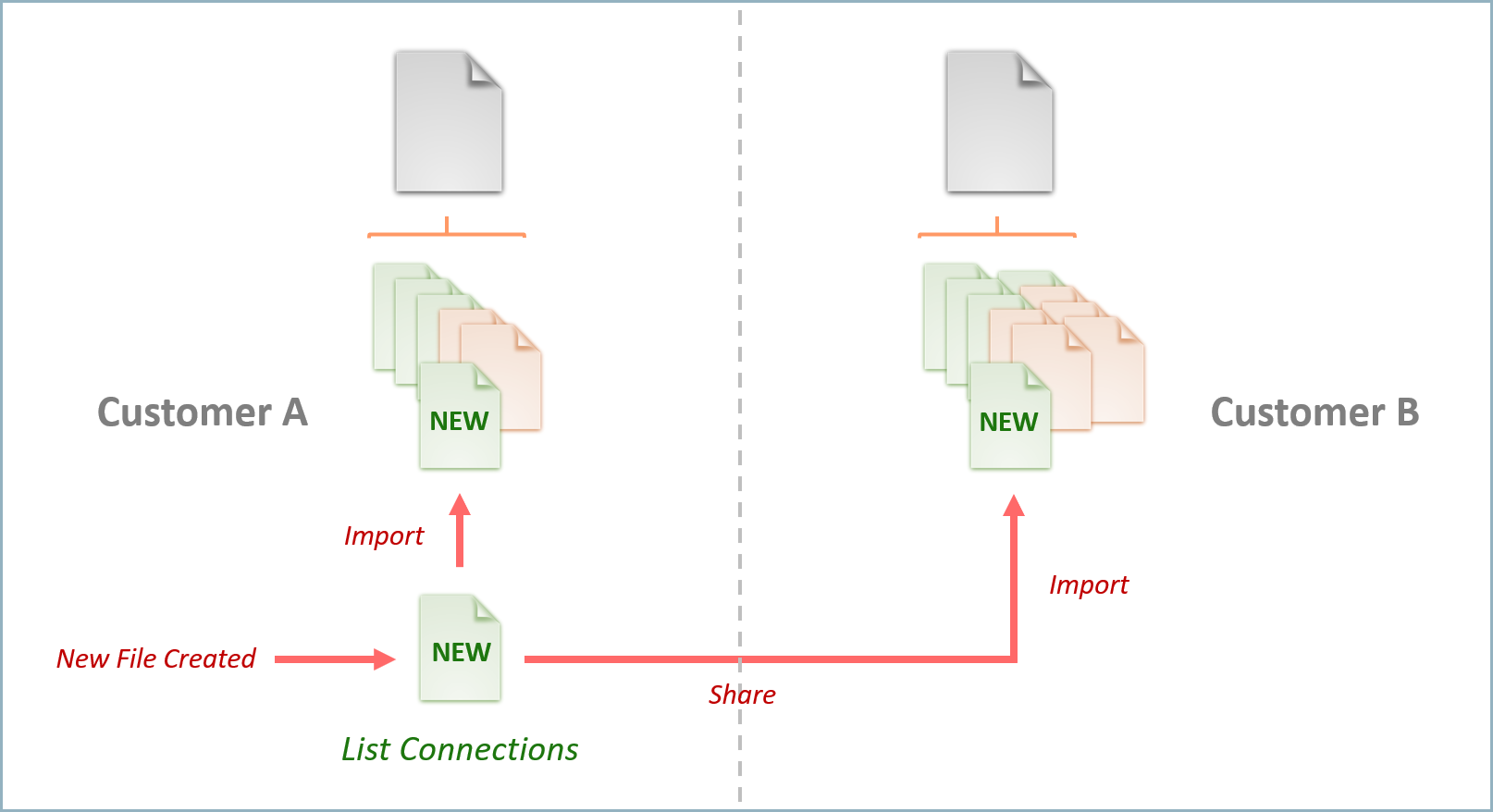
Defining integrations at the action level allows users have greater flexibility in customizing existing integrations and sharing new actions with other users. For example, you may choose to extend the existing RSA NetWitness integration to include an additional action which retrieves all network connections for a given host. Once you create this new action, you can easily add it to the existing RSA Netwitness integration by uploading the new integration action file.
You can also share this new action and use it to extend the functionality of the integration for others. The following diagram shows action file portability:
Integration framework file formats
Both the integration definition file and the action definition file are YAML files. The following sections highlight the formats for each file type. Example files contains samples of completed integration definition and action definition files as a reference. To see YAML files used in a working integration, see an example for Cloud SIEM in Advanced example: Configure a custom integration.
Integration definition file format
* Required fields
- name
*[String]: Name displayed in the UI. It must match theintegrationfield of each action definition file added to the integration. - official_name
*[String] (Cloud SOAR only): To modify the display name of an integration in the Cloud SOAR UI while ensuring the actions YAML remains valid, setofficial_name=OLD-NAMEandname=NEW-NAME. - version
*[String]: File version number. - icon
*[Base64 String]: Integration logo. - script
*:- type
*[String]: Indicates which code parser should be used to execute the code within the integration and action definition files. All action definition files for the integration must use the same code language as defined in the integration definition file. Acceptable values are:bashperlpowershellpython
- test_connection_code
*[String]: Code which can be used to test the integration through the UI by clicking on Test Saved Settings. Exiting with a value of0indicates success, while any other value will indicate failure.
- type
- docker_repo_tag
*[String]: Docker repository tag of the image build the new container is from. Can be from any local or remote repository configured on the server. - local_repo [Boolean] (Cloud SOAR only): Indicates that the Docker image is a local one and not one present in the repository.
- configuration
*:- testable_connection
*[Boolean]: Is test code present (true/false). - require_proxy_config
*[Boolean]: True/false value indicating whether a proxy configuration tab should be available in the UI for the integration. If the value is set to true and a proxy is configured in the UI, the parameterproxy_urlwill be passed to the code on execution as an environment variable. - data_attributes
*: Fields required for configuration.<field_name>*[String]: Name of field which will be passed to code as environment variable. One<field_name>attribute should be added for each configuration parameter that will be required to configure the integration. For example, if a URL, username, and password are required to connect to an integrated solution, the attributesconfiguration:data_attributes:url,configuration:data_attributes:user_name, andconfiguration:data_attributes:passwordshould be added with their appropriate sub-attributes. The<field_name>parameters will be passed to the code on execution.- label
*[String]: Label displayed in the UI. - type
*[String]: Type of field. Acceptable values are:checkboxlistnumberpasswordtexttextarea
- required
*[Boolean]: Is the field required (true/false). - validator [String]: Input validator type. Acceptable values are:
hostintegeripporturl
- default [String]: Default field value.
- values [String]: List of possible values for a list field in key:value format, where the key will be used as the input parameter and the value is what will be shown in the list. For example:
domain: Domainip: IP Addressurl: URL
In this example, if a user selected IP Address from the dropdown list, the valueipwould be passed to the parameter at runtime as an environment variable.
- label
- listing_attributes Configuration fields to show in the resource table.
<field_name>*[String]: Name of field which will be shown in the table.- name
*[String]: Name displayed in the column header.
- testable_connection
- signature [String]: Signature to indicate integration is the original one written by Sumo Logic.
Action definition file format
* Required fields
-
integration
*[String]: Name of integration. This should match thenamefield of the integration definition file for the integration. -
name
*[String]: Name of action which will be displayed in the UI. If the action name does not already exist, it will be added. However, for consistency and simplicity, it is recommended to use one of the existing names in the list of actions, such asip reputationorsystem info. -
type
*[String]: Type of action being performed. Acceptable values are:ContainmentCustomEnrichmentDaemon(Cloud SOAR only)NotificationTrigger(Cloud SOAR only)
-
script
*:- code
*[String]: Action code.
- code
-
fields
*:- id
*[String]: Name of field. One ID attribute should be added for each required or optional parameter that may be provided to the integration action at runtime. The name of the ID attribute will be passed as a environment variable to the code containing the dynamic value provided on execution. - label
*[String]: Label displayed in the UI. - type
*[String]: Type of field. Acceptable values are:checkboxdatetimefileDetonatelistmultilistnumbertagtexttextareaupload
- required
*[Boolean]: Is the field required (true/false). - validator
*[String]: Input validator type. Acceptable values are:datetimedomaine-mailhashintegeripaddressip_domainmd5portsha1sha256url
- default [String]: Default field value.
- values [String]: List of possible values for a list field in key:value format, where the key will be used as the input parameter and the value will be shown in the list. For example:
domain: Domainip: IP Addressurl: URL
In this example, if a user selected IP Address from the dropdown list, the valueipwould be passed to the parameter at runtime.
- incident_artifacts [Boolean]: Allow use of incident artifact values for the field (true/false). When set to
true, incident artifact values such assourceAddresscan be used as inputs for the field. - observables [String] (Cloud SOAR only): This field defines the link between the action and the observables (entity) section. Specifying an observable type here will cause the action to be displayed in the Actions menu for the specified entity type. Acceptable values are:
domainemailfileipaddressmd5sha1sha256urluserdetail
noteCloud SOAR automatically extracts observables from incidents content and converts them to entities (domain, email, file, IP address, hash values, URL, and user details). However, usernames are automatically converted into entities only if the input of an automatic action for users contains the observables statement and is also specified as
userdetail.
- id
-
output
*: Expected fields from results. -
path
*[String]: JSON path for each field which may be returned by the action, using the following JSON as an example:{ country: "US",
response_code: 1,
as_owner: "CloudFlare, Inc.",
detected_urls: {
url: "http://google.com/",
positives: 2
}}The following
output:pathattributes should be added:countryresponse_codeas_ownerdetected_urls.[].urldetected_urls.[].positives
Example with special characters
Use quotation marks [““] when there is a text with special character like a hyphen. Consider the following example JSON:{
"payload": {
"headers": {
"MIME-Version": "1.0",
"From": "Joe Smith <joe.smith@example.com>",
"Message-ID": "<193853.example.com>",
"Subject": "Account Verification Required",
"To": "verify@example.com",
"Content-Type": "multipart/mixed; boundary=\"0000008\""
}
}
}To correctly parse
"MIME-Version"in the example, use one of the following formats:payload.headers."MIME-Version"payload.headers.["MIME-Version"]
In addition to using quotation marks to enclose text with special characters, you must separate nested output fields with a period (.). Note that these formats will not parse correctly:
payload.headers["MIME-Version"]payload.headers[MIME-Version]
-
type
*[String]: Type of data returned. Reserved for future use. All outputs are treated as strings. -
table_view
*: Results to display in table view. The sub-attributes will define which field values returned by the integration will be displayed when viewing the results in table view.- display_name
*[String]: Column name. - value
*[String]: JSON path for each field which may be returned by the action. See theoutput:pathfield above for additional information. - type
*[String]: Type of value which is only possible to specify if the value should be shown as a link.
- display_name
-
use_in_triage [Boolean] (Cloud SOAR only): Action should be manually executable in triage event (default False).
-
hook [List] (Cloud SOAR only): A list of hooks used to fire trigger actions to interact with Cloud SOAR elements. For more information, see Trigger hooks. Valid values are:
addObservableArtifactaddObservableDomainaddObservableIpaddObservableMailaddObservableUrladdObservableUserDetailapproveTaskcloseTaskcreateTaskreassignTasktaskCustomActionupdateTaskdiscardEventgrabEventreassignEventcloseIncidentincidentCustomActionnewIncidentupdateIncidentwebhook
-
check_not_null_field [String] (Cloud SOAR only): For actions with the hook
incidentCustomActionandtaskCustomAction, specifies the internal name of the element field. It should be not null to show the button in the UI. -
src_doc
*[String]: Result path or raw output to take the entire output to show in html5 iframe sandboxed. -
url_preview
*[String]: Result path to show in html5 iframe sandboxed. -
image_base64_png(jpg)
*[String]: Result path of a base64 image png or jpg format. -
signature [String]: Signature to indicate action is the original one written by Sumo Logic. Not to be set by user.
-
exit_condition (Cloud SOAR only): Specify what condition system has to evaluate to decide if continue with next execution or to stop scheduled action and continue with playbook next actions.
- path
*[String]: Result path where to search in JSON structure astable_viewsection or specify an action's input i.e. input.path. - string
*[String\List[String]]: Result path of string to check if is equal to result value or an array of string or specify an action's input, for example,input.matchString.
- path
-
re-execution
*[String] (force) (Cloud SOAR only): By default if previous action run is not yet finished, next scheduled run is skipped. If you setre-execution: 'force', the previous run will be killed, stopping the Docker container. -
scheduled (Cloud SOAR only):
- every
*[String] format<int><interval type>: Time interval between one run and the next one (for example, 10m, 5d, etc.) or specify an action's input i.e. input.every:- d: DAYS
- h: HOURS
- m: MINUTES
- expire
*[String] format<int><interval type>: Time after the first run to stop scheduling or specify an action's input, for example,input.expire. The last result will be kept :- d: DAYS
- h: HOURS
- m: MINUTES
- every
Action parameters
For security reasons, all action parameters are passed to the Docker container as an environment variable, with the variable name equal to the ID specified in YAML. For Python code you can always use:
argparse.ArgumentParser()
But in that case, you have to specify a class to manage the environment variable:
class EnvDefault(argparse.Action):
def __init__(self, required=True, default=None, **kwargs):
envvar = kwargs.get("dest")
default = os.environ.get(envvar, default) if envvar in os.environ else default
required = False if required and default else required
super(EnvDefault, self).__init__(default=default, required=required,**kwargs)
def __call__(self, parser, namespace, values, option_string=None):
setattr(namespace, self.dest, values)
And you must add it into the action kwargs:
parser.add_argument('--host', help='host , REQUIRED', required=True, action=EnvDefault)
Otherwise, if you do not need extra utilities provided by ArgumentParser for validation, you can simply use:
host = os.environ.get("host", "localhost")
Working with integrations
All integrations are configured by navigating to Integrations in the UI.
Integration definitions
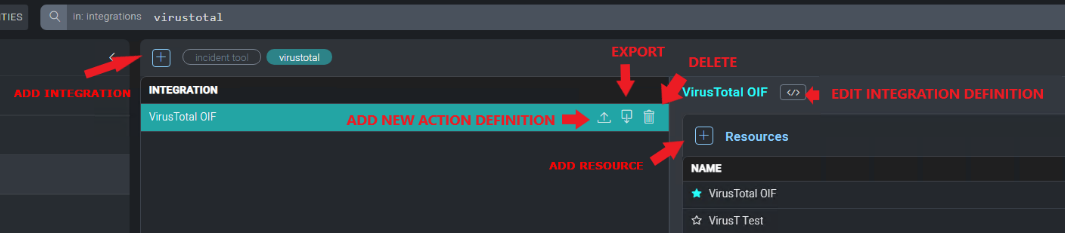
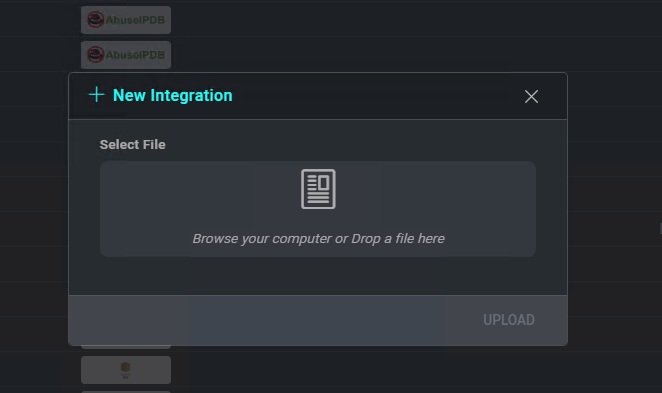
To add a new integration, click on the + icon on the Integrations page.
The New Integration window allows you to upload an integration definition file by clicking Select File. Once you define the integration definition file, click Save to add the new integration.
To edit an existing integration by uploading a new integration definition file , click on the Edit button. To export the integration definition file for the selected integration, click the Export icon.
Action definitions
To add a new action, select the appropriate integration from the integrations list, then click on the Upload button to the right of the integration.
The New Action window allows you to upload an action definition file by clicking Select File, and lets you select the kind of action.
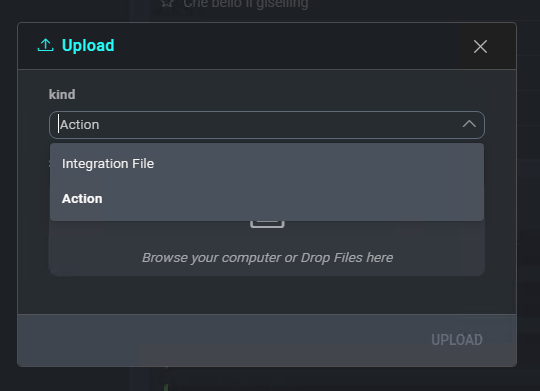
Once the action definition file has been selected, click Save to add the new action.
Existing actions may be edited by clicking the Upload button below the action name to upload a new action definition file, or by clicking the Edit button below the action name to open a text editor and edit the action directly.
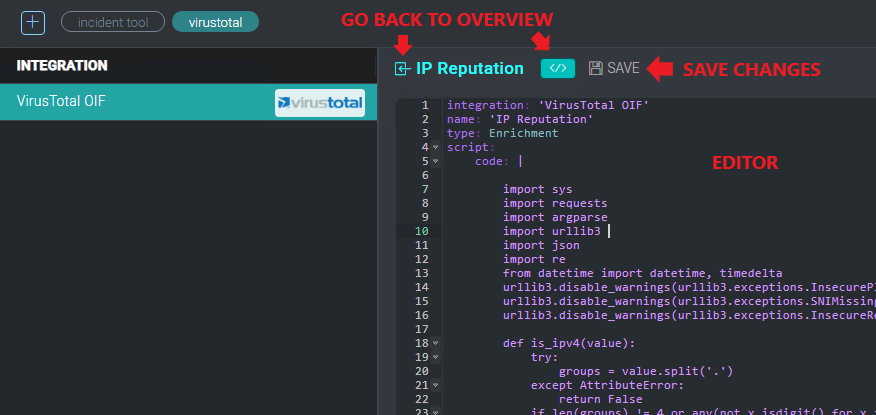
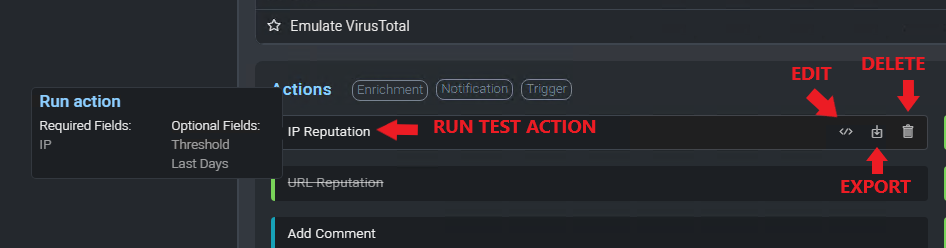
To test an action, click on the Test Action button below the action name.
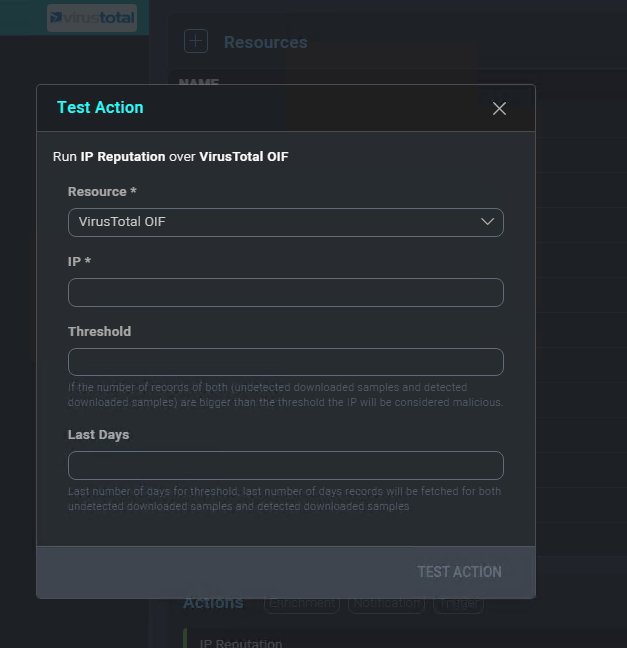
Enter the required parameters and click Test Action.
To export an action, click on the Export button below the action name.
Action definitions for Cloud SOAR
The following action definitions are for Cloud SOAR only.
Daemon action definitions
Uploading an action YAML file with type Daemon allows you to specify Daemon action. You can also define rules associated with Daemon.
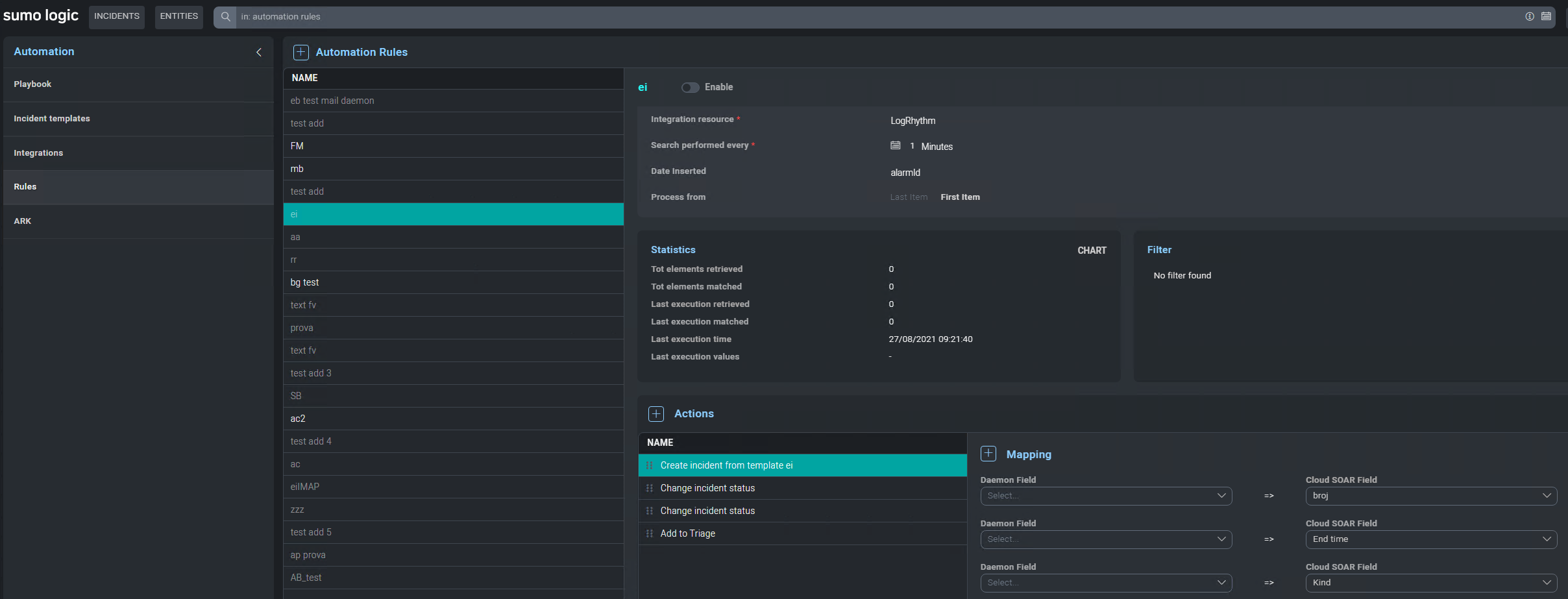
Daemon action must return an array of objects in JSON format:
[{ 'a': 'a1', 'b': 'b1' }, { 'a': 'a2', 'b': 'b2' }]
Every object is processed by filter and action. It is also possible to define which output field should be passed to the next script run and an extra param key value pair to specialize each rule:
All available actions are:
- Create incident from template
- Update incident
- Close Incident
- Change incident status
- Add events to an existing incident
- Change task progress
- Close task
- Add to Triage
Scheduled action definitions
A Scheduled action represents a particular type of action when the execution is iterated until a specific exit condition is met. This type of action permits you to create loops in a playbook.
YAML example:
integration: 'Incident tools'
name: 'intervallo date loop'
type: Scheduled
script:
code: |
[......]
exit_condition:
- path: 'exit_condition'
string: 'false'
re-execution: 'force'
scheduled:
- every: '10s'
expire: '120s'
output:
- path : 'exit_condition'
Or using strings array:
integration: 'Incident tools'
name: 'intervallo date loop'
type: Scheduled
script:
code: |
[......]
exit_condition:
- path: 'exit_condition'
string:
- 'Open'
- 'Pending'
- 'Waiting'
re-execution: 'force'
scheduled:
- every: '10s'
expire: '120s'
output:
- path : 'exit_condition'
Or using action's input:
If you use an action's input, this input field should be required = true*.
integration: 'Testing Purpose'
name: 'testing Scheduled'
type: Scheduled
script:
code: |
[...]
exit_condition:
- path: 'input.exit_condition_path'
string: "input.exit_condition_string"
scheduled:
- every: 'input.scheduler_every'
expire: 'input.scheduler_expire'
fields:
- id: scheduler_every
label: 'scheduler rate'
type: text
required: true
hint: "schedule rate i.e 1m 5m 1d (supported placeholder m=minutes, h=hours, d=days)"
- id: scheduler_expire
label: 'schedule expiration'
type: text
required: true
hint: "schedule expiration i.e 1m 5m 1d (supported placeholder m=minutes, h=hours, d=days)"
- id: exit_condition_path
label: 'output path'
type: text
required: true
hint: "output path to check"
- id: exit_condition_string
label: 'string to check'
type: tag
required: true
hint: "string to check"
output:
- path : '[]."ip-dst_string"'
- path : '[].{Name: name, ID: _id, Address: address, FriendName: friends.[].name}'
- path : '[].tags.[] | unique()'
- path : '[].tags.[]'
- path : '[].guid | join(,)'
- path : '[].guid | join(SEPARATOR)'
- path : '[].guid'
- path : '[]._id'
- path : '[].guid'
- path : '[].isActive'
- path : '[].balance'
- path : '[].picture'
- path : '[].eyeColor'
- path : '[].name'
- path : '[].age'
- path : '[].gender'
- path : '[].company'
- path : '[].email'
- path : '[].phone'
- path : '[].address'
- path : '[].friends'
Field notes:
- re-execution
By default, if the previous action run is not yet finished, the next scheduled run is skipped. If you setre-execution: 'force', the previous run will be killed, stopping the Docker container. - exit_condition
Specify what condition system has to evaluate to decide if continue with next execution or to stop scheduled action and continue with playbook next actions:- exit_condition: path
It's where to search in JSON structure astable_viewsection or an action's input. - exit_condition: string
Value to check in path, or you can use an action's input.
- exit_condition: path
- scheduled
Specify the time interval between one run and the next and action expiration.- scheduled: EVERY
The time interval between one run and the next, or you can use an action's input. - scheduled: EXPIRE
The time after the first run to stop scheduling, or you can use an action's input. The last result will be kept. Time interval:- d => DAYS
- h => HOURS
- m => MINUTES
- scheduled: EVERY
Trigger action definitions
Triggers run when users perform specific actions, or can be invoked automatically by interacting with the appropriate endpoint of the API. For example, a trigger can run when a field value is updated in an incident, new objects are created, or when a button is pressed.
Define a trigger action
To create a new trigger action, you must define a trigger action YAML file with the value type set to Trigger:
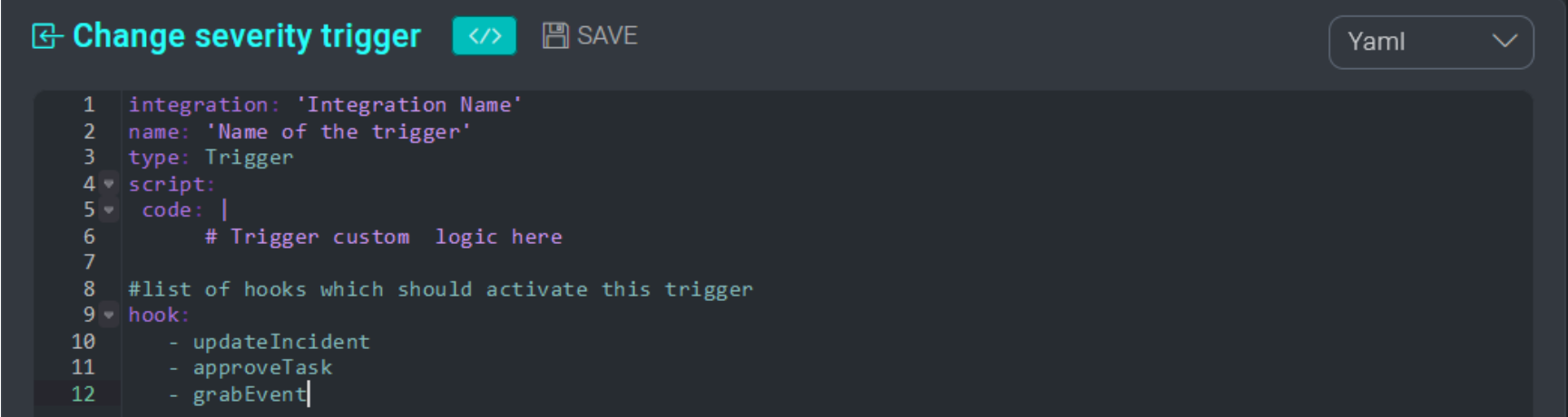
Depending on the logic that you want to implement in your triggers, specify a list of one or more hooks in the trigger YAML file. Each hook represents a manual event or API endpoint that can invoke the trigger. For example, by specifying the hook updateIncident inside a trigger, the trigger will fire whenever the field of any incident is updated either manually from the UI or via the API.
Triggers function as individual actions, executed in the backend, without the capability to review the execution output in the GUI except for triggers on entities (observables). If a trigger fails, error logs printed on the stderr output of the trigger are exported in the audit trail (system log verbosity must be set to ALL to review trigger audit logs). Triggers cannot receive manual input, except for triggers with the incidentCustomActions and taskCustomActionshooks that accept a text input.
Examples of trigger definition files
See the following examples of trigger definition files:
- Trigger definition file (Incident Tools)
- Trigger taskCustomAction definition file (Incident Tools)
- Trigger incidentCustomAction definition file (Incident Tools)
- Trigger webhook definition file
Trigger hooks
Specify hook values in a Trigger type action definition file to run the trigger action in specific situations. For example, to automatically run a trigger action when a task is closed, specify the closeTask hook.
The following sections describe the valid hook values to use in a trigger definition file.
Entities hooks
Following are the hooks for entities (observables) events that run when objects are created:
addObservableArtifact. When an artifact entity is created.addObservableDomain. When a domain entity is created.addObservableIp. When an IP address entity is created.addObservableMail. When an email entity is created.addObservableUrl. When a URL entity is created.addObservableUserDetail. When a user detail entity is created.
Task hooks
Following are the hooks for task events:
approveTask. When task is approved. Param passed to scripttasksDetail.closeTask. When task is closed. Param passed to scripttasksDetail.createTask. When task is created. Param passed to scripttasksDetail.reassignTask. When task is reassigned. Param passed to scripttasksDetail.taskCustomAction. Custom trigger. Param passed to scripttext. For more information, see Trigger taskCustomAction.updateTask. When task is updated. Param is passed to scriptstasksBeforeUpdateandtasksAfterUpdate.
Params tasksDetail, tasksBeforeUpdate, and tasksAfterUpdate are JSON strings with the form:
{
reminder_time: <value>,
report_time: <value>,
assigned_to: <value>,
priority: <value>,
status: <value>,
title: <value>,
end_time: <value>,
hours: <value>,
opt_3: <value>,
opt_6: <value>,
opt_7: <value>,
opt_8: <value>,
opt_9: <value>,
opt_10: <value>,
opt_12: <value>,
[....]
}
Triage hooks
Following are hooks for triage events:
discardEvent. When event is discarded. Param passed to scripttriage_eventsDetail.grabEvent. When event is grabbed. Param passed to scripttriage_eventsDetail.reassignEvent. When event is reassigned. Param passed to scripttriage_eventsDetail.
Param triage_eventsDetail is a JSON string with the form:
{
id: <value>,
status: <value>,
operator: <value>,
username: <value>,
type: <value>,
opt_1: <value>,
opt_3: <value>,
opt_4: <value>,
opt_5: <value>,
opt_7: <value>,
opt_8: <value>,
opt_11: <value>
}
Incident hooks
Following are hooks for incident events:
closeIncident. When incident is closed. Param passed to scriptincidentsBeforeUpdateandincidentsAfterUpdate.incidentCustomAction. Custom trigger. Param passed to scripttextandincidentsDetail. For more information, see Trigger incidentCustomAction.newIncident. When incident is created. Param passed to scriptincidentsDetail.updateIncident. When incident is updated. Param passed to scriptincidentsBeforeUpdateandincidentsAfterUpdate.
Params incidentsDetail, incidentsBeforeUpdate, and incidentsAfterUpdate are JSON strings with the form:
{
id: <value>,
additional_info: <value>,
status: <value>,
investigation_number: <value>,
starttime: <value>,
type: [<value>],
incident_kind: <value>,
incident_category: [<value>],
[...]
opt_3: <value>,
opt_6: <value>,
opt_7: <value>,
opt_8: <value>,
opt_9: <value>,
opt_10: <value>,
opt_12: <value>,
[....]
}
External hooks
Use the webhook hook for external events. For more information, see Define a webhook trigger.
Trigger incidentCustomAction and taskCustomAction
It is possible to create a GUI shortcut (button) to a trigger in the incident or task details by defining the hooks incidentCustomAction or taskCustomAction.
The name of the button will correspond to the name of the trigger defined inside the YAML:
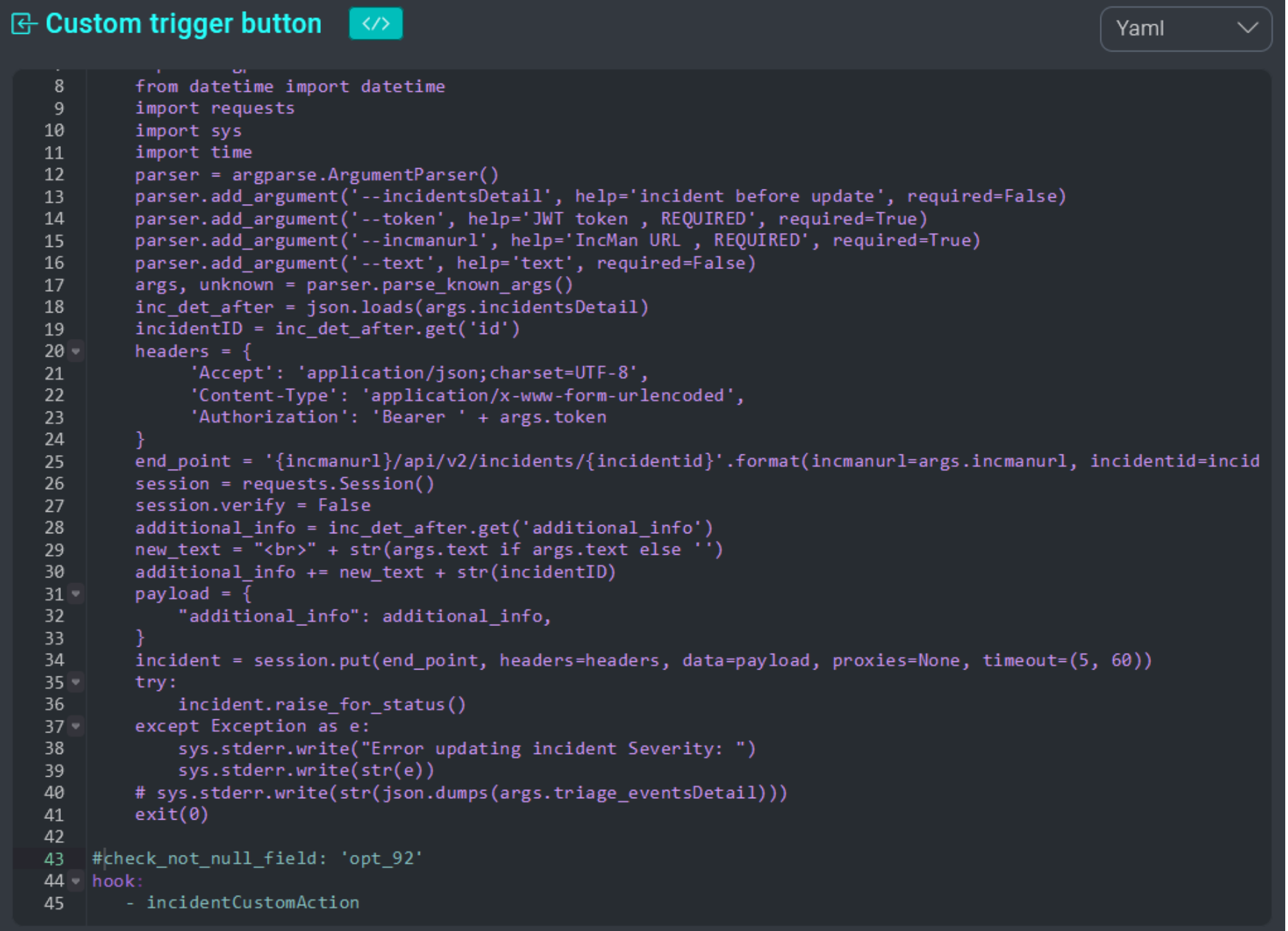
Clicking the button in the UI runs the trigger:
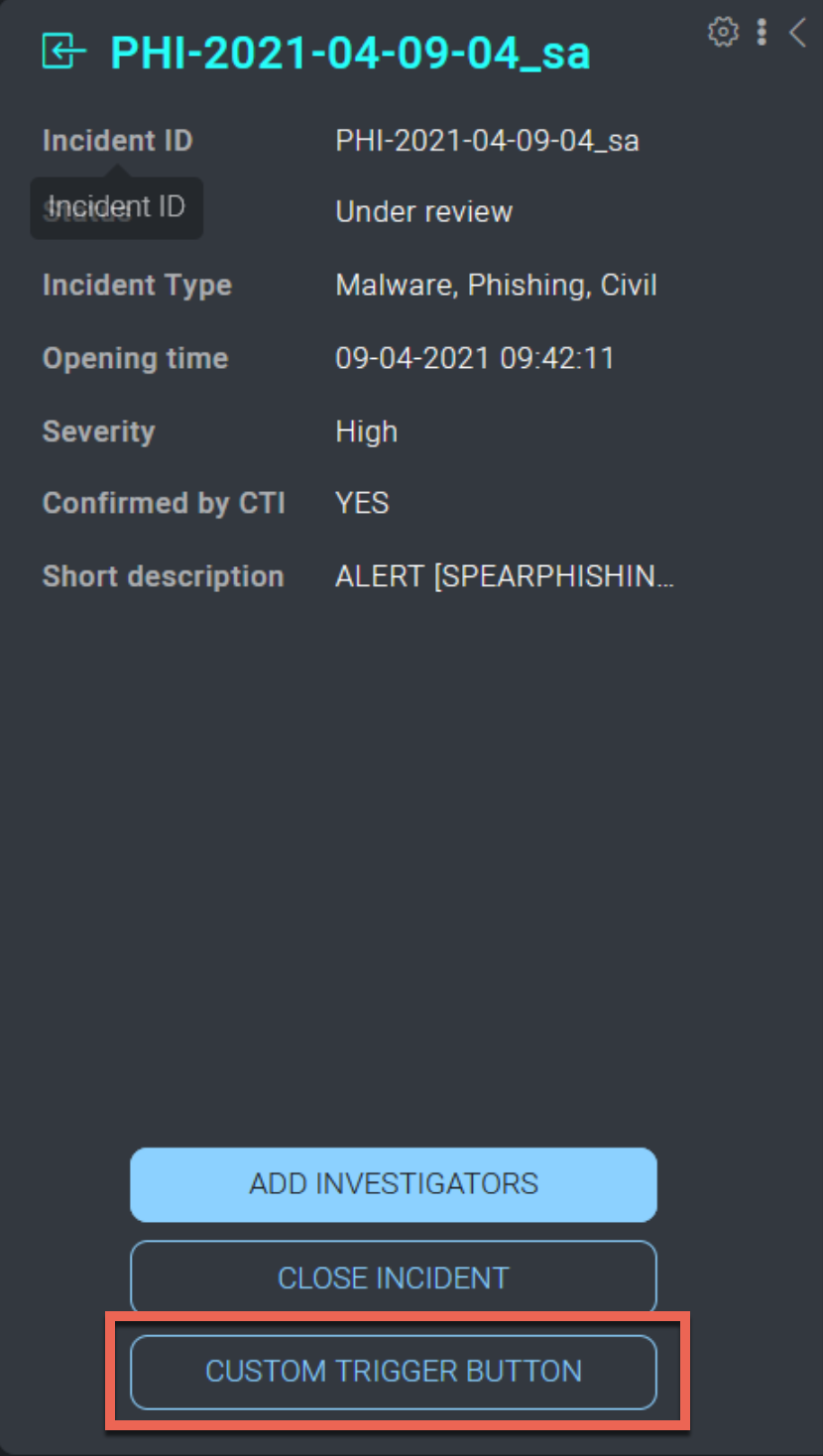
When users interact with the custom action trigger button, they can provide a textual input that can be elaborated by the trigger. To elaborate the input of a custom action trigger, use the text param inside the code:
integration: 'Incident Tools'
name: 'Custom trigger button'
type: Trigger
show_modal: true
script:
code: |
import json
import argparse
import requests
import sys
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--incidentsDetail', help='incident before update', required=False) #param inherited by
hook defined in the yaml
parser.add_argument('--token', help='JWT token , REQUIRED', required=True)
parser.add_argument('--incmanurl', help='IncMan URL , REQUIRED', required=True)
parser.add_argument('--text', help='text', required=False) #param inherited by hook defined in the yaml
args, unknown = parser.parse_known_args()
inc_det_after = json.loads(args.incidentsDetail)
incidentID = inc_det_after.get('id')
headers = {
'Accept': 'application/json;charset=UTF-8',
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
'Authorization': 'Bearer ' + args.token
}
end_point = '{incmanurl}/api/v2/incidents/{incidentid}'.format(incmanurl=args.incmanurl, incidentid=incidentID)
session = requests.Session()
session.verify = False
additional_info = inc_det_after.get('additional_info')
new_text = "<br>" + str(args.text if args.text else '')
additional_info += new_text
payload = {
"additional_info": additional_info,
}
incident = session.put(end_point, headers=headers, data=payload, proxies=None, timeout=(5, 60))
try:
incident.raise_for_status()
except Exception as e:
sys.stderr.write(str(e))
exit(0)
check_not_null_field: 'opt_92' #specify that the custom field with internal id “opt_92” should be populated in
order to display this button in the GUI.
hook:
- incidentCustomAction #hook that generates a custom button in the incident tombstone when field opt_92 is not
null
integration: 'Incident Tools'
name: 'Custom trigger button'
type: Trigger
show_modal: false
script:
code: |
import json
import argparse
import requests
import sys
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--incidentsDetail', help='incident before update', required=False) #param inherited by
hook defined in the yaml
parser.add_argument('--token', help='JWT token , REQUIRED', required=True)
parser.add_argument('--incmanurl', help='IncMan URL , REQUIRED', required=True)
args, unknown = parser.parse_known_args()
inc_det_after = json.loads(args.incidentsDetail)
incidentID = inc_det_after.get('id')
headers = {
'Accept': 'application/json;charset=UTF-8',
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
'Authorization': 'Bearer ' + args.token
}
end_point = '{incmanurl}/api/v2/incidents/{incidentid}'.format(incmanurl=args.incmanurl, incidentid=incidentID)
session = requests.Session()
session.verify = False
additional_info = inc_det_after.get('additional_info')
payload = {
"additional_info": additional_info,
}
incident = session.put(end_point, headers=headers, data=payload, proxies=None, timeout=(5, 60))
try:
incident.raise_for_status()
except Exception as e:
sys.stderr.write(str(e))
exit(0)
check_not_null_field: 'opt_92' #specify that the custom field with internal id “opt_92” should be populated in
order to display this button in the GUI.
hook:
- incidentCustomAction #hook that generates a custom button in the incident tombstone when field opt_92 is not
null
For other example YAML files, see:
- Trigger taskCustomAction definition file (Incident Tools)
- Trigger incidentCustomAction definition file (Incident Tools)
show_modal
Specifies whether to display the textual input. Default value is true.
check_not_null_field
Specifying the YAML field check_not_null_field : <field ID> inside a trigger, you can ensure that the trigger is only executed (or displayed in case of custom actions buttons) when a specific incident field is populated.
For example, if we want to display our custom action trigger button only when our custom field with field ID opt_15 is populated, inside the YAML file you can set:
check_not_null_field: 'opt_15'
hook:
- incidentCustomAction
Define a webhook trigger
Triggers with the hook webhook specified can interact with the payload that is posted on your webhook endpoint:
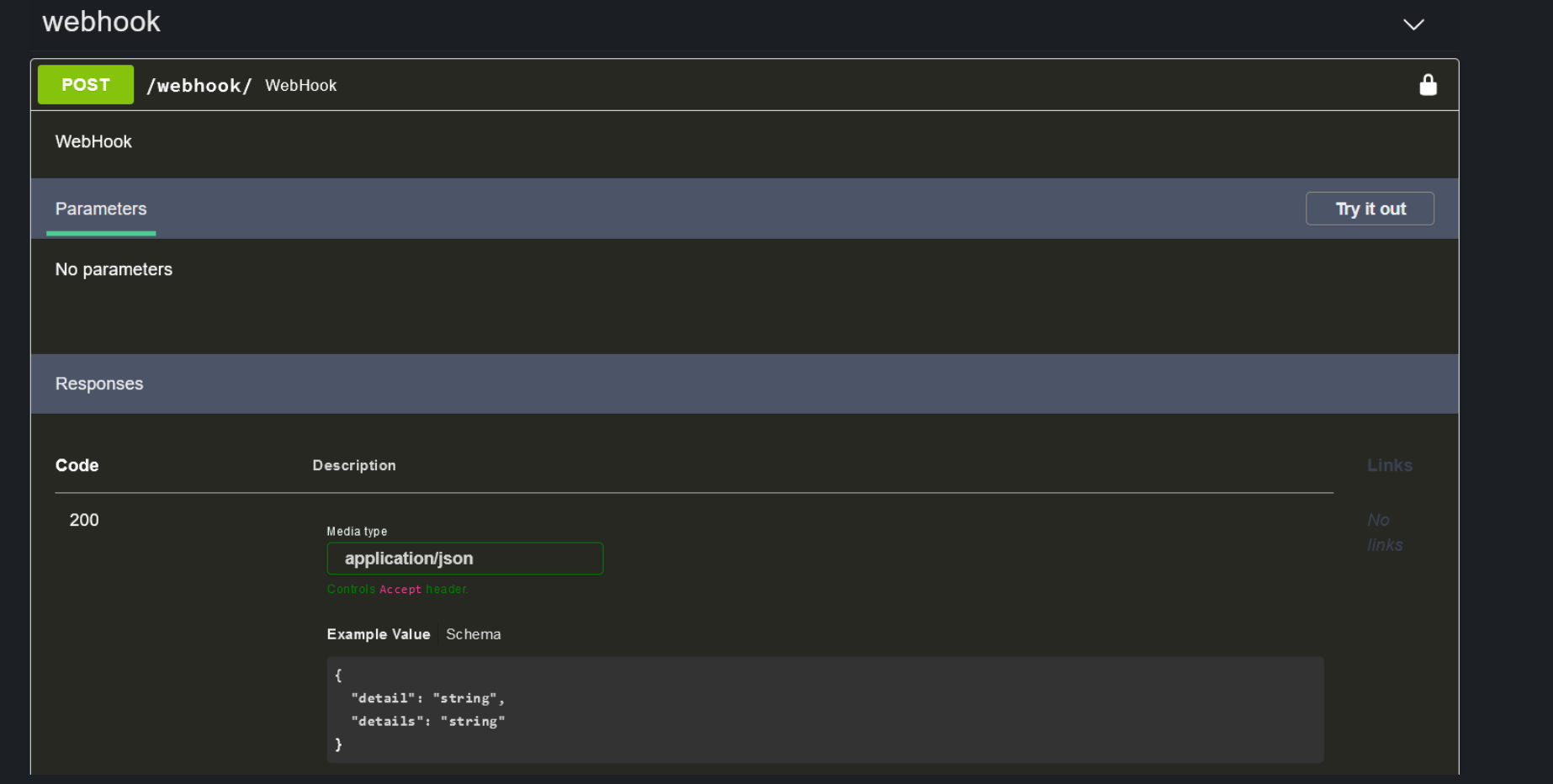
In the following example, a trigger ingests the JSON payload posted to the webhook endpoint, and writes its content in the description widget of a specific incident (ID 1743):
type: Trigger
script:
code: |
import json
import argparse
from datetime import datetime
import sys
import requests
import time
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--payload', help='WebHook payload , REQUIRED', required=True)
parser.add_argument('--token', help='JWT token , REQUIRED', required=True)
parser.add_argument('--incmanurl', help='IncMan URL , REQUIRED', required=True)
args, unknown = parser.parse_known_args()
payload = json.dumps(args.payload)
incidentID = 1743
headers = {
'Accept': 'application/json;charset=UTF-8',
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
'Authorization': 'Bearer ' + args.token
}
end_point = '{incmanurl}/api/v2/incidents/{incidentid}'.format(incmanurl=args.incmanurl,
incidentid=incidentID)
session = requests.Session()
session.verify = False
additional_info = json.loads(payload)
payload = {
"additional_info": additional_info,
}
incident = session.put(end_point, headers=headers, data=payload, proxies=None, timeout=(5,60))
sys.stderr.write(str(incident.content))
try:
incident.raise_for_status()
except Exception as e:
sys.stderr.write("Error updating incident Severity: ")
sys.stderr.write(str(e))
# sys.stderr.write(str(json.dumps(args.triage_eventsDetail)))
exit(0)
hook:
- webhook
For another example YAML file of a webhook trigger, see Trigger webhook definition file.
Additional resources
Blogs: