Parse Variable Patterns Using Regex
The Parse Regex operator (also called the extract operator) enables users comfortable with regular expression syntax to extract more complex data from log lines. Parse regex can be used, for example, to extract nested fields.
User added fields, such as extracted or parsed fields, can be named using alphanumeric characters as well as underscores (_). They must start and end with an alphanumeric character.
For more information on Regular Expressions, see the Perl documentation. Or try the regex tester at regex101.com.
Syntax
| parse regex "<start_expression>(?<field_name><field_expression>)<stop_expression>"| parse regex "<start_expression>(?<field_name><field_expression>)<stop_expression>" [nodrop]| parse regex [field=<field_name>] "<start_expression>(?<field_name><field_expression>)<stop_expression>"You can use the alternate termextract:
| extract "<start_expression>(?<field_name><field_expression>)<stop_expression>"
Options
field=<field_name>. This option allows you to specify a field to parse other than the default message. For details, see Parse field.nodrop. This option forces results to also include messages that do not match any segment of the parse term. For details, see Parse nodrop.multi. This option allows you to parse multiple values within a single log message.
parse multi is not supported in Field Extraction Rules (FERs).
Rules
- Regex must be a valid JAVA or RE2 regular expression enclosed within quotes.
- Matching is case sensitive. If any of the text segments cannot be matched, then none of the variables will be assigned.
- If no field is specified, then the entire text of incoming messages is used.
- Multiple parse expressions are processed in the order they are specified. Each expression always starts matching from the beginning of the message string.
- Multiple parse expressions can be written with shorthand using comma-separated terms.
- Can be used with the parse anchor operator.
- Nesting named capture groups is not supported.
- The parse regex operator only supports regular expressions that contain at least one named capturing group. We do not support regular expressions that either do not have any capturing groups or contain unnamed/numbered capturing group. See Named Capturing Groups for further details.
You can convert your normal regular expressions into named capturing groups with the following steps:
Wrap everything in parenthesis, and append ? followed by a capturing group name enclosed within < >. Let's see an example below, the highlighted portions is what has been added.
- Normal Regex:
\d{3}-[\w]* - Regex with named capturing group:
(?<regex>\d{3}-[\w]*)
If your regex contains a capturing group (part of the regex is enclosed within parentheses), then you have two options:
You can convert it into a non-capturing group. In this case we will not extract out that part of your regex into a Sumo Logic field. You can convert these easily by appending ?: to the group right after the starting parenthesis.
This approach will not work in cases where you only have non-capturing groups in your regex. You need to have at least one capturing group in your regex.
- Normal Regex:
(abc|\d{3}) - Regex with non-capturing group:
(?:abc|\d{3})
If you want to extract out the value from your numbered capturing group to a named capturing group within your regex you can convert it into a named capturing group. Do this by appending a ? and enclosing the name of the capturing group within < >. Sumo Logic will generate a field with the same name that is specified in the named capturing group.
- Normal Regex:
(abc|\d{3}) - Regex with named capturing group:
(?<test_group>abc|\d{3})
Examples
Parsing an IP address
Extracting IP addresses from logs is straight-forward using a parse regex similar to:
... | parse regex "(?<ip_address>\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})"
| ...
Parsing multiple fields in a single query.
Parse regex supports parsing out multiple fields in one query. For example, say we want to parse username and host information from logs. Use a query similar to:
... | parse regex "user=(?<user>.*?):"
| parse regex "host=(?<msg_host>.*?):"
| ...
Indicating an OR condition to use non-capturing groups
In situations where you want to use an OR condition, where you have multiple possibilities that may match the regular expression, the best practice is to use non-capturing groups (?: regex).
The Sumo Logic query language requires groups that are not captured to an alias be marked explicitly as non-capturing groups.
To specify a list of alternative strings in a regular expression, use the group syntax. For example, for the following two log lines:
Oct 11 18:20:49 host123.example.com 16234563: Oct 11 18:20:49: %SEC-6-IPACCESSLOGP: list 101 denied tcp 10.1.2.3(1234) > 10.1.2.4(5678), 1 packet
Oct 11 18:20:49 host123.example.com 16234564: Oct 11 18:20:49: %SEC-6-IPACCESSLOGP: list 101 accepted tcp 10.1.2.5(4321) > 10.1.2.6(8765), 1 packet
you can write the following query to extract the protocol:
| parse regex "list 101 (accepted|denied) (?<protocol>.*?) "
So, you'd actually write:
| parse regex "list 101 (?:accepted|denied) (?<protocol>.*?) "
But if you mean to also capture whether it is an accepted or a denied into an alias, then you'd include:
| parse regex "list 101 (?<status>accepted|denied) (?<protocol>.*?) "
Parse multi
parse multi is not supported in Field Extraction Rules.
In addition to parsing a field value, the multi option (also called parse multi) allows you to parse multiple values within a single log message. This means that the multi keyword instructs the parse regex operator to not just look for the first value in a log message, but for all of the values, even in messages with a varying number of values. As a part of this process, the multi keyword creates copies of each message so that each individual value in a field can be counted.
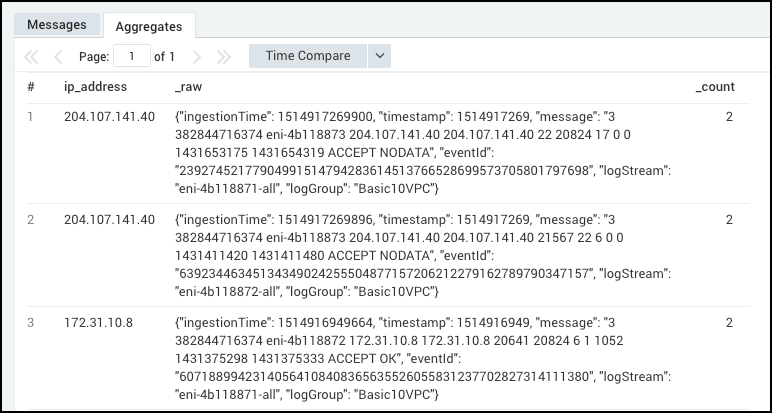
For example, in the Amazon VPC flow logs you can identify the messages with the same source and destination IP addresses using parse regex multi.
_sourceCategory=aws/vpc
| parse regex "(?<ip_address>\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3})" multi
| count by ip_address, _raw
| where _count >1
The output looks like:
Case insensitive parse regex
You can tell the parser to use case insensitivity by supplying the regex parameter of (?i). For example, let's say we have the following log messages:
Line1: The following exception was reported: error in log
Line2: The following exception was reported: Error in log
Line3: The following exception was reported: ERROR in log
Use the following parse regex expression to match the "error" in the logs. The (?i) tells the parser to ignore case for the trailing expression.
| parse regex "reported:\s(?<exception>(?i)error)\s"
This would result in the following parsed fields
| Exception | Message |
|---|---|
| ERROR | Line3: The following exception was reported: ERROR in log |
| Error | Line2: The following exception was reported: Error in log |
| error | Line1: The following exception was reported: error in log |
You can also use the toLowerCase and toUpperCase operators.