Collect AWS Lambda Logs using an Extension
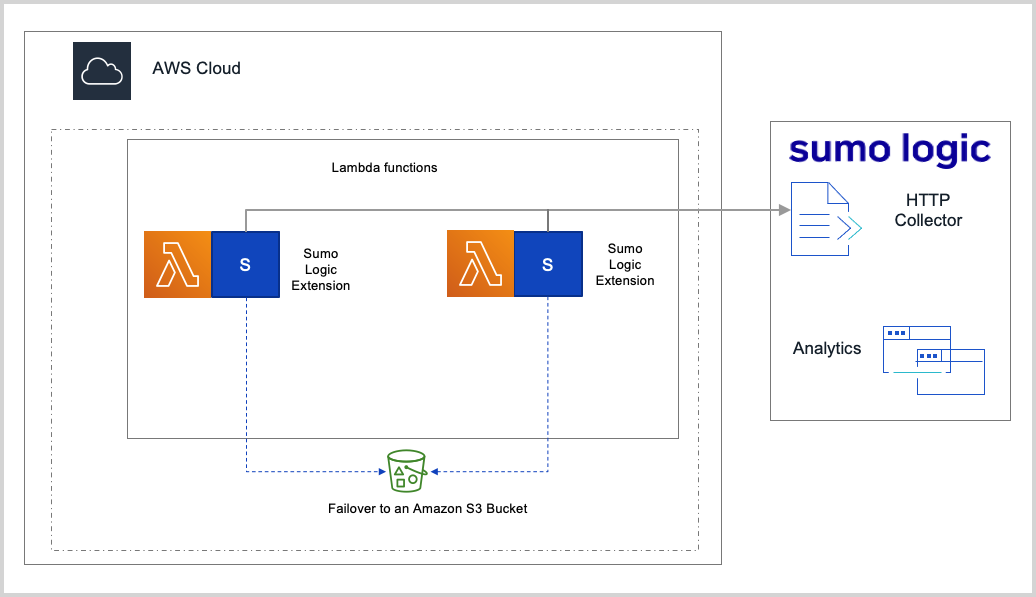
AWS Lambda Extensions enable us to more easily integrate into the AWS Lambda execution environment to control and participate in the AWS Lambda lifecycle and the AWS Lambda Telemetry API enables us to collect AWS Lambda logs, metrics, and spans. Sumo Logic, therefore, has developed a new open-source AWS Lambda extension that is a lightweight process that runs within the same execution environment as your Lambda functions and uses the Lambda Telemetry API to send platform, function, and extension logs along with metrics and spans to Sumo Logic. Sumo Logic's Lambda Extension works with AWS Lambda functions that are built for both x86_64 and ARM 64 (Graviton2) architectures.
To learn more please see the following links:
- Performance Impact of the Sumo Logic AWS Lambda extension and Failover Capabilities
- About AWS Lambda Extensions
- How to build AWS Lambda Extensions
- Sending logs to custom destinations
To review and submit enhancements for this extension, please visit the Sumo Logic GitHub repository.
AWS Lambda Supported Runtimes
Sumo Logic supports all Lambda runtimes that support extensions. For a complete list, see AWS Lambda runtimes.
Follow the steps below, to use the new extension to collect your Lambda logs.
Step 1: Add a Hosted Collector and HTTP Source
Identify an existing Sumo Logic Hosted Collector you want to use, or create a new Hosted Collector as described in the following task.
When you configure the HTTP Source, make sure to save the HTTP Source Address URL. You will need this while configuring the AWS Environment variables.
To add a hosted collector and HTTP source, do the following:
- Create a new Sumo Logic Hosted Collector by performing the steps in Configure a Hosted Collector.
- Create a new HTTP Log Source in the hosted collector created above by following these instructions.
Step 2: Adding the Sumo Logic Lambda Extension to your AWS Lambda function
The Sumo Logic Lambda Extension can be added to your AWS Lambda function that is created through all supported methods.
- AWS Lambda functions created using Zip files, blueprint or serverless applications
- AWS Lambda functions created using Container Images
AWS Lambda functions created using zip files, blueprint, serverless applications
For AWS Lambda functions created using Zip files, blueprint or serverless applications:
To add the Sumo Logic Lambda Extension to your AWS Lambda function, please follow the steps below:
-
In the AWS Management Console, navigate to the definition of your Lambda function, Select Layers and click Add a Layer.
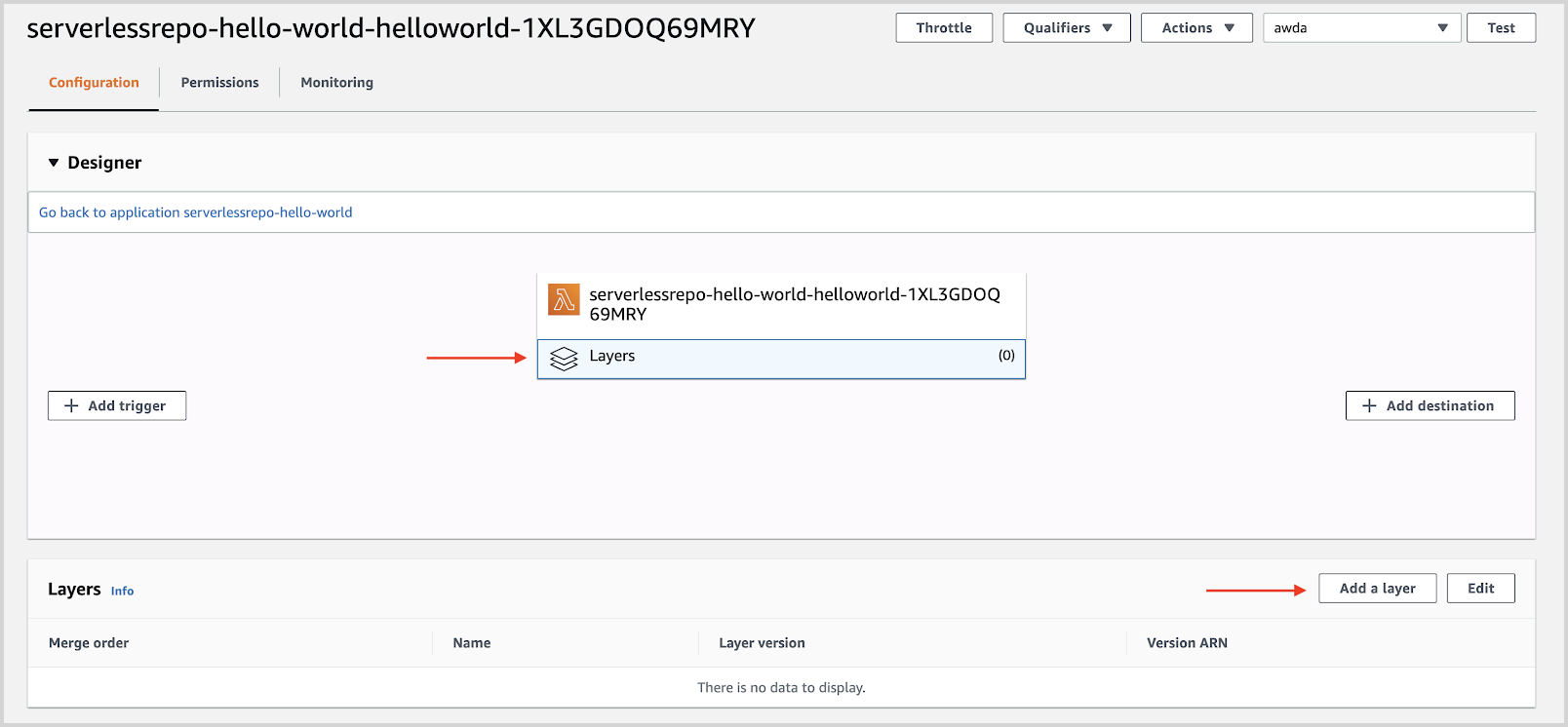
-
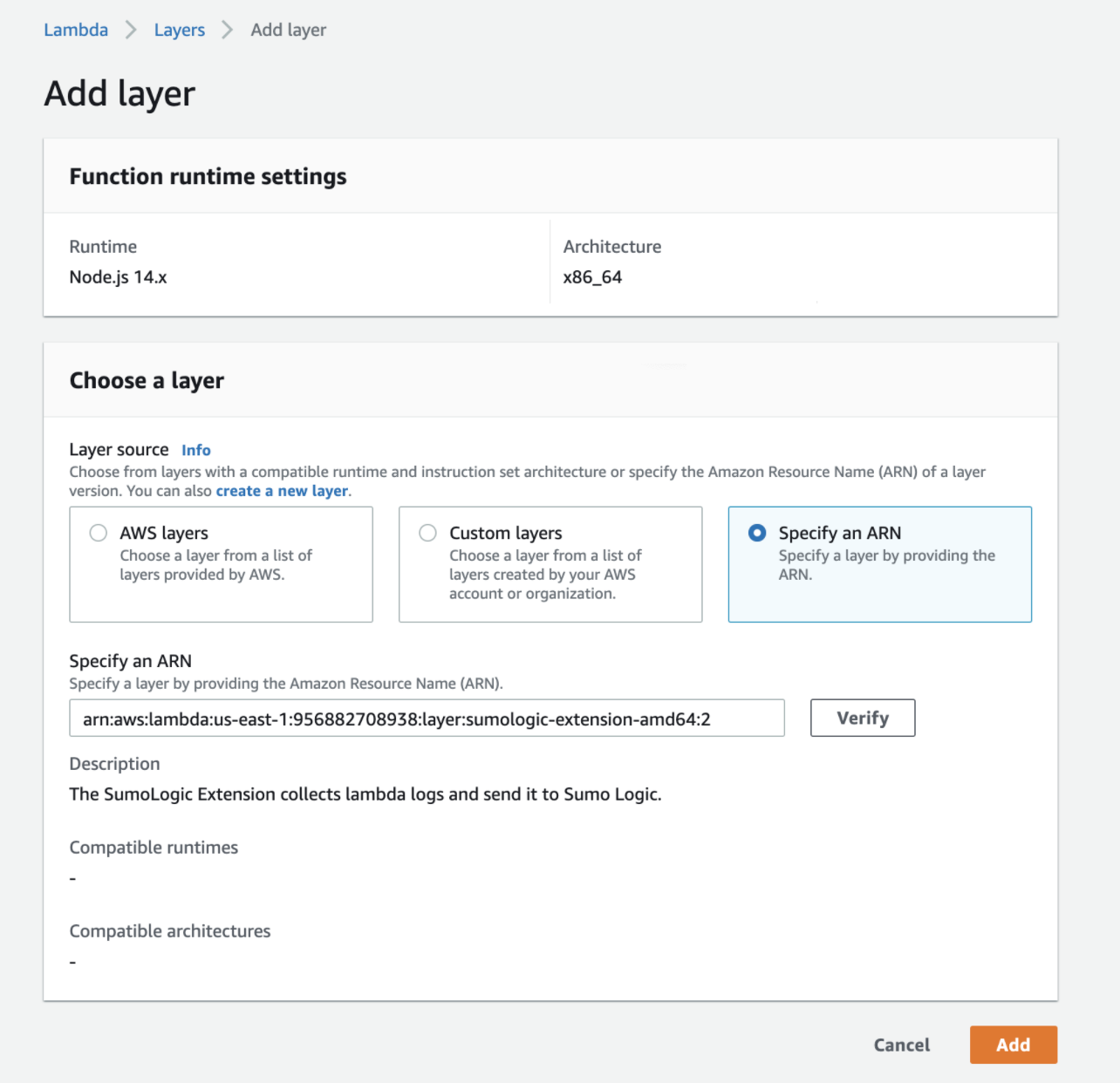
Select Specify an ARN.
- For x86_64 architecture, enter the following ARN:
<AWS_REGION>:956882708938:layer:sumologic-extension-amd64:<VERSION>- AWS_REGION. Replace with the AWS Region of your Lambda function
- VERSION. The latest version of the Sumo Logic Extension.
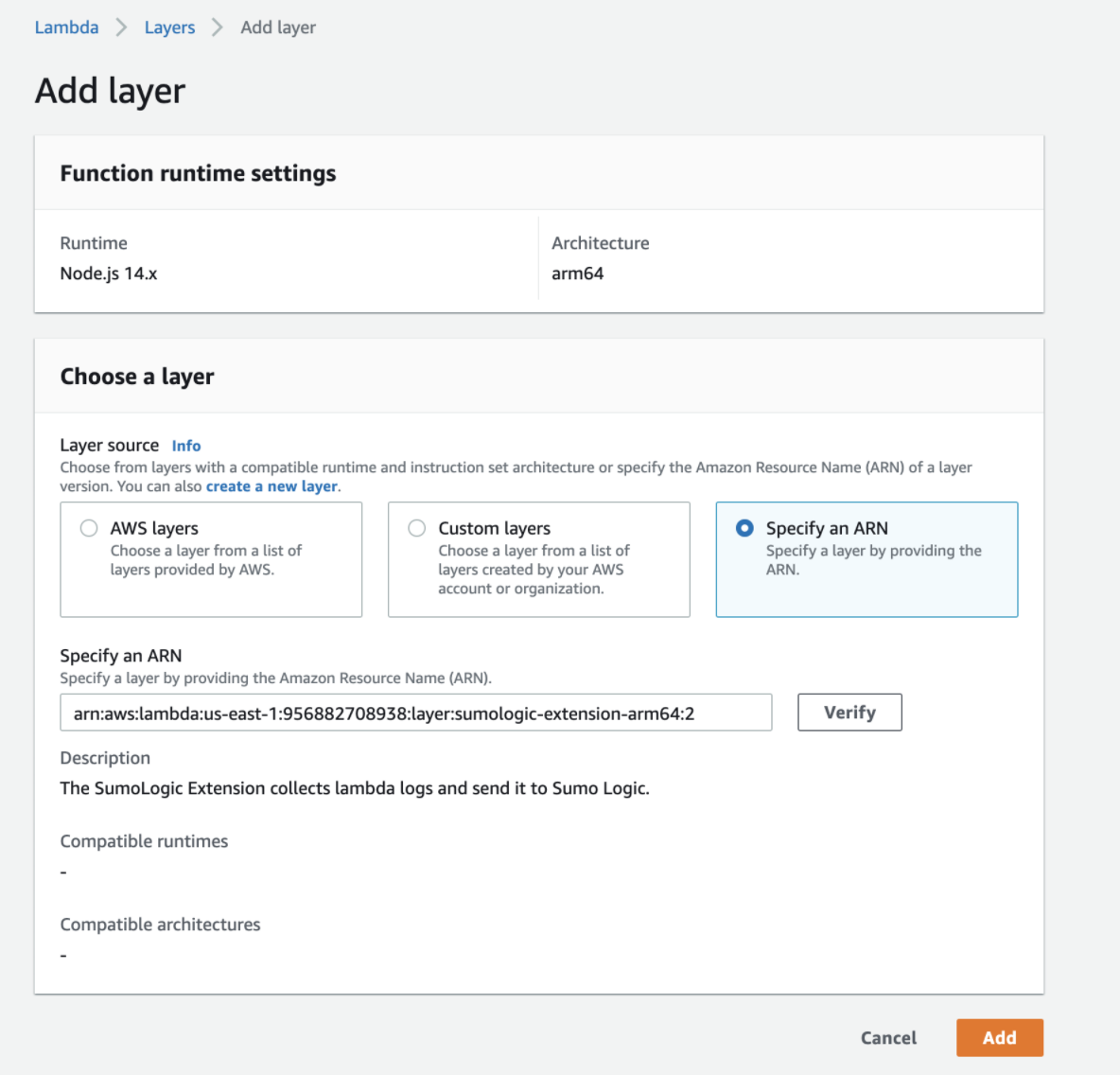
- For arm64 architecture, enter the following ARN:
<AWS_REGION>:956882708938:layer:sumologic-extension-arm64:<VERSION>- AWS_REGION. Replace with the AWS Region of your Lambda function
- VERSION. The latest version of the Sumo Logic Extension.
AWS Lambda Functions Created Container Images
To package the Sumo Logic Lambda Extension with the AWS Lambda function created using container images, please follow the steps below:
-
Download the latest binary tar file from the GitHub Release page.
-
For functions based on the x86_64 architecture:
wget
https://github.com/SumoLogic/sumologic-lambda-extensions/releases/latest/download/sumologic-extension-amd64.tar.gz -
For functions based on the ARM 64 architecture:
wget
https://github.com/SumoLogic/sumologic-lambda-extensions/releases/latest/download/sumologic-extension-arm64.tar.gz
-
-
In your AWS Lambda container image Dockerfile, add the command below.
ADD <Location-where-you-downloaded-the-tar-file>/sumologic-extension-<architecture>.tar.gz /opt/ -
Validate if the extension is added to the directory and execute the below command.
docker run -it --entrypoint sh <ImageName>:<ImageTag> -
Execute the command
ls -R /opt/to see the directory structure. It should look as per the screenshot below.

-
Deploy your AWS Lambda function using the container images.
noteThe command will extract the Sumo Logic Lambda extension binary file into the folder structure as
/opt/extensions. Do not change the directory structure as it is required by AWS Lambda to identify all the external extensions.
Step 3: Adding the Environment variables
Add the following environment variables to your Lambda function:
| Variable Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
SUMO_HTTP_ENDPOINT | This is the URL of the Sumo Logic HTTP source created in Step 1. | Required |
SUMO_LOG_TYPES | Provide a comma-separated list of values that are one or more "platform", "function" or "extension" to indicate which AWS Lambda logs you want to send to Sumo Logic. By default, all of these three values are assumed. | Optional |
SUMO_ENABLE_FAILOVER | Set to True to failover in case you would like the extension to send logs to an Amazon S3 bucket. In the case of throttling or, exceptions the default value assumed is False. | Optional |
SUMO_S3_BUCKET_NAME | The name of an Amazon S3 bucket. | Optional |
SUMO_S3_BUCKET_REGION | The Region where the above Amazon S3 bucket is located. | Optional |
SUMO_MAX_RETRY | A Number of retries to send logs to Sumo Logic. The default is 0. | Optional |
SUMO_LOG_LEVEL | Log level, which can be one of info, error, or debug. The default value is info. | Optional |
SOURCE_CATEGORY_OVERRIDE | The Source Category for all incoming data is set to that of the HTTP endpoint by default. You can however override it with this parameter | Optional |
SUMO_SPAN_DROP | Set to true in case you would like the extension to drop spans from ingested into Sumo Logic. The default value assumed is false. | Optional |
SUMO_ENHANCE_JSON_LOGS | Ingest the logs in JSON format with a message key containing raw log message and other metadata such as loggroup, isColdStart, and logStream. Default is true. | Optional |
KMS_KEY_ID | KMS Key ARN of the "Customer managed key" (used for decrypting the SUMO_HTTP_ENDPOINT), which can be obtained from the AWS console. | Optional |
KMS_CACHE_SECONDS | Set the cache timeout in seconds. Default is 5 seconds. | Optional |
TELEMETRY_MAX_BYTES | The maximum volume of telemetry (in bytes) to buffer in memory. Default is 262,144. Minimum is 262,144. Maximum is 1,048,576. | Optional |
TELEMETRY_MAX_ITEMS | The maximum number of events to buffer in memory. Default is 10,000. Minimum is 1000. Maximum is 10,000. | Optional |
TELEMETRY_TIMEOUT_MS | The maximum time (in milliseconds) to buffer a batch. Default is 1000. Minimum is 25. Maximum is 30,000. | Optional |
Using KMS to secure the SUMO_HTTP_ENDPOINT
-
Follow the Security in transit " section in AWS docs to encrypt the
SUMO_HTTP_ENDPOINTenvironment variable. You can use SymmetricKey typewith Encrypt and decryptKey usage.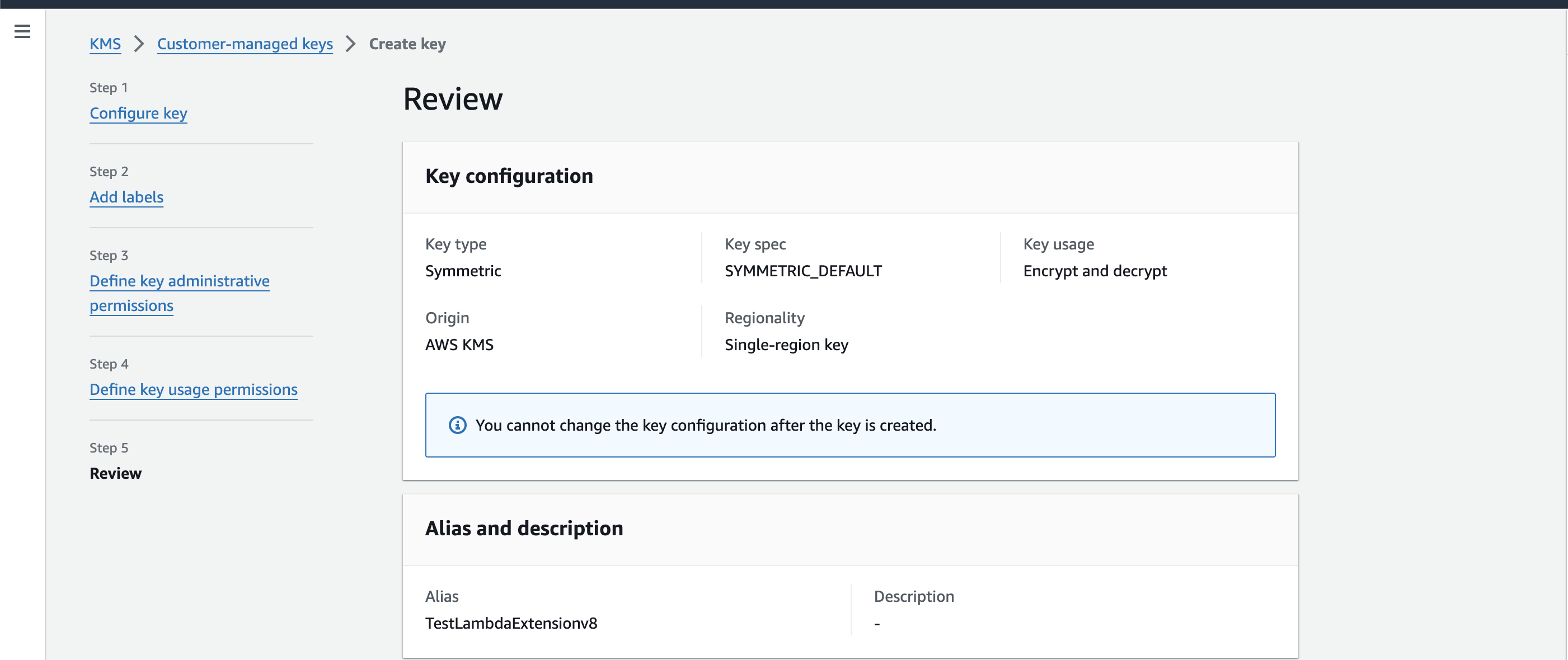
-
Make sure to add Lambda's role as Key Users to allow your lambda function to use the key.
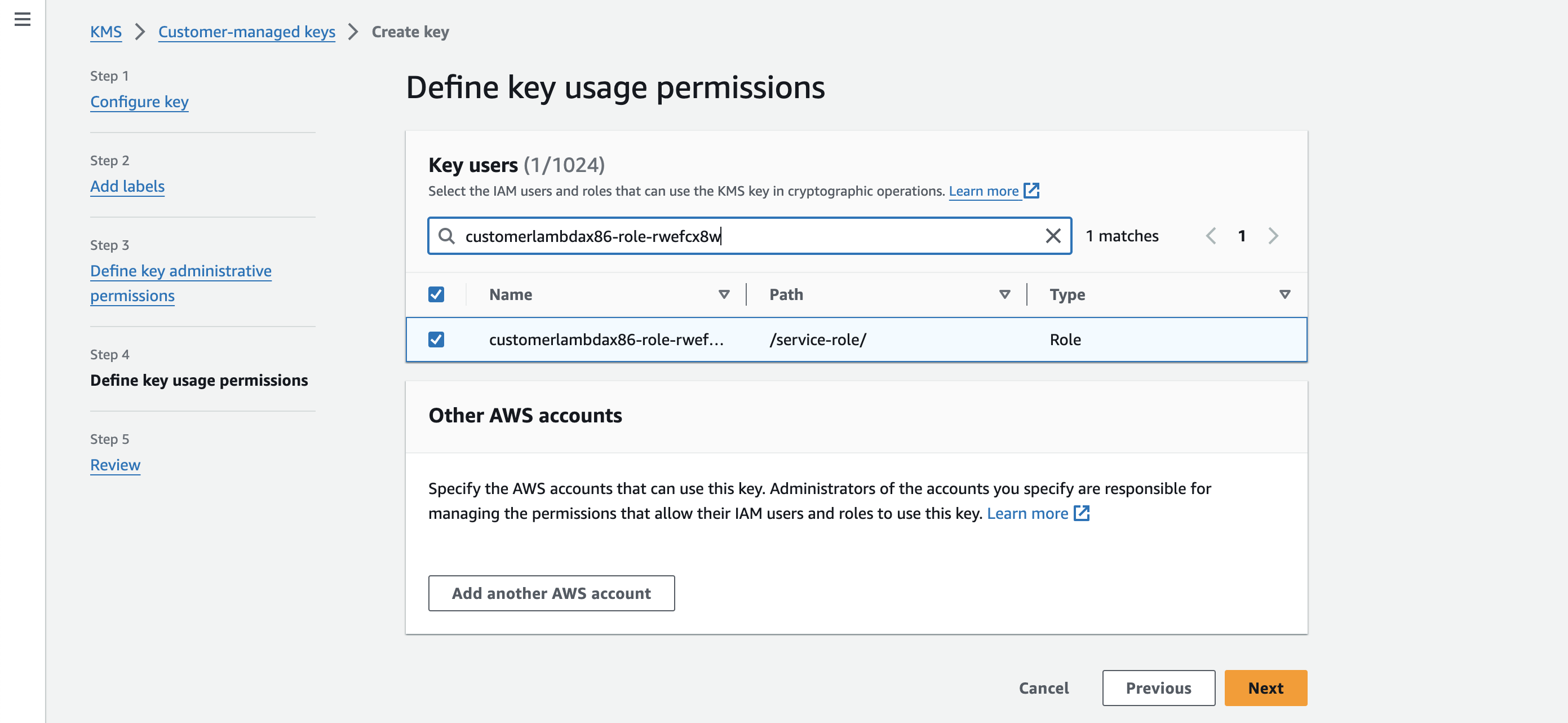
-
In Edit environment variables section, add
KMS_KEY_IDenvironment variable with value as KMS key ARN of the "Customer managed key" created earlier, you can obtain it from the AWS console. Also encrypt theSUMO_HTTP_ENDPOINTusing the same KMS key by clicking Encrypt button. It will replace the endpoint with the base64 encoded string.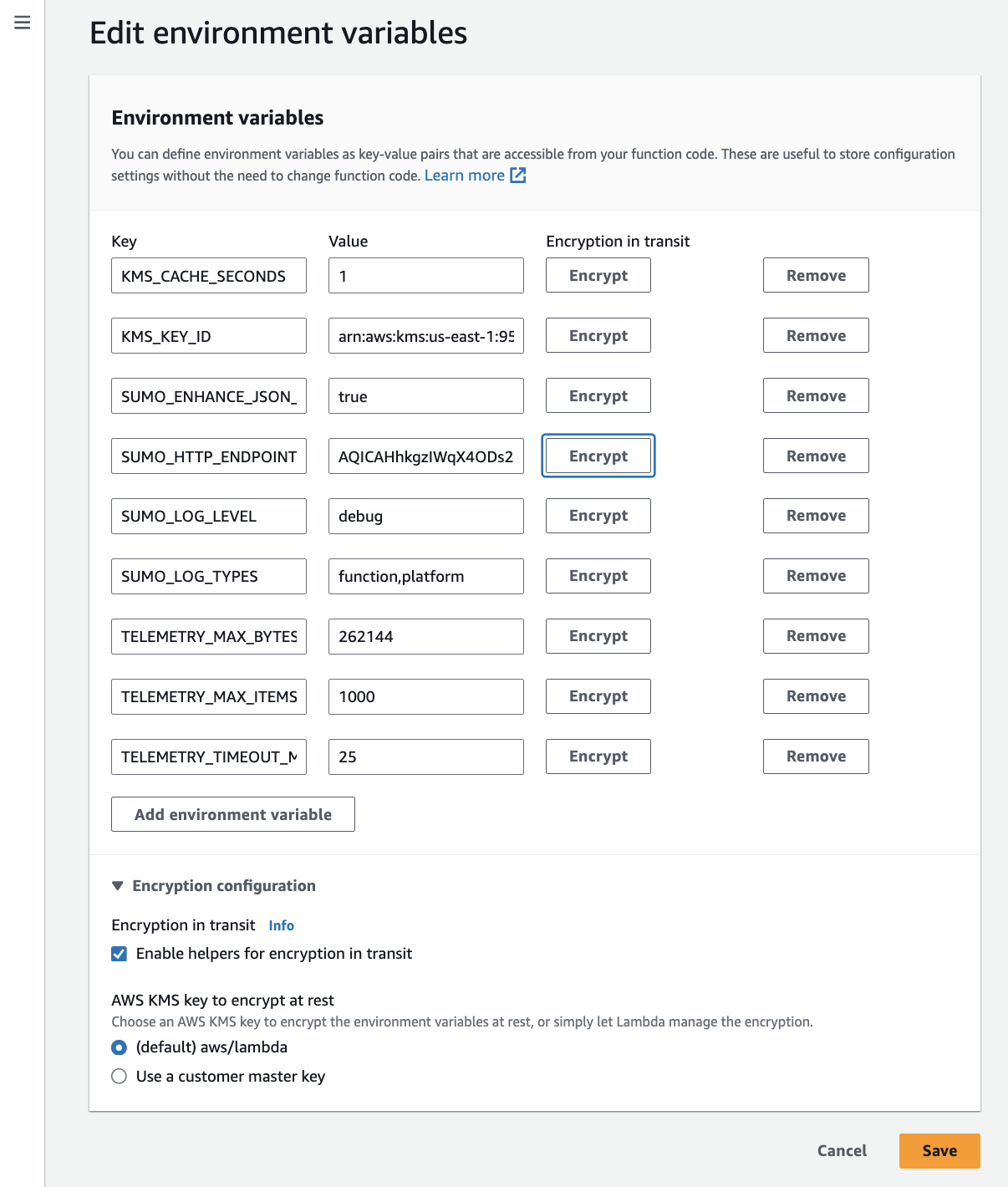
-
Once you have set your parameters, execute your AWS Lambda function, and validate that the logs are coming into Sumo Logic.
-
If you have enabled failover, do the following:
- Add the following inline policy to the IAM role associated with your lambda function.
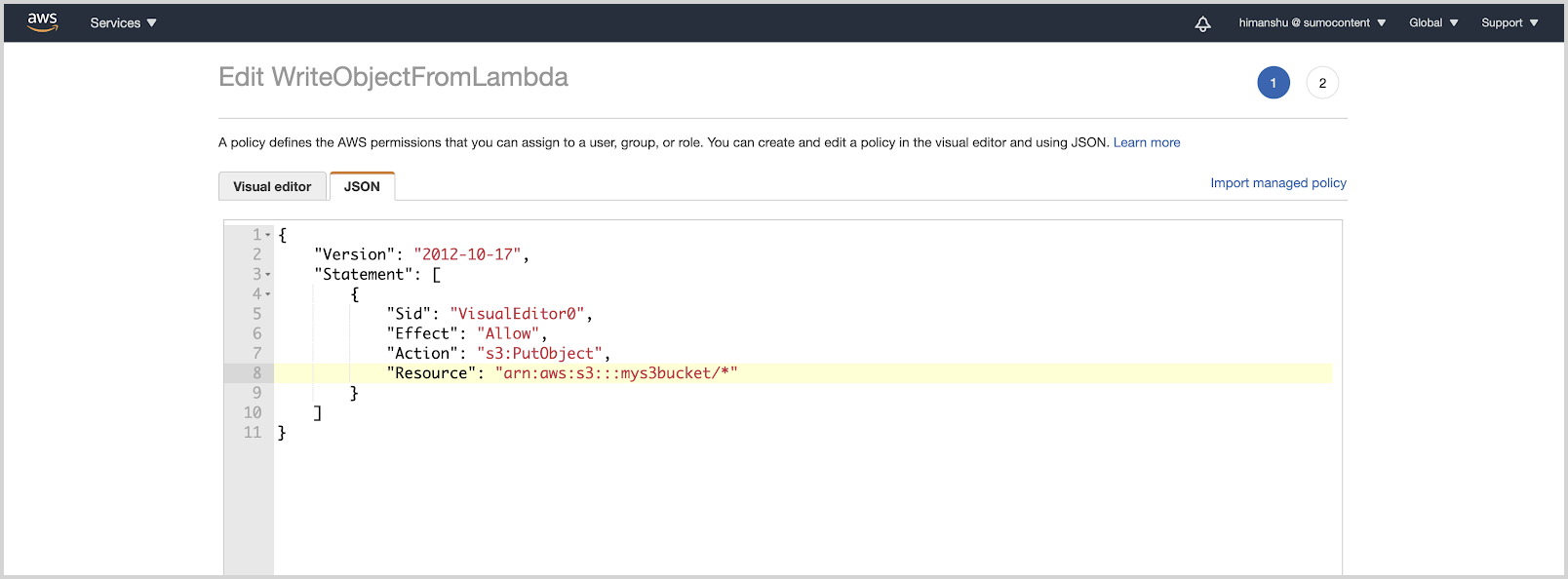
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "s3:PutObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::<AWS S3 Bucket Name>/*"
}
]
}- Configure a Sumo Logic Amazon S3 source with the same source category as that of the HTTP Source created in Step 1 to read from this bucket.
noteLogs from the Sumo Logic Lambda extension are stored and compressed in the following prefix path
sumologic-extension/<aws-region>/<Function>/<Version>/<Year>/<Month>/<Day>/<Hour>/<Min>/<UUID>.gz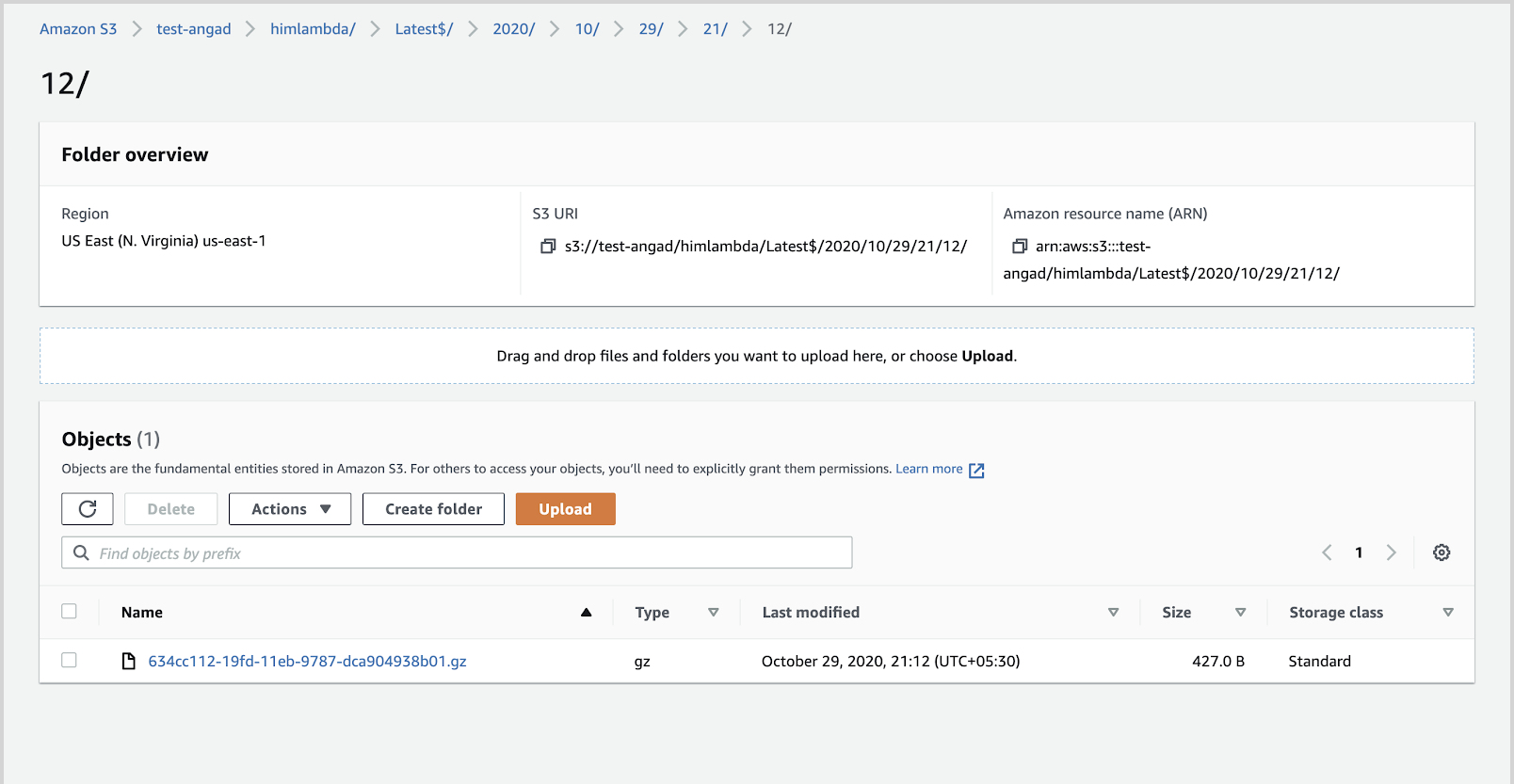
Step 4 (Optional): Disable logging to CloudWatch logs
Since AWS Lambda continues to send logs to CloudWatch Logs even if extensions subscribe to the logs stream, you can disable logging to CloudWatch Logs for your function as described in the documentation.
Step 5 (Optional): Receive logs during AWS Lambda execution time
All the logs that are not sent to Sumo Logic during the Execution phase of the AWS Lambda, are sent during the shutdown phase instead. The platform.report and platform.end events are sent in next execution. If the time period is longer, AWS calls the shutdown event. In that case, Sumo Logic flushes out all of the logs.
If you would like to always send logs during the execution phase however, you can add extra execution time via a sleep function at the end of lambda code, which will give your extension time to run and send logs to Sumo Logic. We recommend setting this to two seconds.
For more details on phases on the lifecycle and AWS Lambda phases please see the AWS documentation.