Arrays in Playbooks
An array is a collection of related data values grouped together. When you are handling output from a playbook action, you may want to treat the entire array as a single item you want to pass to the next action, or you may want to treat each element in the array as a separate item. In playbooks, you can do either.
Arrays in text areas
When you create an action, sometimes you are presented with a text area that includes an "Insert placeholder" icon ![]() . When you click the icon, it allows you to add placeholders to the text area for input or output.
. When you click the icon, it allows you to add placeholders to the text area for input or output.
Perform the following steps to add a placeholder to a text area to handle an array in output from a previous action. This allows you to process an array as a single element or multiple elements.
- Create a playbook and add action nodes.
- Edit an action node that displays a text area.
- In the following example, the Send Email action shows text areas for the email's subject, body, and HTML. Click an "Insert placeholder" icon
 for one of the fields, for example, HTML Content.
for one of the fields, for example, HTML Content.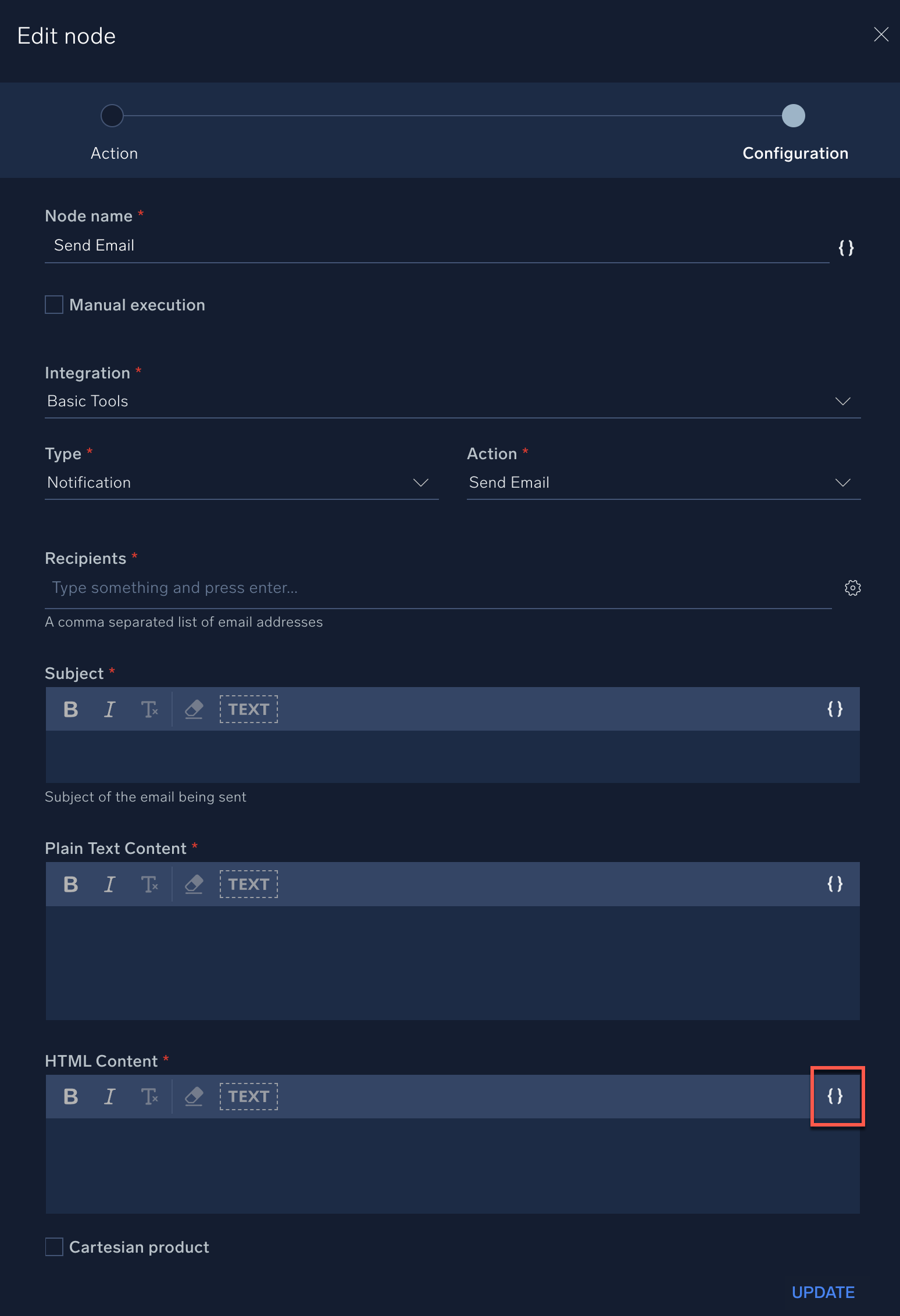
- Select a value from a previous action. In this example, we'll choose Get Insight.
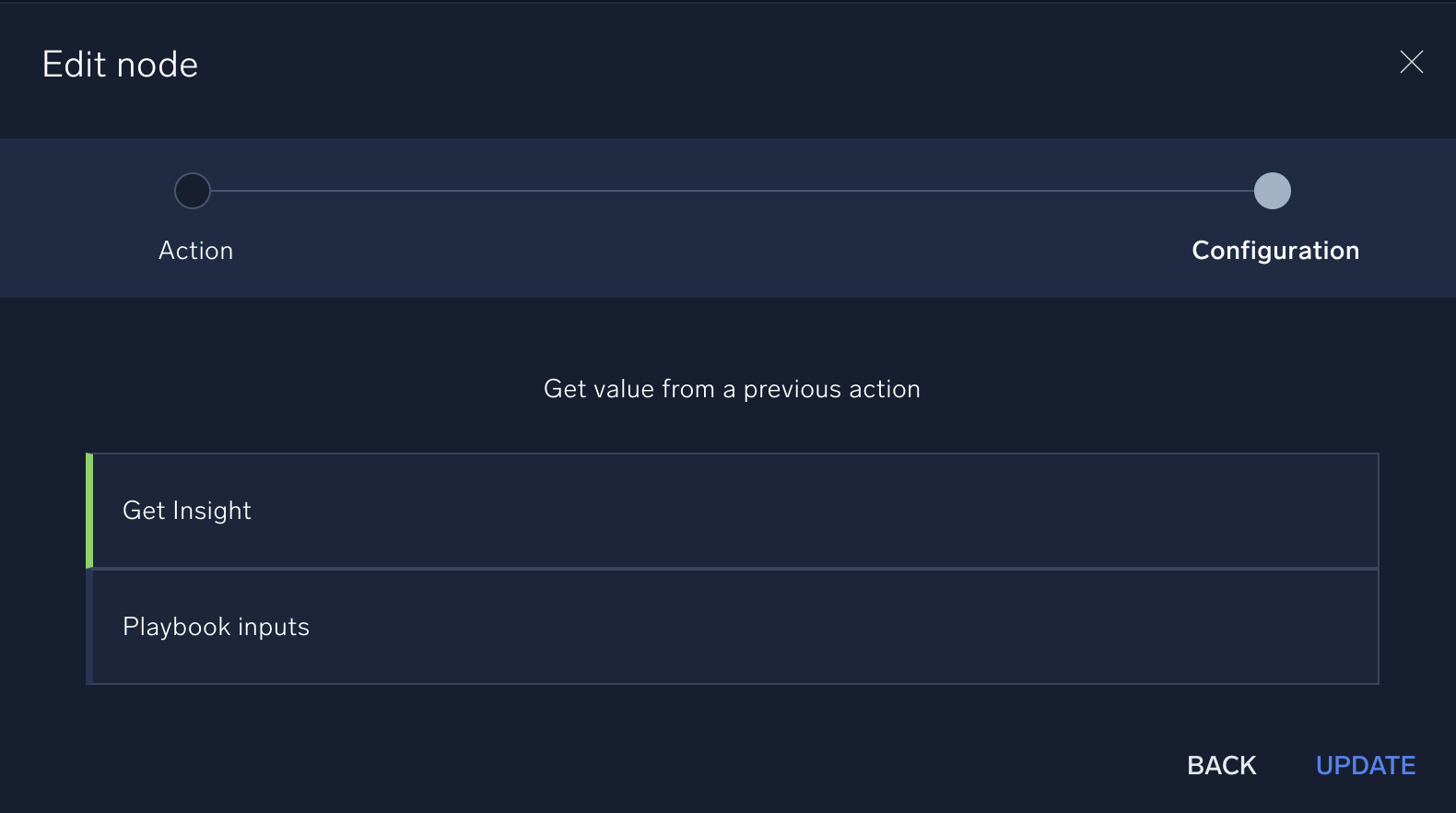
- Select Outputs. Only the arrays in the output show these icons:

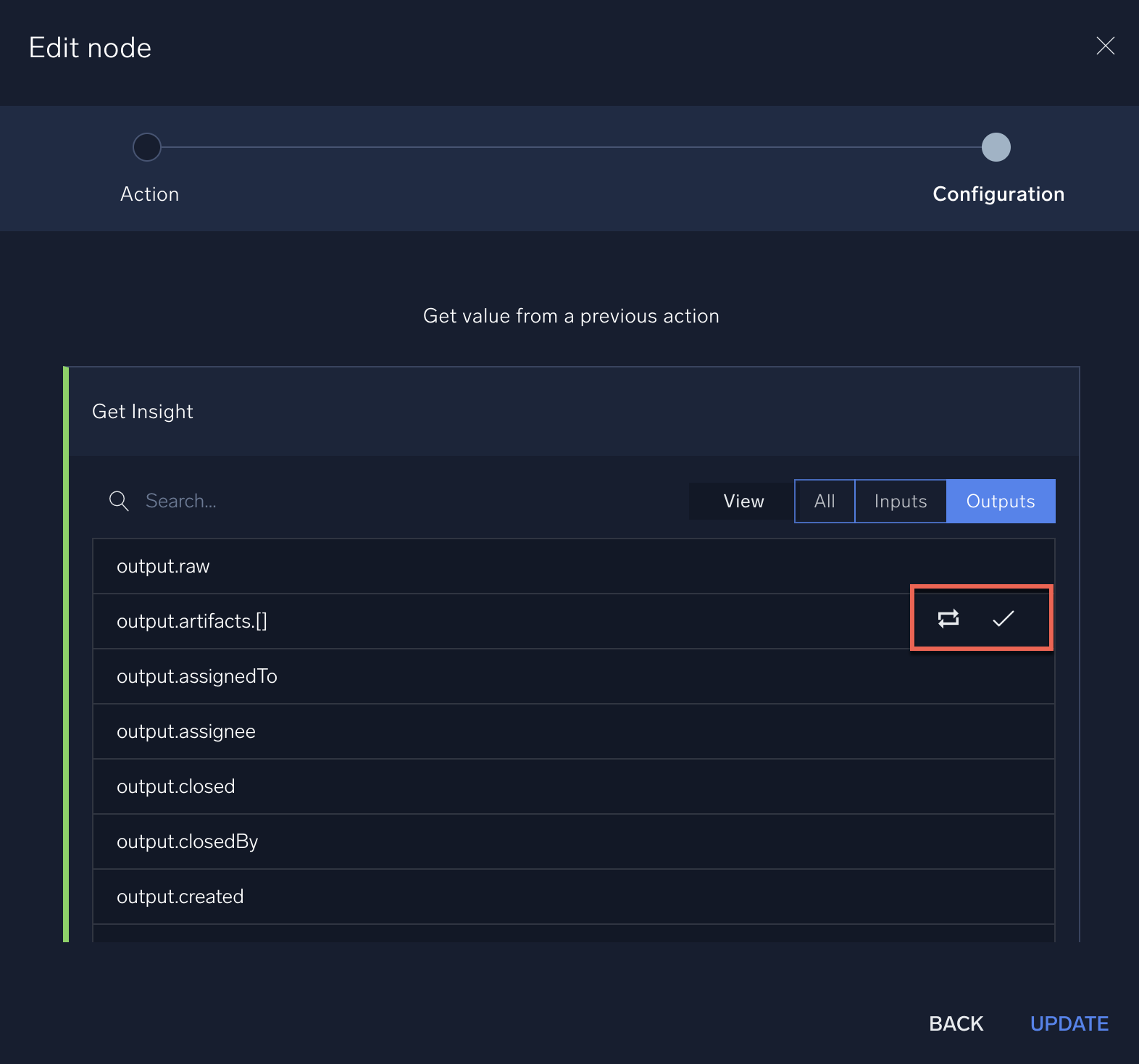
- Click the icon for how you want the array to be handled by the action:
 Loop. Loops through the array so that the action is run for each item in the array.
Loop. Loops through the array so that the action is run for each item in the array. Combine. Combines all items in the array into a single value run by the action.
Combine. Combines all items in the array into a single value run by the action.
- The variable is inserted into the text area preceded by the icon for whether the contents of the array are looped or combined.
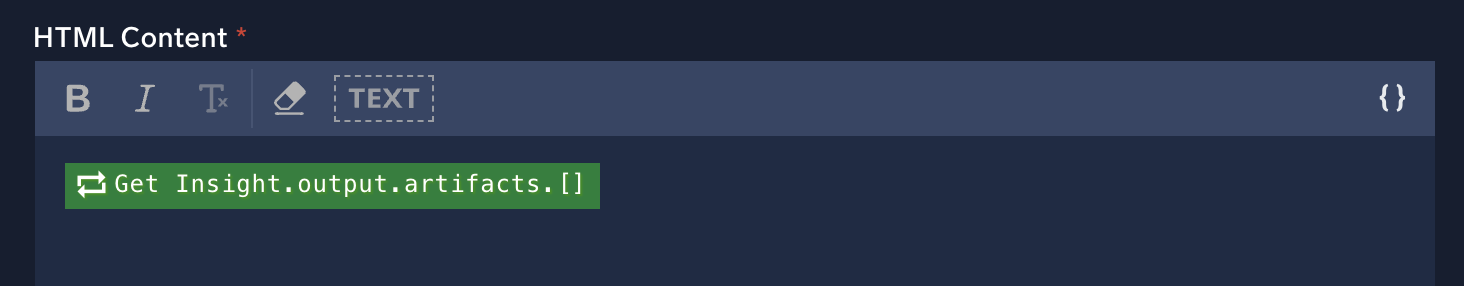
In this example, the action will be run for each item in the array ("looped").
The Cartesian Product checkbox is disabled if any variable is selected using the loop feature in the text area.

Cartesian product
The Cartesian product checkbox appears on nodes you add to playbooks. Clicking this checkbox causes the node to use the Cartesian product method to loop through items in arrays processed by the node.

For example, suppose one input field is for signal name, and another is for signal value. If you have 2 arrays like this, and each array has 3 items, the Cartesian product evaluation pairs each item from the first set with each item from the second set, which will produce 9 pairs (3x3). Without Cartesian product evaluation, only matching position items are paired, which will produce 3 pairs (equal to the number of items).
Use the Cartesian product checkbox with caution. For most cases, deselect the Cartesian product checkbox when creating playbooks. Large array fields in the input can result in the action being called many times, causing the action to exceed the actions limit. Only select this checkbox if you want to evaluate data from array input fields using the Cartesian product method.
"Split by" field in a filter node
When you add a filter node, use the Split by field to evaluate each item separately in arrays (lists).
Each item in arrays is checked against the filter condition. If the condition is true for an item, the item is passed to the next node. If you do not use the Split by field on an output that is a list, then if the condition is true for any item in the list, the entire list moves forward to the next node.