Azure Blob Storage (append blobs)
This page describes a Sumo Logic integration that provides an event-based pipeline for shipping monitoring data from Azure Blob Storage(stored as append blobs) to an HTTP source on Sumo Logic.
This solution is good for monitoring Azure services that do not support exporting logs to Azure Event Hubs. If your service supports exporting to Event Hub, then use Azure Event Hubs Source for Logs .
This solution is for newly created blobs only (not for existing blobs).
For step-by-step instructions for configuring the Azure-Sumo Logic pipeline, see Collect Logs from Azure Blob Storage (append blobs).
Azure-Sumo Logic pipeline
The diagram below illustrates the Azure-Sumo Logic pipeline for Azure logs collection(stored as append blobs) from Azure Blob Storage. Monitoring data flow describes the flow of logs from Azure Blob Storage to Sumo Logic. Pipeline components describes the actors in the flow.
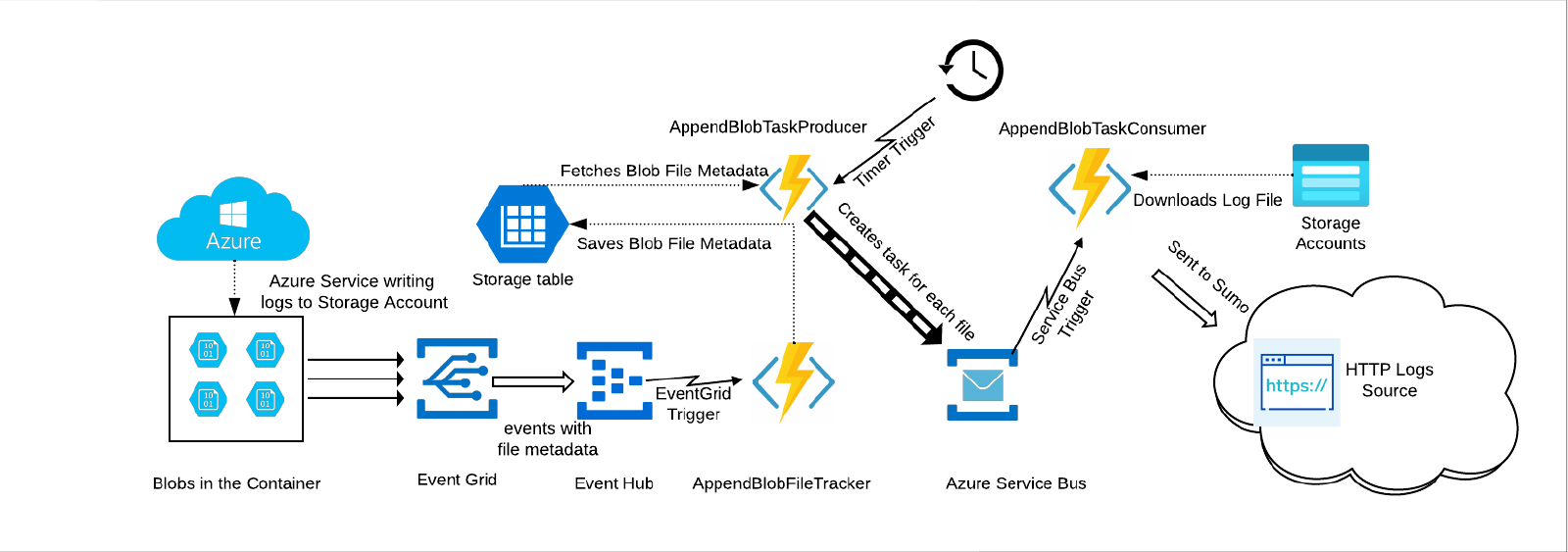
Monitoring data flow
Here’s a summary of how various components are stitched together in the pipeline.
- Azure services send monitoring data (logs as append blobs type) to Azure Blob containers in a storage account. General-purpose v2 (GPv2) and Blob storage accounts are supported.
- An Event subscription is configured with Azure Blob container as the publisher and Event Hub as the subscriber. Event Grid then routes all the create append events to Event Hub.
- On receipt of data from Event Grid, an event hub triggers its Azure function named AppendBlobFileTracker to create an entry in FileOffSetMap table.
- Periodically a Azure function named AppendBlobTaskProducer, fetches list of blobs from FileOffSetMap table and creates a task with metadata. (This is a JSON object that includes the start of the append blob, file path, container name and storage name). These tasks are then pushed to Azure Service Bus Queue.
- Another Azure function named AppendBlobTaskConsumer is triggered in response to a new task in Azure Service Bus Queue. This function reads the data in the given range (from start byte), transforms the data, and sends it to an HTTP source on a hosted collector in Sumo Logic. Each of the three Azure functions sends their logs to storage accounts (named
SUMOAB<unique_prefix>) created by an Azure Resource Template (ARM).
Pipeline components
The table below describes the key components in the Azure-Sumo Logic pipeline.
| Component Description | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure Event Grid | A fully-managed intelligent event routing service that allows for uniform event consumption using a publish-subscribe model. You select the Azure resource you would like to subscribe to, and specify the event handler or webhook endpoint to which to send the event. |
| Azure Event Hubs | A data streaming platform and event ingestion service capable of receiving, storing. and processing millions of events per second. Event Grid routes “create append blob” events to an event hub, which triggers a Sumo Logic-provided Azure function. |
| Sumo Logic-provided Azure functions | Small pieces of code that are triggered by an Event Hub to send monitoring data to a Sumo Logic HTTP source. Each of the functions also maintains its own logs for function debug information. |
| Sumo Logic HTTP source | A Sumo Logic HTTP source on a hosted collector receives the monitoring data from the TaskConsumer Azure function. |
| Azure Blob Storage | Microsoft's object storage solution for the cloud, optimized for storing large amounts of unstructured data, such as text or binary data. |
| Azure Service Bus Queue | A generic, cloud-based, one-directional messaging system for connecting resources—applications, services, and devices—regardless of location. Each queue acts as an intermediary (sometimes called a broker) that stores sent messages until they are received. Each message is received by a single recipient. |
About the configuration process
Sumo Logic provides an Azure Resource Management (ARM) template to build most of the components in the pipeline. The template creates:
- An event hub to which Azure Event Grid routes create append blobs events.
- A Service Bus for storing tasks.
- Three Azure functions — AppendBlobFileTracker, AppendTaskProducer, AppendBlobTaskConsumer, that are responsible for sending monitoring data to Sumo Logic.
- A storage account to which the Azure functions write their log messages about successful and failed transmissions.
You download the Sumo Logic-provided ARM template, upload the template to the Azure Portal, set the parameters that identify the URL of your Sumo Logic HTTP source, and the name of the Azure Storage Account and its resource group (where Azure services export their logs), and deploy the template. For detailed instructions, see Collect Logs from Azure Blob Storage.
After deployment if you want to collect from multiple storage accounts, you create an Event Grid subscription with an Azure Storage Account as a publisher and the event hub created by the ARM template as the subscriber.You can also specify prefix/suffix filters to filter the events based container name and blob name.
For more information, see Filtering events in Azure help. Then, you can start exporting your monitoring data from the Azure Service to Azure Blob Storage.